C Language Lecture 17
- 1. Computing Fundamentals Dr. Muhammad Yousaf Hamza Deputy Chief Engineer, PIEAS
- 2. // Addition of two integers using //Function #include<stdio.h> int addnumbers(int x, int y); int main() { int num1, num2, add_result; printf("Enter first numbern"); scanf("%d", &num1); printf("Enter second numbern"); scanf("%d", &num2); add_result = addnumbers(num1, num2); printf("Addition result is %dn",add_result); getchar(); return 0; } int addnumbers(int x, int y) { int z; z = x +y; return z; } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 3. // Addition of two integers using //Function #include<stdio.h> int addnumbers(int x, int y); int main() { int num1, num2, add_result; printf("Enter first numbern"); scanf("%d", &num1); printf("Enter second numbern"); scanf("%d", &num2); add_result = addnumbers(num1, num2); printf("Addition result is %dn",add_result); printf(“%d”, z) // Error getchar(); return 0; } int addnumbers(int x, int y) { int z; z = x +y; printf(“%d”, num1) // Error return z; } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS Any variable declared in a function is not visible inside main and vice versa.
- 4. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS Example of Function // To determine the even or odd using // a function #include<stdio.h> void EvenOrOdd(int num); int main() { int num; printf("Enter a number to know even or oddn"); printf("Enter -100 to exitn"); while (1) { scanf("%d", &num); if (num == -100) break; EvenOrOdd(num); } printf("OK"); getchar(); return 0; } void EvenOrOdd(int num) { if(num%2==0) printf("Evenn"); else printf("Oddn"); }
- 5. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS Example of Function #include<stdio.h> void printLine(void) { printf("n*****************n"); } void main () { int num; printLine(); printf("Enter a Number :"); scanf("%d",&num); if(num%2==0) printf("Even Number"); else printf("Odd Number"); printLine(); getchar(); } Output ***************** Enter a Number :13 Odd Number *****************
- 6. Returning a value using if else statement A single value is returned, however, multiple return statements can be used within a single function using “if-then-else” statement. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 7. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS // Returning a value and if else #include<stdio.h> int myfunc(int x, int y); int main() { int num1, num2, smaller; printf("Enter first numbern"); scanf("%d", &num1); printf("Enter second numbern"); scanf("%d", &num2); smaller = myfunc(num1, num2); printf("%d is smallern",smaller); getchar(); getchar(); return 0; } int myfunc(int x, int y) { if(x < y ) return x; else return y; }
- 8. Home/Lab Assignments Write a function that returns the greater of the two numbers i.e. make a function that takes two integer arguments and returns the greater of the two. Write program to use this function. (Try Yourself) Write a function should accept two arguments i.e. length and width of the rectangle and should return the area of the rectangle, the prototype of the function is as under: float areaRect(float, float); (Try Yourself) Develop a function that accepts two values as length and width of a shape and returns 0 or 1. A 1 will be returned if the shape is a square otherwise a 0 will be returned. (Try Yourself). Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 9. Home/Lab Assignments A normal dice has 6 sides numbered from 1 to 6, when the dice is rolled the number on top side of the dice is considered to be the result of rolling the dice. Dices are used in many games etc. Your task is to write a function int rollDice(), the function should return an integer value ranging from 1 to 6, to make function return a random number each time use the library function rand() and srand() (. Write a program that allow the user to call this function multiple times , display the value returned by the function. (Try Yourself) Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 10. Pass by Value Versus Pass by Reference Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 11. // Addition of two integers using Function #include<stdio.h> int addnumbers(int x, int y); int main() { int num1, num2, add_result; printf("Enter first numbern"); scanf("%d", &num1); printf("Enter second numbern"); scanf("%d", &num2); add_result = addnumbers(num1, num2); printf("Addition result is %dn",add_result); getchar(); return 0; } int addnumbers(int x, int y) { int z; z = x +y; return z; } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS Pass by Value
- 12. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS /* Passing arguments by value */ //Page Example 366 #include <stdio.h> void by_value(int x, int y, int z); int main() { int x = 2, y = 4, z = 6; printf("n Before calling by_value, x = %d, y = %d, z = %d.", x, y, z); by_value(x, y, z); printf("nn After calling by_value, x = %d, y = %d, z = %d.", x, y, z); getchar(); return(0); } void by_value(int x, int y, int z) { printf("nn Within function by_value, x = %d, y = %d, z = %d.", x, y, z); x = 0; y = 0; z = 0; printf("nn Again within function by_value , x = %d, y = %d, z = %d.", x, y, z); } Before calling by_value, x = 2, y = 4, z = 6. // Within function by_value, x = 2, y = 4, z = 6. // Again Within function by_value, x = 0, y = 0, z = 0. //After calling y_value(), x = 2, y = 4, z = 6. Pass by Value
