Best practices in Accounts payables.ppt
- 1. Best Practice Financial Processes: Accounts Payable
- 2. 2 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable Objectives Organisation People Processes Controls Measures Information Systems To maximise processing efficiency To ensure invoices are processed to agreed terms To ensure payments made only when due and payable To ensure liabilities are fully recorded and distributed correctly To achieve effective balance between extending credit and maintaining good relations with suppliers To take full advantage of opportunities to recover VAT Centralised processing Outsourcing potential Maintaining supplier details Process vouchers Process payments Period end processing and reporting Authorisation rules System access controls User procedures Validation and matching rules Speed of processing supplier amendments Invoices processed Invoice processing time Number of payments Period end closure time Interface between Accounts Payable and other related processes Shared employee and supplier details System validation and approval checks Supplier relations Creditor control Accounts Payable - Best Practice Objectives
- 3. 3 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Best practice features Authorise and set up new suppliers payment details Maintain supplier payment details Segregation of duties between supplier set up, voucher processing and payment processing Accounts payable process vouchers: invoices, expense claims, credit notes, debit memos and prepayment requests Suppliers required to use PO number on all documents and three way match wherever possible Consolidated periodic invoicing for high frequency suppliers Process Features Maintain supplier details Process vouchers Optimisation of early payment discounts Payment runs properly authorised Process payments All transactions completed before period closed Reconciliation of Accounts Payable activity and reconciliation with General Ledger control account Management reports run once period is finally closed Period end processing and reporting
- 4. 4 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Best practice features Single supplier database Single employee database Audit trail of changes to supplier payment details Purchase invoices transacted via EDI with major suppliers wherever possible Electronic validation and approval of invoices Automatic matching of invoice to order and goods received note (GRN) Interface with General Ledger, Purchasing, Fixed Assets and Project Accounting Use of workflow software to resolve queries and monitor process System Features Maintain supplier details Process vouchers Electronic payments Default payment terms held on supplier file with manual override at P.O. and invoice Production of forward payment entry schedules to aid cash flow management Interface with General Ledger, Fixed Assets, Project Accounting and Cash Management Facility to suspend payments Process payments Integration with General Ledger minimises reconciliation adjustments Transaction processing prevented for closed periods Period end processing and reporting
- 5. 5 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Measures/Cost drivers Number of invoices received per month Number of suppliers Number of different terms and conditions Complexity of authorisation process Proportion of invoices automatically matched with PO's Number of supplier queries Proportion of invoices received electronically Proportion of payments made electronically Median 16 days 90 percentile 49 days 90 percentile Median 10 percentile Number of purchase invoices per FTE per annum 15,000 7,000 3,000 or less Cost per purchase invoice processed 10 percentile Median 90 percentile £2 £6 £17 10 percentile 6 days Invoice processing time in days Cost drivers Source: statistics taken from Benchmarking database 21 January 1997
- 6. 6 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Trends From To Separate AP module Payment by cheque Manual matching Performed by finance department Integrated systems Electronic payment On-line matching Shared Service Centres or outsourced services
- 7. 7 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Critical Success Factors These are a summary of the key business requirements, which must be met to achieve the objectives. Single supplier database Staff trained in AP process and have clear roles and responsibilities Payment terms defined and agreed with supplier Effective communication and feedback mechanisms in place to handle queries Establish and maintain good supplier relations Process in place for monitoring the status of invoices and payment schedules AP calendar in place and communicated to staff Authorisation levels and payment terms held on the system Automated workflow to route documents to relevant personnel when problems need to be resolved Forward payment schedule to cashflow management Flexible matching criteria
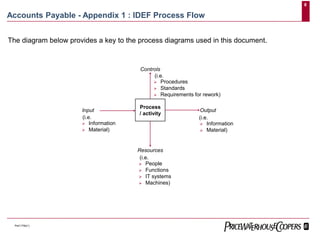
- 8. 8 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Appendix 1 : IDEF Process Flow The diagram below provides a key to the process diagrams used in this document. Process / activity Controls (i.e. Procedures Standards Requirements for rework) Output (i.e. Information Material) Resources (i.e. People Functions IT systems Machines) Input (i.e. Information Material)
- 9. 9 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Level 0 Context Diagram Group / Mgt. team Fixed Asset Register Purchasing General Ledger Suppliers / Employees Supplier/Employee amendments Invoice / Payment details Human Resources Cash Management Project Accounting Accounts Payable
