Scalability Issues of Firefly-Based Self-Synchronization in Collective Adaptive Systems
- 1. Scalability Issues of Firefly-Based Self-Synchronization in Collective Adaptive Systems Iva Bojic*, Tomislav Lipic and Mario Kusek *Department of Urban Studies and Planning Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA, US FoCAS 2014 September 8, 2014, London, UK
- 2. Heterogeneous Collective Adaptive Systems Machine-to-Machine systems 2 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 3. Problem no global notion of time In distributed systems each node has its own internal clock and its own notion of time In practice these clocks drift apart accumulating errors over time Global notion of time is prerequisite for: common resource sharing (e.g., channel) depend events tracking (e.g., consistency of distributed databases) simultaneous events detection (e.g., data collection) 3 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
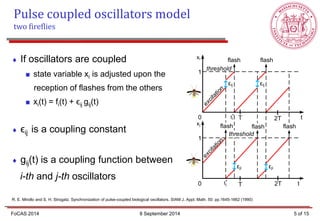
- 4. If oscillators are not coupled, their state variables change following only their own excitations xi denotes state variable xi(t) = fi(t) ti * denotes a moment when i-th oscillator flashes R. E. Mirollo and S. H. Strogatz. Synchronization of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 50: pp.1645-1662 (1990) Pulse coupled oscillators model one firefly 0 1 t xi threshold excitation flash flash = T 2T * ti FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014 4 of 15
- 5. If oscillators are coupled state variable xi is adjusted upon the reception of flashes from the others xi(t) = fi(t) + ϵij gij(t) ϵij is a coupling constant gij(t) is a coupling function between i-th and j-th oscillators R. E. Mirollo and S. H. Strogatz. Synchronization of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 50: pp.1645-1662 (1990) Pulse coupled oscillators model two fireflies 0 1 t xi threshold flash flash T 2T 0 1 t xj T 2T εij ti * tj * εij εji εji flash flash flash threshold FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014 5 of 15
- 6. Pulse coupled oscillators model assumptions oscillators are the same (i.e., have same frequencies) oscillators are connected in a fully-connected network no delays in the message exchange among oscillators no oscillators with a faulty behavior that desynchronizes the network oscillators cannot join or leave the network nor change their positions in the network (i.e., no mobility) Pulse coupled oscillators model limitations 6 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 7. Synchrony – ”firing” in unison Phase locking – differences between state variable values are constant and nonzero Frequency locking – differences between state variable values are not constant because of frequency fluctuations Forms of time synchronization synchrony, phase locking and frequency locking 7 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 8. Rate of successful synchronization outcomes synchronization precision is acceptable Time to synchronization time needed to achieve synchronization of desired precision Network traffic number of messages exchanged during synchronization process The goal of this paper is to reduce network traffic Frequency locking time to synchronization and network traffic 8 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 9. Results of simulations all-to-all connectivity is not the best one considering both time to synchronization and network traffic [1, 2] smaller transmission radius leads to lower energy consumption [3] Constraints in testbeds calculation and memory costs of finding neighbors time cost of sending multicast messages [1] I. Bojic, et al. “A Self-Optimizing Mobile Network: Auto-Tuning the Network with Firefly-Synchronized Agents”, Information Sciences, vol. 182, no. 1, pp. 77– 92 (2012) [2] I. Bojic and M. Kusek, “Comparing Different Overlay Topologies and Metrics in Pulse-Coupled Multi-Agent Systems,” in Proceedings of the 6th KES International Conference on Agent and Multi-Agent Systems: Technologies and Applications, 2012, pp. 464–473 [3] Y. Niu, et a. “Selective Pulse Coupling Synchronicity for Sensor Network,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, 2008, pp. 123–128 Network traffic reduction overlay network topologies 9 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 10. Selective coupling implemented on the sender side at the end of each synchronization cycle before sending the synchronization messages Proposed solution mechanism for selective coupling implemented on the sender side 10 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 11. Selective coupling implemented on the receiver side selective coupling leads to faster synchronization convergence [4] halving the probability to send synchronization messages meant doubling time to synchronization [5] selective reduction of transmitted information saves energy and improves the convergence rate of desired synchronization precision [6] [4] Y. Niu, et a. “Selective Pulse Coupling Synchronicity for Sensor Network,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, 2008, pp. 123–128. [5] I. Scholtes, J. Botev, M. Esch, and P. Sturm, “Epidemic Self-Synchronization in Complex Networks of Kuramoto Oscillators,” Advances in Complex Systems, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 33–58, 2010 [6] J. Degesys, P. Basu, and J. Redi, “Synchronization of Strongly Pulse-Coupled Oscillators with Refractory Periods and Random Medium Access,” in Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, 2008, pp. 1976–1980 Related work mechanism for selective coupling implemented on the receiver side 11 of 15 FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014
