C lang7age programming powerpoint presentation
- 1. UNIT – I Introduction to C Language
- 2. Introduction to C Language Background, C Programs, Identifiers, Data Types, Variables, Constants, Input / Output Statements Arithmetic Operators and Expressions: Evaluating Expressions, Precedence and Associativity of Operators, Type Conversions.
- 3. Background C programming is a general-purpose, procedural computer programming language developed in 1972 by Dennis M. Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories to develop the UNIX operating system. C is a structured programming language. It is considered a high-level language because it allows the programmer to concentrate on the problem at hand and not worry about the machine that the program will be using.
- 4. Why to Learn C Programming • Easy to learn • Structured language • It produces efficient programs • It can handle low-level activities • It can be compiled on a variety of computer platforms
- 5. Facts about C • C was invented to write an operating system called UNIX. • C is a successor of B language which was introduced around the early 1970s. • The language was formalized in 1988 by the American National Standard Institute (ANSI). • The UNIX OS was totally written in C. • Today C is the most widely used and popular System Programming Language. • Most of the state-of-the-art software have been implemented using C.
- 6. Applications of C Programming • Operating Systems • Language Compilers • Assemblers • Text Editors • Print Spoolers • Network Drivers • Modern Programs • Databases • Language Interpreters
- 7. 7 Basics of a Typical C Program Development Environment Phases of C Programs: 1. Edit 2. Preprocess 3. Compile 4. Link 5. Load 6. Execute Program is created in the editor and stored on disk. Preprocessor program processes the code. Loader puts program in memory. CPU takes each instruction and executes it, possibly storing new data values as the program executes. Compiler creates object code and stores it on disk. Linker links the object code with the libraries Loader Primary Memory Compiler Editor Preprocessor Linker Primary Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . Disk Disk Disk CPU Disk Disk
- 8. Structure of a C Program
- 12. 12 Anatomy of a simple C program #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { printf("Hello World!n"); return (0); } #include <stdio.h> – Preprocessor directive • Tells computer to load contents of a certain file • Begins with a # symbol – <stdio.h> contains standard input/output operations • Allows C program to perform I/O from keyboard/screen C program comprises two parts: - Preprocessor directives - Program code Preprocessor directives give commands to C preprocessor which “modifies” C program text before complilation.
- 13. 13 int main() { – C programs contain one or more functions, exactly one of which must be function main – Parenthesis () used to indicate a function – int means that main "returns" an integer value (status code) to operating system when it terminates. – void means that the main function receives no data from the operating system when it starts executing. – Left brace { indicates start of a block (of code) • The “bodies” of all functions must be contained in braces - the body of a function is a block of code • Here it is the body of the function main
- 14. 14 printf( “Hello World!n" ); – Instructs computer to perform an action • Specifically, print the string of characters within quotes (“ ”) • Makes use of standard I/O function, printf – Entire line called a statement • All statements must end with a semicolon (;) • the semicolon is a statement terminator – Escape character () • Indicates that printf should do something out of the ordinary • n is the newline character
- 15. 15 return (0); } – A way to exit a function – return (0) means that the program terminated normally – Right brace } indicates end of a block (of code) – Here indicates end of main function has been reached Comments – Comments are like helping text in your C program and they are ignored by the compiler. They start with /* and terminate with the characters */ as shown below − – xyz – /* my first program in C */
- 18. IDENTIFIERS One feature present in all computer languages is the identifier. Identifiers allow us to name data and other objects in the program. Each identified object in the computer is stored at a unique address. An identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function, or any other user-defined item. RULES 1.An identifier starts with a letter A to Z, a to z, or an underscore '_' followed by zero or more letters, underscores, and digits (0 to 9). 2. There must not be any white space in the string. 3. And, all the subsequent characters after the first character must not consist of any special characters like $, #, % etc.
- 19. Examples of Valid and Invalid Names C does not allow punctuation characters such as @, $, and % within identifiers
- 20. Keywords • Keywords are reserved words that have special meaning in the C language. The meaning of C language keywords has already been described in the C compiler. • They are explicitly reserved and cannot be redefined. • ANSII C has 32 key words. • Some implementations such as Borland’s C or Microsoft’s C have additional key words.
- 21. •A keyword name can not be used as a variable name. •Keywords must be written in lower case. •It specifies the type/kind of entity.
