C programming decision making
- 1. C Programming 45 Decision-making structures require that the programmer specifies one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be true, and optionally, other statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be false. Shown below is the general form of a typical decision-making structure found in most of the programming languages: C programming language assumes any non-zero and non-null values as true, and if it is either zero or null, then it is assumed as false value. C programming language provides the following types of decision-making statements. Statement Description if statement An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. if...else statement An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when 10. DECISION MAKING
- 2. C Programming 46 the Boolean expression is false. nested if statements You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s). switch statement A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. nested switch statements You can use one switch statement inside another switch statement(s). ifStatement An if statement consists of a Boolean expression followed by one or more statements. Syntax The syntax of an ‘if’ statement in C programming language is: if(boolean_expression) { /* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */ } If the Boolean expression evaluates to true, then the block of code inside the ‘if’ statement will be executed. If the Boolean expression evaluates to false, then the first set of code after the end of the ‘if’ statement (after the closing curly brace) will be executed. C programming language assumes any non-zero and non-null values as true and if it is either zero or null, then it is assumed as false value. Flow Diagram
- 3. C Programming 47 Example #include <stdio.h> int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 10; /* check the boolean condition using if statement */ if( a < 20 ) { /* if condition is true then print the following */ printf("a is less than 20n" ); } printf("value of a is : %dn", a); return 0; } When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result: a is less than 20;
- 4. C Programming 48 value of a is : 10 if…elseStatement An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the Boolean expression is false. Syntax The syntax of an if...else statement in C programming language is: if(boolean_expression) { /* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */ } else { /* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false */ } If the Boolean expression evaluates to true, then the if block will be executed, otherwise, the else block will be executed. C programming language assumes any non-zero and non-null values as true, and if it is either zero or null, then it is assumed as false value. Flow Diagram
- 5. C Programming 49 Example #include <stdio.h> int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; /* check the boolean condition */ if( a < 20 ) { /* if condition is true then print the following */ printf("a is less than 20n" ); } else { /* if condition is false then print the following */ printf("a is not less than 20n" ); } printf("value of a is : %dn", a); return 0; } When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result: a is not less than 20; value of a is : 100 if...elseif...elseStatement An if statement can be followed by an optional else if...else statement, which is very useful to test various conditions using single if...else if statement. When using if…else if…else statements, there are few points to keep in mind: An if can have zero or one else's and it must come after any else if's. An if can have zero to many else if's and they must come before the else.
- 6. C Programming 50 Once an else if succeeds, none of the remaining else if's or else's will be tested. Syntax The syntax of an if...else if...else statement in C programming language is: if(boolean_expression 1) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */ } else if( boolean_expression 2) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */ } else if( boolean_expression 3) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true */ } else { /* executes when the none of the above condition is true */ } Example #include <stdio.h> int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; /* check the boolean condition */ if( a == 10 ) { /* if condition is true then print the following */
- 7. C Programming 51 printf("Value of a is 10n" ); } else if( a == 20 ) { /* if else if condition is true */ printf("Value of a is 20n" ); } else if( a == 30 ) { /* if else if condition is true */ printf("Value of a is 30n" ); } else { /* if none of the conditions is true */ printf("None of the values is matchingn" ); } printf("Exact value of a is: %dn", a ); return 0; } When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result: None of the values is matching Exact value of a is: 100 NestedifStatements It is always legal in C programming to nest if-else statements, which means you can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s). Syntax The syntax for a nested if statement is as follows: if( boolean_expression 1) {
- 8. C Programming 52 /* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */ if(boolean_expression 2) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */ } } You can nest else if...else in the similar way as you have nested if statements. Example #include <stdio.h> int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; int b = 200; /* check the boolean condition */ if( a == 100 ) { /* if condition is true then check the following */ if( b == 200 ) { /* if condition is true then print the following */ printf("Value of a is 100 and b is 200n" ); } } printf("Exact value of a is : %dn", a ); printf("Exact value of b is : %dn", b ); return 0; } When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
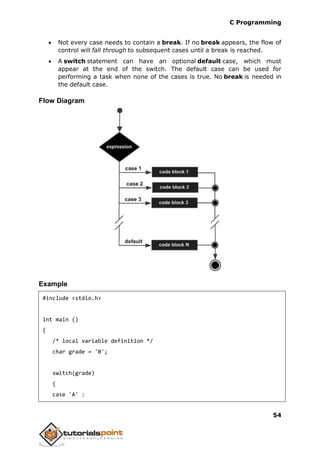
- 9. C Programming 53 Value of a is 100 and b is 200 Exact value of a is : 100 Exact value of b is : 200 switchStatement A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being switched on is checked for each switch case. Syntax The syntax for a switch statement in C programming language is as follows: switch(expression){ case constant-expression : statement(s); break; /* optional */ case constant-expression : statement(s); break; /* optional */ /* you can have any number of case statements */ default : /* Optional */ statement(s); } The following rules apply to a switch statement: The expression used in a switch statement must have an integral or enumerated type, or be of a class type in which the class has a single conversion function to an integral or enumerated type. You can have any number of case statements within a switch. Each case is followed by the value to be compared to and a colon. The constant-expression for a case must be the same data type as the variable in the switch, and it must be a constant or a literal. When the variable being switched on is equal to a case, the statements following that case will execute until a break statement is reached. When a break statement is reached, the switch terminates, and the flow of control jumps to the next line following the switch statement.
- 10. C Programming 54 Not every case needs to contain a break. If no break appears, the flow of control will fall through to subsequent cases until a break is reached. A switch statement can have an optional default case, which must appear at the end of the switch. The default case can be used for performing a task when none of the cases is true. No break is needed in the default case. Flow Diagram Example #include <stdio.h> int main () { /* local variable definition */ char grade = 'B'; switch(grade) { case 'A' :
- 11. C Programming 55 printf("Excellent!n" ); break; case 'B' : case 'C' : printf("Well donen" ); break; case 'D' : printf("You passedn" ); break; case 'F' : printf("Better try againn" ); break; default : printf("Invalid graden" ); } printf("Your grade is %cn", grade ); return 0; } When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result: Well done Your grade is B NestedswitchStatements It is possible to have a switch as a part of the statement sequence of an outer switch. Even if the case constants of the inner and outer switch contain common values, no conflicts will arise. Syntax The syntax for a nested switch statement is as follows: switch(ch1) { case 'A': printf("This A is part of outer switch" );
- 12. C Programming 56 switch(ch2) { case 'A': printf("This A is part of inner switch" ); break; case 'B': /* case code */ } break; case 'B': /* case code */ } Example #include <stdio.h> int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; int b = 200; switch(a) { case 100: printf("This is part of outer switchn", a ); switch(b) { case 200: printf("This is part of inner switchn", a ); } } printf("Exact value of a is : %dn", a ); printf("Exact value of b is : %dn", b ); return 0; } When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
- 13. C Programming 57 This is part of outer switch This is part of inner switch Exact value of a is : 100 Exact value of b is : 200 The?:Operator: We have covered conditional operator ? : in the previous chapter which can be used to replace if...else statements. It has the following general form: Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3; Where Exp1, Exp2, and Exp3 are expressions. Notice the use and placement of the colon. The value of a ? expression is determined like this: 1. Exp1 is evaluated. If it is true, then Exp2 is evaluated and becomes the value of the entire ? expression. 2. If Exp1 is false, then Exp3 is evaluated and its value becomes the value of the expression.