- 12. Multi-Agent Simulator Of Neighborhoods Graphs generated by Watts/Strogatz model [7] reconnection probability = 0.5 number of nearest neighbors in initial ring lattice = 10 Future work – graphs generated by Barabasi/Albert model synchronization benefits from networks in which high degree devices are connected to low degree devices [8] [7] I. Scholtes, J. Botev, M. Esch, and P. Sturm, “Epidemic Self-Synchronization in Complex Networks of Kuramoto Oscillators,” Advances in Complex Systems, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 33–58, 2010 [8] M. di Bernardo, F. Garofalo, and F. Sorrentino, “Effects of Degree Correlation on the Synchronization of Networks of Oscillators,” International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, vol. 17, no. 10, pp. 3499–3506, 2007. 12 of 15 FoCAS 2014 Simulation environment mechanism for selective coupling implemented on the receiver side 8 September 2014
- 13. 13 of 15 FoCAS 2014 Simulation results relative difference of exchanged messages and time to synchronization 8 September 2014
- 14. M2M systems with 10000 devices (0.1 for thresholdSyn and 0.3 for thresholdProbability) 2.5 million (i.e., 52 %) less messages are exchanged around 1300 (i.e., 53 %) less steps are needed to achieve synchronization indications that this mechanism can improve the synchronization rate Open issues lack of the practical implementation in real-world environments can Watts/Strogatz model represent heterogeneous M2M systems? communication latency and different distributions of device frequencies 14 of 15 FoCAS 2014 Conclusions and open issues mechanism for selective coupling implemented on the receiver side 8 September 2014
- 15. Thank you for your attention Questions? FoCAS 2014 8 September 2014 15 of 15







![Results of simulations
all-to-all connectivity is not the best one considering both time to synchronization and network traffic [1, 2]
smaller transmission radius leads to lower energy consumption [3]
Constraints in testbeds
calculation and memory costs of finding neighbors
time cost of sending multicast messages [1] I. Bojic, et al. “A Self-Optimizing Mobile Network: Auto-Tuning the Network with Firefly-Synchronized Agents”, Information Sciences, vol. 182, no. 1, pp. 77– 92 (2012) [2] I. Bojic and M. Kusek, “Comparing Different Overlay Topologies and Metrics in Pulse-Coupled Multi-Agent Systems,” in Proceedings of the 6th KES International Conference on Agent and Multi-Agent Systems: Technologies and Applications, 2012, pp. 464–473 [3] Y. Niu, et a. “Selective Pulse Coupling Synchronicity for Sensor Network,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, 2008, pp. 123–128
Network traffic reduction overlay network topologies
9 of 15
FoCAS 2014
8 September 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bojic-140919044722-phpapp01/85/Scalability-Issues-of-Firefly-Based-Self-Synchronization-in-Collective-Adaptive-Systems-9-320.jpg)

![Selective coupling implemented on the receiver side
selective coupling leads to faster synchronization convergence [4]
halving the probability to send synchronization messages meant doubling time to synchronization [5]
selective reduction of transmitted information saves energy and improves the convergence rate of desired synchronization precision [6] [4] Y. Niu, et a. “Selective Pulse Coupling Synchronicity for Sensor Network,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, 2008, pp. 123–128. [5] I. Scholtes, J. Botev, M. Esch, and P. Sturm, “Epidemic Self-Synchronization in Complex Networks of Kuramoto Oscillators,” Advances in Complex Systems, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 33–58, 2010 [6] J. Degesys, P. Basu, and J. Redi, “Synchronization of Strongly Pulse-Coupled Oscillators with Refractory Periods and Random Medium Access,” in Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, 2008, pp. 1976–1980
Related work
mechanism for selective coupling implemented on the receiver side
11 of 15
FoCAS 2014
8 September 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bojic-140919044722-phpapp01/85/Scalability-Issues-of-Firefly-Based-Self-Synchronization-in-Collective-Adaptive-Systems-11-320.jpg)
![Multi-Agent Simulator Of Neighborhoods
Graphs generated by Watts/Strogatz model [7]
reconnection probability = 0.5
number of nearest neighbors in initial ring lattice = 10
Future work – graphs generated by Barabasi/Albert model
synchronization benefits from networks in which high degree devices are connected to low degree devices [8] [7] I. Scholtes, J. Botev, M. Esch, and P. Sturm, “Epidemic Self-Synchronization in Complex Networks of Kuramoto Oscillators,” Advances in Complex Systems, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 33–58, 2010 [8] M. di Bernardo, F. Garofalo, and F. Sorrentino, “Effects of Degree Correlation on the Synchronization of Networks of Oscillators,” International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, vol. 17, no. 10, pp. 3499–3506, 2007.
12 of 15
FoCAS 2014
Simulation environment
mechanism for selective coupling implemented on the receiver side
8 September 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bojic-140919044722-phpapp01/85/Scalability-Issues-of-Firefly-Based-Self-Synchronization-in-Collective-Adaptive-Systems-12-320.jpg)