- 22. ANSII C Keywords auto do goto signed unsigned break double if sizeof void case else int static volatile char enum long struct while const extern register switch continue float return typedef default for short union
- 23. Check Valid/ Invalid Identifiers • int • Char • X+y • 1x • Sum • Average _x • _sum_ • a_ Mark_Maths
- 24. Keyword Identifier Keyword is a pre-defined word. The identifier is a user-defined word It must be written in a lowercase letter. It can be written in both lowercase and uppercase letters. Its meaning is pre-defined in the c compiler. Its meaning is not defined in the c compiler. It is a combination of alphabetical characters. It is a combination of alphanumeric characters. It does not contain the underscore character. It can contain the underscore character. Differences between Keyword and Identifier
- 25. Data Types A data type defines a set of values and a set of operations that can be applied on those values.
- 26. sizeof (short) ≤ sizeof (int) ≤ sizeof (long) ≤ sizeof (long long)
- 27. sizeof (float) ≤ sizeof (double) ≤ sizeof (long double)
- 28. Type Summary
- 31. Some Strings A string literal is a sequence of characters enclosed in double- quote marks.
- 32. Null Characters and Null Strings Use single quotes for character constants. Use double quotes for string constants.
- 33. Symbolic Names for Control Characters
- 34. Variables Variables are named memory locations that have a type, such as integer or character, which is inherited from their type. The type determines the values that a variable may contain and the operations that may be used with its values. Rules for naming a variable • A variable name can only have letters (both uppercase and lowercase letters), digits and underscore. • The first letter of a variable should be either a letter or an underscore. • There is no rule on how long a variable name (identifier) can be. However, you may run into problems in some compilers if the variable name is longer than 31 characters.
- 35. Examples of Variable Declarations and Definitions
- 38. When a variable is defined, it is not initialized. We must initialize any variable requiring prescribed data when the function starts.
- 39. PROGRAM 2 Print Sum of Three Numbers
- 40. PROGRAM 2 Print Sum of Three Numbers (continued)
- 41. PROGRAM 2 Print Sum of Three Numbers (continued)
- 42. Constants Constants are data values that cannot be changed during the execution of a program. Like variables, constants have a type. In this section, we discuss Boolean, character, integer, real, complex, and string constants. A character constant is enclosed in single quotes. There are two simple ways in C to define constants − •Using #define preprocessor. •Using const keyword.
- 43. Examples of Integer Constants
- 44. Examples of Real Constants
- 45. PROGRAM 3 Memory Constants
- 46. PROGRAM 3 Memory Constants (continued)
- 47. Input / Output Statements • Input means to provide the program with some data to be used in the program and • Output means to display data on screen or write the data to a printer or a file. • C programming language provides many built-in functions to read any given input and to display data on screen
- 48. How does this program work? • All valid C programs must contain the main() function. The code execution begins from the start of the main() function. • The printf() is a library function to send formatted output to the screen. The function prints the string inside quotations. • To use printf() in our program, we need to include stdio.h header file using the #include <stdio.h> statement. • The return 0; statement inside the main() function is the "Exit status" of the program. It's optional.
- 49. • Libc.so file contains the implementation of printf( ), and scanf( ). • Stdio.h contains declaration of printf( ), scanf( ),etc.
- 50. 1. C Output Example 1 Example 2
- 52. 2. C Input Example 6: Float and Double Input/Output
- 56. gets( ) & puts( ) functions • The gets() function reads a line from stdin(standard input) into the buffer pointed to by str pointer, until either a terminating newline or EOF (end of file) occurs. The puts() function writes the string str and a trailing newline to stdout.
- 57. Console Input/Output function access the three major files before the execution of a C Program.
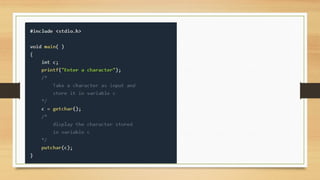
- 58. getchar() & putchar() functions • The getchar() function reads a character from the terminal and returns it as an integer. This function reads only single character at a time. • The putchar() function displays the character passed to it on the screen and returns the same character. This function too displays only a single character at a time.
Editor's Notes
- #26: wchar_t is a wide character: The increased datatype size allows for the use of larger coded character sets. Width is compiler specific (not portable).