C language computer introduction to the computer hardware
- 1. Department of Computer and Information Science, School of Science, IUPUI Dale Roberts, Lecturer Computer Science, IUPUI E-mail: [email protected] CSCI 230 Introduction to Computers - Hardware
- 2. What is a Computer?What is a Computer? ComputerComputer Device capable of performing computations and makingDevice capable of performing computations and making logical decisionslogical decisions Computers process data under the control of sets ofComputers process data under the control of sets of instructions called computer programsinstructions called computer programs Personal computersPersonal computers: economical enough for individual: economical enough for individual Distributed computingDistributed computing: computing distributed over: computing distributed over networksnetworks Client/server computingClient/server computing: sharing of information across: sharing of information across computer networks between file servers and clientscomputer networks between file servers and clients (personal computers)(personal computers) Dale Roberts
- 3. What is a Computer?What is a Computer? (cont.)(cont.) Computer HardwareComputer Hardware Various devices comprising a computer:Various devices comprising a computer: Keyboard, screen, mouse, disks, memory, CD-Keyboard, screen, mouse, disks, memory, CD- ROM, and processing unitsROM, and processing units Hardware Trends: every year or two the followingHardware Trends: every year or two the following approximately double (Moore’s Law):approximately double (Moore’s Law): Amount of memory in which to execute programsAmount of memory in which to execute programs Amount of secondary storage (such as disk storage)Amount of secondary storage (such as disk storage) Used to hold programs and data over the longer termUsed to hold programs and data over the longer term Processor speedsProcessor speeds The speeds at which computers execute their programsThe speeds at which computers execute their programs High-level Language Assembly Language Firmware Machine Code Hardware User Application Software OS
- 4. What is a Computer?What is a Computer? (cont.)(cont.) Computer SoftwareComputer Software Computer Programs that run on a computer, includingComputer Programs that run on a computer, including Operation System (OS)Operation System (OS) Application SoftwareApplication Software Computer LanguageComputer Language High-level Language Assembly Language Firmware Machine Code Hardware User Application Software OS
- 5. Moore's LawMoore's Law Defined byDefined by Dr. Gordon MooreDr. Gordon Moore during theduring the sixties.sixties. Predicts an exponential increase inPredicts an exponential increase in component density over time, with acomponent density over time, with a doubling time of 18 months.doubling time of 18 months. Applicable to microprocessors, DRAMs ,Applicable to microprocessors, DRAMs , DSPs and other microelectronics.DSPs and other microelectronics. Monotonic increase in density observedMonotonic increase in density observed since the 1960s.since the 1960s.
- 6. Moore’s Law - DensityMoore’s Law - Density
- 7. Moore's Law and PerformanceMoore's Law and Performance The performance of computers isThe performance of computers is determined by architecture and clockdetermined by architecture and clock speed.speed. Clock speed doubles over a 3 year periodClock speed doubles over a 3 year period due to the scaling laws on chip.due to the scaling laws on chip. Processors using identical or similarProcessors using identical or similar architectures gain performance directly asarchitectures gain performance directly as a function of Moore's Law.a function of Moore's Law. Improvements in internal architecture canImprovements in internal architecture can yield better gains than predicted byyield better gains than predicted by Moore's Law.Moore's Law.
- 8. Moore’s Law - Clock SpeedMoore’s Law - Clock Speed
- 9. What is a Computer?What is a Computer? (cont.)(cont.) InternetInternet The Internet enablesThe Internet enables Quick and easy communication via e-mailQuick and easy communication via e-mail International networking of computersInternational networking of computers Packet switchingPacket switching The transfer of digital data via small packetsThe transfer of digital data via small packets Allows multiple users to send and receive data simultaneouslyAllows multiple users to send and receive data simultaneously No centralized controlNo centralized control If one part of the Internet fails, other parts can still operateIf one part of the Internet fails, other parts can still operate BandwidthBandwidth Information carrying capacity of communications linesInformation carrying capacity of communications lines Ex: Internet T2 at IUPUIEx: Internet T2 at IUPUI World Wide WebWorld Wide Web Locate and view multimedia-based documents on almost any subjectLocate and view multimedia-based documents on almost any subject Makes information instantly and conveniently accessible worldwideMakes information instantly and conveniently accessible worldwide Possible for individuals and small businesses to get worldwide exposurePossible for individuals and small businesses to get worldwide exposure Changing the way business is doneChanging the way business is done
