C++ metaprogramming
- 1. Arindam Mukherjee Pune C++ and Boost Meetup C++TEMPLATE METAPROGRAMMING
- 2. Template type computations Templates provide a Turing complete computation subsystem – that runs during compilation. This capability was not entirely consciously designed. Erwin Unruh found this somewhat accidentally ~ early 90s.
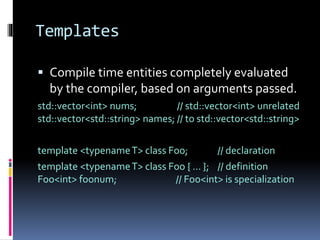
- 3. Templates Compile time entities completely evaluated by the compiler, based on arguments passed. std::vector<int> nums; // std::vector<int> unrelated std::vector<std::string> names; // to std::vector<std::string> template <typenameT> class Foo; // declaration template <typenameT> class Foo { … }; // definition Foo<int> foonum; // Foo<int> is specialization
- 4. Non-type template parameters Templates can have non-type parameters: template <typename T, int N> struct array { T data[N]; …. } Non-type args are compile time constants. array<int, 10> arr; // array of 10 ints sizeof is evaluated at compile time. int arr[sizeof(int)]; // array of 4* ints
- 5. Embedded types Typedefs inside a class / class template. template <typename T> struct add_const { typedef const T type; }; add_const<int>::type ci; // const int
- 6. Embedded constants Enums inside a class / class template. template <int M, int N> struct add { enum { value = M + N } } int array[add<10, 20>::value];
- 7. Branching: specializations Specialize for specific types. template <typename T> struct Foo { … }; // default impl template <> struct Foo<int> { … }; // int-specific Applicable to function templates too.
- 8. Partial specializations Specialize for type families. template <typename T, typename U> struct Foo { … }; // default impl template <typename T> struct Foo<T, T> { … }; // Foo<char, char> template <typename T> struct Foo<T*, T> { … }; // Foo<int*, int> NOT applicable to function templates.
- 9. Recursion by specializations Compute factorial at compile time: template <int N> struct factorial { enum { value = N*factorial<N-1>::value }; }; template <> struct factorial<0> { // terminating condition enum { value = 1 }; };
- 10. Applying the techniques Remove const: template <typename T> struct remove_const { typedef T type; }; template <typename T> // partial struct remove_const<const T> { // speclzn typedef T type; }; Called as: remove_const<const int>::type x; // int
- 11. Applying the techniques Querying types: template <typename T, typename U> struct are_same { enum { value = 0 }; }; template <typename T> / partial struct are_same<T, T> // specialization { enum { value = 1 }; }; Called as: are_same<int, int>::value == 1;
- 12. Applying the techniques Remove levels of indirection: template <typename T> struct deref { typedef T type; }; template <typename T> // partial struct deref<T*> { // specialization typedef typename deref<T>::type type; } Called as: deref<int*****>::type x; // x is int
- 13. Boost Type Traits A header-only library to query and manipulate types at compile time. Lots of trait metafunctions. #include <boost/type_traits.hpp> typedef int* intptr; assert(boost::is_ptr<intptr>::value); struct Foo {int a; void *b; float c; }; assert(boost::is_pod<Foo>::value);
- 14. SFINAE Compiler tries to resolve function calls to a unique overload, or unique template with appropriate arguments. Multiple templates may be candidates but a unique one must survive. All candidates instantiated. Those that fail instantiation eliminated. Not An Error if a single candidate survives.
- 15. SFINAE & enable_if Exploit SFINAE to resolve to apt template. boost::enable_if #include <boost/utility/enable_if.hpp> boost::enable_if<true, T>::type x; // T boost::enable_if<false, T>::type y; //!def boost::disable_if (opposite of enable_if).
- 16. SFINAE & enable_if (contd.) Serialize arbitrary types: #include <boost/utility/enable_if.hpp> typedef vector<char> buffer_t; template <typename T> buffer_t serialize(const T&); Need a fast version for POD types and generic version for non-POD types. template <typename T> enable_if<is_pod<T>, vector<char>>::type serialize(const T&) {…} // pod version // Use disable_if for the non-POD version
- 17. Metafunctions Metafunction: a class or class template taking only type parameters, with a single embedded typedef. All the Boost type traits are metafunctions. Boost TMP Library: library of metafunctions. Provides means of composing and generating metafunctions from simpler metafunctions.
- 18. Composing metafunctions Metafunctions need to be combined: #include <boost/type_traits.hpp> template <typename T> void foo(T obj) { if (boost::is_pointer<T>::value || boost::is_array<T>::value) //runtime { … } else { … } }
- 19. Boost MPL (contd.) How to make another metafunction that OR’s two type traits. #include <boost/mpl/or.hpp> #include <boost/type_traits.hpp> template <typename T> void foo(T obj) { if (boost::mpl::or_< boost::is_pointer<T> , boost::is_array<T> >::value) { … } else { … } }
- 20. Boost MPL (contd.) Numbers can be wrapped in types: #include <boost/mpl/integral_c.hpp> #include <boost/mpl/greater.hpp> #include <boost/type_traits.hpp> namespace mpl = boost::mpl; template <typename T, typename U> struct is_larger : mpl::greater< mpl::integral_c<size_t, sizeof T> , mpl::integral_c<size_t, sizeof U> > {};
- 21. Thank you! Q & A Book: Modern C++ Design – Andrei Alexandrescu Book: Advanced C++ Template Metaprogramming – Davide di Gennaro Book: C++ Template Metaprogramming – Dave Abrahams, Aleksey Gurtovoy



![Non-type template parameters
Templates can have non-type parameters:
template <typename T, int N>
struct array {
T data[N];
….
}
Non-type args are compile time constants.
array<int, 10> arr; // array of 10 ints
sizeof is evaluated at compile time.
int arr[sizeof(int)]; // array of 4* ints](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmetaprogramming-141212152454-conversion-gate02/85/C-metaprogramming-4-320.jpg)

![Embedded constants
Enums inside a class / class template.
template <int M, int N> struct add {
enum { value = M + N }
}
int array[add<10, 20>::value];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmetaprogramming-141212152454-conversion-gate02/85/C-metaprogramming-6-320.jpg)