- 13. Calling Functions: Call by Value and Call by Reference • Used when invoking functions • Call by value – Copy of argument passed to function – Changes in function do not effect original – Use when function does not need to modify argument • Avoids accidental changes • Call by reference – Passes original argument – Changes in function effect original – Only used with trusted functions • At this stage, we focus on call by value • We will discuss call by reference later. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 14. Parameters Passed by Value • Parameters passed by value!! – This means they are basically local variables initialized to the values that the function is called with. – They can be modified as you wish but these modifications will not be seen in the calling routine! #include<stdio.h> int twice(int x); int main() { int x=10,y; y=twice(x); printf("%d,%dn",x,y); getchar(); retun 0; } int twice(int x) { x=x+x; return x; } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 15. Functions can Access Other Functions Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 16. Functions can access other functions Once you have written a function, it can be accessed from other functions. We can therefore build more complex functions from simpler functions Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 17. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS // Function calling other function #include <stdio.h> float getavg(float x, float y, float z, int totnum); float calavg(float sum_res, int totalnum); int main() { float num1 = 3.5, num2 = 5.9, num3 = 1.7, avg; int totnumbers = 3; avg = getavg(num1,num2,num3,totnumbers); printf("Average is %fn",avg); getchar(); return 0; } float getavg(float x, float y, float z, int totnum) { float sum = x + y + z, average; average = calavg(sum, totnum); return average; } float calavg(float sum_res, int totalnum) { float avrg = sum_res/totalnum; return avrg; }
- 18. Calling a function by Another Function void a(void) { printf(“Function a”); b(); } void b(void) { printf(“Function b”); } void main() { a(); b(); } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS Can we call function b() inside function a() ? No, as function a() does not know anything about function b(). A function can call only those functions which are defined or declared before it.
- 19. More discussion on input and output of Functions Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 20. // Calculate factorial without function #include<stdio.h> int main() { int i, fact, num1; printf("Enter a positive integern"); scanf("%d", &num1); fact = 1; for (i = num1; i >=1; i--) { fact = fact * i; } printf("Factorial of %d is %dn",num1, fact); getchar(); return 0; } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 21. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS // Calculate factorial using //Functions #include<stdio.h> int cal_fac(int x); int main() { int i, fact, num1; printf("Enter a positive integren"); scanf("%d", &num1); fact = cal_fac(num1); printf("Factorial of %d is %dn",num1, fact); getchar(); return 0; } int cal_fac(int x) { int i, fact; fact = 1; if(x == 0) fact = 1; else { for (i = x; i >=1; i--) { fact = fact*i; } } return fact; }
- 22. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS /* demonstrates a function that does not take any arguments and does not provide output to main. */ #include <stdio.h> void stars (); //function declaration // (prototype) int main() { int x = 5, y = 13; stars (); //call to function x = x+10; y = x*x + (10/2); stars (); //call to function getchar(); return 0; } // function definition void stars () { int j; for(j=0; j < 10; j++) printf("*"); printf("n"); } Printing stars through a function
- 23. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS // demonstrates of passing //constants to a function #include <stdio.h> void stars (char ch, int n) ; int main() { int x = 5, y = 13, z; stars (‘%’, 7); //call to function x = x+10; y = x*x + (10/2); stars (‘$’, 18); //call to function z = x + y; return 0; } // function definition void stars (char ch, int n) { int j; for(j=0; j < n; j++) printf(“%c“, ch); printf("n"); } Printing any symbol any times
- 24. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS // demonstrates of passing values from //variables to a function #include <stdio.h> void stars (char ch, int n) ; int main() { char chp; int nt ; printf(“Please enter a symbol you want to printn”); chp = getchar(); printf(“Please enter the number of times you want to print the charactern”); scanf(“%d”, nt); stars (chp, nt); //call to function // Rest of the code here return 0; } // function definition void stars (char ch, int n) { int j; for(j=0; j < n; j++) printf(“%c“, ch); printf("n"); } Passing Variables
- 25. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS // Demonstration of missing arguments #include <stdio.h> void stars (char ch = ‘*’, int n = 10) ; int main() { char chp; int nt ; // Rest of the code stars (); //call to function stars (‘#’); //call to function stars (‘+’, 5); //call to function chp = ‘~’; nt = 12; stars (chp, nt); //call to function stars(); // Rest of the code here return 0; } // function definition void stars (char ch, int n) { int j; for(j=0; j < n; j++) printf(“%c“, ch); printf("n"); } Missing Arguments
- 26. Returning a value from function Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS /* Program that will pass temperature in centigrade to a function that converts it into Fahrenheit and returns the value to the main function*/ #include <stdio.h> float ctof (float); //declaration int main() { float centi, farhen; printf("nEnter temperature in centigraden"); scanf("%f",¢i); farhen = ctof(centi); printf(“ %f Centigrade = %f Faherenheit”, centi, fahren); getchar(); return 0; } /* converts centigrade to Fahrenheit */ float ctof (float cgrade) { float fgrade; fgrade = (9/5)*cgrade+ 32.0; return fgrade; }