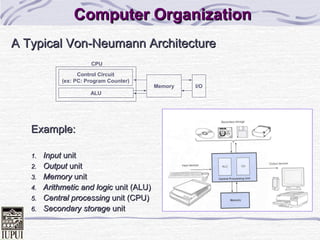
- 10. Computer OrganizationComputer Organization A Typical Von-Neumann ArchitectureA Typical Von-Neumann Architecture Example:Example: 1.1. InputInput unitunit 2.2. OutputOutput unitunit 3.3. MemoryMemory unitunit 4.4. Arithmetic and logicArithmetic and logic unit (ALU)unit (ALU) 5.5. Central processingCentral processing unit (CPU)unit (CPU) 6.6. Secondary storageSecondary storage unitunit Control Circuit (ex: PC: Program Counter) ALU Memory I/O CPU
- 11. Computer OrganizationComputer Organization (cont.)(cont.) Six logical units in every computer:Six logical units in every computer: 1.1. InputInput unitunit Obtains information from input devices (keyboard, mouse)Obtains information from input devices (keyboard, mouse) 1.1. OutputOutput unitunit Outputs information (to screen, to printer, to control otherOutputs information (to screen, to printer, to control other devices)devices) 1.1. MemoryMemory unitunit Rapid access, low capacity, stores input informationRapid access, low capacity, stores input information ROM (Read Only Memory): CMOS, EPROM …ROM (Read Only Memory): CMOS, EPROM … RAM (Random Access Memory): SRAM, DRAM, SIMM, DIMMRAM (Random Access Memory): SRAM, DRAM, SIMM, DIMM ……
- 12. Computer OrganizationComputer Organization (cont.)(cont.) Six logical units in every computer (cont):Six logical units in every computer (cont): 3.3. Arithmetic and logicArithmetic and logic unit (ALU) – part of CPUunit (ALU) – part of CPU Performs arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction...) andPerforms arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction...) and logic decisionslogic decisions 3.3. ControlControl unit (CU) - part of CPUunit (CU) - part of CPU Supervises and coordinates the other sections of the computerSupervises and coordinates the other sections of the computer 3.3. Secondary storageSecondary storage unitunit Cheap, long-term, high-capacity storageCheap, long-term, high-capacity storage Stores inactive programsStores inactive programs
- 13. Computer OrganizationComputer Organization (cont.)(cont.) Central Processing Unit (CPU),Central Processing Unit (CPU), ““brain” of a computer, consisting ofbrain” of a computer, consisting of Arithmetic and logic unitArithmetic and logic unit (ALU): performs arithmetic calculations(ALU): performs arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction...) and logic decisions (>, <, =, ...)(addition, subtraction...) and logic decisions (>, <, =, ...) Control Unit (CU): decodes each machine instruction and sendsControl Unit (CU): decodes each machine instruction and sends signal to other components for carrying out the instruction.signal to other components for carrying out the instruction. An integrated circuit (IC) that is a full central processing unitAn integrated circuit (IC) that is a full central processing unit is called a microprocessor (is called a microprocessor (µµpp); a CPU’s current instruction); a CPU’s current instruction and data values are stored temporally inside the CPU inand data values are stored temporally inside the CPU in special high-speed memory location called registers.special high-speed memory location called registers. CPU speed: ? MHz (M: Mega = 10CPU speed: ? MHz (M: Mega = 1066 , Hz=1/sec);, Hz=1/sec);
- 14. Computer OrganizationComputer Organization (cont.)(cont.) MemoryMemory A large collection of circuits, each capable ofA large collection of circuits, each capable of storing bitstoring bit Cells (words): manageable units; typical size is 8Cells (words): manageable units; typical size is 8 bits (1 byte), some machines are 16 bits (2bits (1 byte), some machines are 16 bits (2 bytes) and some are 32 bits or 64 bitsbytes) and some are 32 bits or 64 bits Byte (8 bits), KB (kilobyte, 10Byte (8 bits), KB (kilobyte, 1033 ≈≈ 221010 bytes), MBbytes), MB (Megabyte, 10(Megabyte, 1066 ≈≈ 222020 bytes), GB (Gigabyte, 10bytes), GB (Gigabyte, 1099 ≈≈ 223030 bytes). Note: kbytes). Note: k ≠ K because 1000 ≠ 1024.≠ K because 1000 ≠ 1024.
- 15. Computer OrganizationComputer Organization (cont.)(cont.) Computer memory is comparable to a collection ofComputer memory is comparable to a collection of numbered mailboxes. To identify individual cells in anumbered mailboxes. To identify individual cells in a machine’s main memory, each cell is assigned a uniquemachine’s main memory, each cell is assigned a unique name, called its addressname, called its address The organization of byte-size memory cellThe organization of byte-size memory cell ...01001000 01100101 01101100 0110111101101100 00101110 H e l l o ,ASCII ...Data Address 0000 0101 0000 0110 0000 0111 0000 1000 0001 0001 0001 0010 Address Bus Data Bus 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 Low-order endHigh-order end Least Significant Bit (LSB)Most Significant Bit (MSB)
- 16. AcknowledgementsAcknowledgements Moore’s Law: Kopp, Carlo. Monash University.Moore’s Law: Kopp, Carlo. Monash University. Melbourne, Australia. 2000.Melbourne, Australia. 2000.