- 10. 10 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Level 1 Overview Voucher approved for payment New period open Payment details ready to post to General Ledger Payment and remittance advice Voucher : Invoice/expense claim/ Credit note/prepayment request Notification of changes from supplier or employee Maintain supplier details AP 1.1 Process vouchers AP 1.2 Process payments AP 1.3 Period end processing and reporting AP 1.4 Voucher processing procedures Authorisation rules Matching rules System validation and approval checks Exception handling procedures AP dept AP system PO system Supplier Requisitioner Batch controls Authorisation rules Reporting guidelines Posting controls Reconciliation procedures Period end timetable AP dept AP system Payment device Authorised personnel AP AP System HR Authorisation procedures System access controls Up to date supplier records Vouchers filed AP dept AP system GL system Management Reports Employee joiners and leavers details Maintenance request Approved vouchers ready to post to General Ledger Voucher details available on-lne to Fixed Assets and Project Accounting Cancelled vouchers reversed out of AP and filed Payment details available on-line to cash management Payment cancelled
- 11. 11 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Notes Maintain Supplier Details Best Practice Features Shared supplier database with Purchasing. Purchasing responsible for approving suppliers (having made the required checks), agreeing terms and conditions and maintaining general and purchasing related supplier details on the database, including payment terms. Accounts Payable responsible for maintaining all payment related supplier data, such as bank details, payment method, payee name and address, payment contacts. Shared employee database with Human Resources. Employee details are maintained by Human Resources, but sufficient details must be held and maintained by Accounts Payable, to allow payment of expenses. Employee details required include payment method, bank details, remittance address, payee name and employee cost centre. Accounts Payable should not have access to other confidential employee data. One payment address for each vendor. Where a vendor provides goods or services from a number of locations, the consolidation of the payment process not only reduces the number of payments necessary but also removes the potential need to reconcile a number of individual accounts. Centralise the vendor set-up capability in order to minimise the risk of unauthorised or duplicate vendors being set up more than once. From an audit point of view, the control over vendor set up is also viewed as a critical activity which needs to be tightly controlled. Changes to supplier details are processed expeditiously. If, the vendor is also a customer, details are consistent in both databases.
- 12. 12 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Notes Maintain Supplier Details Internal Control requirements New suppliers must be checked and approved by Purchasing in accordance with company policy. Similarly, Purchasing are responsible for processing any mergers, acquisitions or deletions. To enable efficient invoice payment processing and ensure segregation of duties, Accounts Payable are responsible for the maintenance of all payment related supplier data. In addition, authorisation for payments within Accounts Payable should be separate from the responsibility of maintaining supplier payment data and processing vouchers. Audit of changes to supplier payment details must be possible. Key Performance Indicators Time taken to process supplier amendments.
- 13. 13 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Notes Process Payments Best Practice Features Use of electronic banking systems for payments, thus minimising the need for manual intervention in the process. Centralisation of the payment processing in order to minimise the risk of making duplicate payments. Payments made no sooner than the due date in order to maximise cash flow benefits. Facility to suspend individual payments. The withholding of payment can be a powerful tool in ensuring that the vendor complies with any requirements asked of it. Avoid payments in cash. Apart from being costly to administer, the potential for fraud is greatly increased.
- 14. 14 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Notes Process Payments Internal Control requirements Payment processing needs to be tightly controlled and totally segregated from vendor set-up and invoice processing activities. Key Performance Indicators Number of payments per FTE. Number of overdue payments. Number of payments made too early.
- 15. 15 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Notes Process Payments Cost Drivers The following generate the costs for the processing of payments:- Number of payment runs. Number of manually prepared payments. Number of payment media (cheques, vouchers, diskettes, etc.). Number of foreign payments. Varied payment terms. Reports Summary of payments per run. Payments on hold. Reports on Key Performance Indicators. Overdue unpaid invoices
- 16. 16 PwC175b(1) Accounts Payable - Notes Period end processing and reporting Best Practice Features Automatic process requiring little or no manual intervention. Posting to GL should be daily. This ensures GL data is up to date and also reduces the time taken for the period end posting as fewer records are being processed. Internal Control requirements The basic requirement is to ensure that the data transmitted to the general ledger is complete and on time. There is a requirement to ensure that the information recorded in the general ledger agrees with the output from accounts payable. Key Performance Indicators Delivery of information to general ledger on time Timely delivery of end of period reports Cost Drivers Volume of transactions Time to close periods Degree of automation in the interface with general ledger