- 27. Arguments and Parameters • stars (‘%’, 7); //call to function • Arguments: The values as ‘%’, 7 that are passed to a function are called arguments. • void stars (char ch, int n) • The variables within the function that hold the arguments are called parameters. In this example, ch and n are parameters. • We should note that many programmers use the terms argument and parameter somewhat interchangeably. • When the function is called, its parameters are automatically initialized to the values passed by the calling program. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 28. // Finding the maximum of three numbers using a function #include<stdio.h> int maximum( int, int, int ); int main() { int a, b, c; printf("Enter three integers: " ); scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c ); printf( "Maximum is: %dn", maximum( a, b, c ) ); getchar(); return 0; } int maximum( int x, int y, int z ) { int max = x; if ( y > max ) max = y; if ( z > max ) max = z; return max;} Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 29. Passing string to a function #include <stdio.h> void Display(char ch[]); int main() { char c[50]; printf("Enter string: "); gets(c); Display(c); // Passing string c to function. getchar(); return 0; } // Function definition void Display(char ch[]) // It will automatically fix its size { printf("String Output: "); puts(ch); } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 30. #include <stdio.h> void func1(void); int main() { int count; for (count = 0; count < 20; count++) { printf("At iteration %d: ", count); func1(); } getchar(); return 0; } void func1(void) { int x = 0; int y = 0; printf("x = %d, y = %dn", x, y); x++; y++; } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS • At iteration 0: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 1: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 2: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 3: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 4: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 5: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 6: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 7: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 8: x = 0, y = 0 • At iteration 9: x = 0, y = 0 • and so on
- 31. Scope of Variables Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 32. //Concept of local variables #include <stdio.h> void demo(void); int main() { int x = 1, y = 2; printf("nnBefore calling demo(), x = %d and y = %d", x, y); //x=1, y=2 demo(); printf("nnAfter calling demo(), x = %d and y = %dn", x, y); //x=1,y=2 getchar(); return 0; } void demo(void) // Function header and definition { /* Declare and initialize two local variables. */ int x = 88, y = 99; /* Display their values. */ printf("nnWithin demo(), x = %d and y = %d", x, y); // x=88, y=89 } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 33. What is scope? • The scope of a variable is where it can be used in a program LOCAL VARIABLES • Normally variables are local in scope - this means they can only be used in the function where they are declared. • All variables declared inside functions are local variables – Known only in function defined Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 34. Local Variables • Local Variables int func1 (int y) { int a, b = 10; float rate; double cost = 12.55; ....... } • Those variables declared “within” the function are considered “local variables”. • They values can only be used inside the function they were declared in, and not elsewhere. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
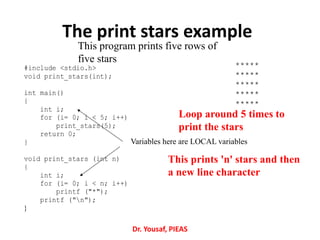
- 35. The print stars example #include <stdio.h> void print_stars(int); int main() { int i; for (i= 0; i < 5; i++) print_stars(5); return 0; } void print_stars (int n) { int i; for (i= 0; i < n; i++) printf ("*"); printf ("n"); } This program prints five rows of five stars This prints 'n' stars and then a new line character Loop around 5 times to print the stars ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** Variables here are LOCAL variables Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 36. Local and Global Variables Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 37. // Scope of variables, Page 80 //Local versus global (external) variables, pages; 207-209 // Local Variable #include<stdio.h> void demo(int x); int main() { int x = 10; printf("n in main, before demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 10 demo(x); printf("in main, after demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 10 getchar(); return 0; } void demo (int x) { x = x+20; printf("inside demo x= %d nn", x); // x = 30 } • Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 38. // Global variable #include<stdio.h> void demo(); int x = 10; // note the declaration above the main int main() { printf("nin main, before demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 10 demo(); printf("in main, after demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 30 getchar(); return 0; } void demo () { x = x + 20; // x has not been declared in demo printf("in demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 30 } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 39. Global Variables • We can also declare global variables. • If we declare a variable outside a function it can be used in any function beneath where it is declared, hence called global variables. • Global variables are also sometimes called external variables, since they are defined external to any function. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 40. // Again x is global variable #include<stdio.h> void demo(int y); // y is local variable int x = 10; // x is global variable int main() { printf("nin main, before demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 10 demo(x); printf("in main, after demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 30 getchar(); return 0; } void demo (int y) // y has been declared in demo { x = y + 20; // x has not been declared in demo printf("in demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 30 } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 41. // Still Local variable #include<stdio.h> void demo(int x); int x = 10; int main() { printf("nin main, before demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 10 demo(x); printf("nin main, after demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 10 getchar(); return 0; } void demo (int x) // demo has its own x, so now local for this function. { x = x + 20; printf("in demo x = %d nn", x); // x = 30 } Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 42. Example: Global Variable Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS #include <stdio.h> float total = 0.0; void caltot (float num1, float num2, float num3); //declaration void printtot (); int main() { float x = 4.5, y = 3.7, z = 8.1; caltot(x, y, z); printtot(); printf(“Total is %fn”, total); getchar(); return 0; } void caltot (float num1, float num2, float num3) { total = num1 + num2 + num3; } void printtot () { printf(“Total is %fn”, total); }
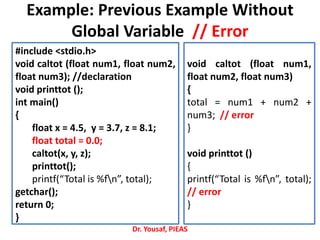
- 43. Example: Previous Example Without Global Variable // Error Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS #include <stdio.h> void caltot (float num1, float num2, float num3); //declaration void printtot (); int main() { float x = 4.5, y = 3.7, z = 8.1; float total = 0.0; caltot(x, y, z); printtot(); printf(“Total is %fn”, total); getchar(); return 0; } void caltot (float num1, float num2, float num3) { total = num1 + num2 + num3; // error } void printtot () { printf(“Total is %fn”, total); // error }
- 44. Notes About Global Variables – Global variables are also called extern variables. – Global variables are known in any function • A global variable is used when it must be accessible to more than one function in a program. • Global variables are often the most important variables in procedural programs. • However, global variables create organizational problems because they can be accessed by any function. • The wrong functions may access them, or functions may access them incorrectly. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 45. Notes About Global Variables Question: Can there be a local and a global variable of same name? Ans: Yes, if a function has a variable whose name is same as previously declared global variable, then the local variable will take precedence inside such a function Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 46. Home Take Assignment (1) Declare a global array of 10 integers, declare a variable size that will store the size of the array, now write the following functions. A. void PrintArray(void) : This function should print the global array B. void SumArray(void): This function should print the sum of all elements of the array (2) A palindrome is a number that reads the same from left to right or from right to left. For example 121 , 222, 62226 are all palindrome numbers. Write a program (without function) that should accept three digits number from the user. You code should tell whether the given number is palindrome or not? (3) Modify the above program such that it should accept three digits number from the user. Write a function isPalindrome. Pass the number provided by the user from main to this function. This function should determine whether the number is palindrome or not? The function should return the result to the main. The main should display it. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS
- 47. Home Take Assignment A stack is a container of objects such that objects are placed on top of each other just like dishes are placed on top of each other. Write a program that declares a global array of 10 integers, name this array as stack. 2‐ Write the following functions 1‐push: This function should put the value of a variable to the stack. 2‐pop: This function should return the first element of the array 3‐show: The function should display the contents of the array stack 4-shift_right : This function should shift the elements of the array 1 place toward right i.e. element at index 0 will move to index 1 , element at index 1 will move to index 2 and so on till the last array element is processed 5. void shift_left(void) : this function should shift the elements of the array 1 place towards left i.e. element at index 1 will be shifted to index 0, element at index 2 will be shifted to index 1. Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS




























![Passing string to a function
#include <stdio.h>
void Display(char ch[]);
int main()
{
char c[50];
printf("Enter string: ");
gets(c);
Display(c); // Passing string c to function.
getchar(); return 0;
}
// Function definition
void Display(char ch[]) // It will automatically fix its size
{
printf("String Output: ");
puts(ch);
}
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17-190313191802/85/C-Language-Lecture-17-29-320.jpg)