Chapter 2-Lecture 3.pptx
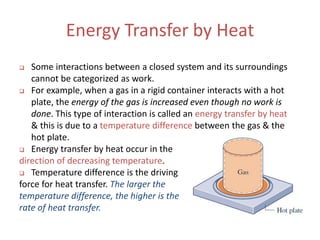
- 1. Energy Transfer by Heat Some interactions between a closed system and its surroundings cannot be categorized as work. For example, when a gas in a rigid container interacts with a hot plate, the energy of the gas is increased even though no work is done. This type of interaction is called an energy transfer by heat & this is due to a temperature difference between the gas & the hot plate. Energy transfer by heat occur in the direction of decreasing temperature. Temperature difference is the driving force for heat transfer. The larger the temperature difference, the higher is the rate of heat transfer.
- 2. Energy transfer by heat: Q (in J) Q > 0 : heat transfer to the system Q < 0 : heat transfer from the system Sign convention for heat transfer is the reverse of work. Similar to work, the value of heat transfer depends on the process and not the just the end states, where Q is not a property. The amount of energy transfer by heat for a process is given by: The amount of energy transfer by heat during a period of time can be found by integrating from time t1 to t2: where 𝑄 is the net rate of heat transfer. Sign Convention, Notation & Heat Transfer Rate
- 3. The net rate of heat transfer, 𝑄, is related to the heat flux 𝑞 by: A = area on the system boundary where heat transfer occurs. Units of Q & 𝑄 are the same as W and 𝑊, respectively. Units for 𝑞 are those of heat transfer rate per unit area: kW/m2 or Btu/h·ft2. The word adiabatic means without heat transfer. Thus, if a system undergoes a process with no heat transfer with its surroundings, that process is called an adiabatic process. Sign Convention, Notation & Heat Transfer Rate
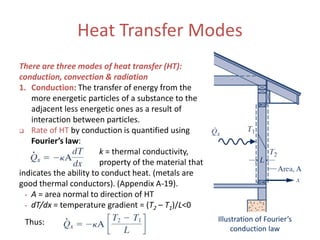
- 4. Illustration of Fourier’s conduction law Heat Transfer Modes There are three modes of heat transfer (HT): conduction, convection & radiation 1. Conduction: The transfer of energy from the more energetic particles of a substance to the adjacent less energetic ones as a result of interaction between particles. Rate of HT by conduction is quantified using Fourier’s law: k = thermal conductivity, property of the material that indicates the ability to conduct heat. (metals are good thermal conductors). (Appendix A-19). • A = area normal to direction of HT • dT/dx = temperature gradient = (T2 – T1)/L<0 Thus:
- 5. Illustration of Newton’s law of cooling Heat Transfer Modes 2. Convection: The transfer of energy between a solid surface at temperature Tb (shown in figure) & an adjacent fluid that is in motion & has a temperature Tf, & it involves combined effects of conduction & fluid motion. (In figure shown heat is transferred from the surface to the air since Tb >Tf) Rate of HT by convection is quantified using Newton’s law of cooling: • h = HT coefficient (empirical parameter that depends on the nature of the flow, fluid properties & geometry) • A = surface area undergoing HT
- 6. Heat Transfer Modes When fans or pumps cause the fluid to move, the value of the HT coefficient is generally greater than when relatively slow buoyancy-induced motions occur. Thus, convection can be forced or natural (free). Typical values of HT coefficient for forced & free convection:
- 7. Heat Transfer Modes 3.Radiation: Transfer of energy due to emission of electromagnetic waves or photons. Unlike conduction, thermal radiation requires no medium to propagate & can even take place in vacuum. Solid surfaces, gases, & liquids all emit, absorb, & transmit thermal radiation to varying degrees. The rate at which energy is emitted from a surface of area A & absolute temperature Tb is quantified by a modified form of the Stefan–Boltzmann law: • ε = emissivity, a surface property that indicates how effectively the surface radiates & 0 ≤ ε ≤ 1. • σ = Stefan–Boltzmann constant:
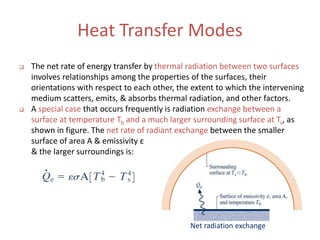
- 8. Net radiation exchange Heat Transfer Modes The net rate of energy transfer by thermal radiation between two surfaces involves relationships among the properties of the surfaces, their orientations with respect to each other, the extent to which the intervening medium scatters, emits, & absorbs thermal radiation, and other factors. A special case that occurs frequently is radiation exchange between a surface at temperature Tb and a much larger surrounding surface at Ts, as shown in figure. The net rate of radiant exchange between the smaller surface of area A & emissivity ε & the larger surroundings is:
- 9. Closing Comments The first step in a thermodynamic analysis is to define the system & its boundaries. It is only after this that possible heat interactions with the surroundings are considered, since these are always evaluated at the system boundary. In some cases, Q will be provided in problems. If not, then Q is found using the energy balance that will be discussed next.
- 10. Energy Accounting: Energy Balance for Closed Systems First law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy principle): It states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed during a process; it can only change forms. Thus it allows for studying the relationships among the various forms of energy and their interactions. The energy balance requires that in any process of a closed system the energy of the system increases or decreases by an amount equal to the net amount of energy transferred across its boundary: OR: The signs of Q & W are different, since +ve Q is heat transfer to system & –W is work is done on system by surroundings.
- 11. Energy Accounting: Energy Balance for Closed Systems First law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy principle): In many cases, the changes in PE & KE for a closed stationary system are zero, so both ∆KE & ∆PE are = 0. For all adiabatic processes between two specified states of a closed system, the net work done is the same regardless of the nature of the closed system and the details of the process. For a cyclic process in which a system is changed in several ways but in the end returns to its original state: the first law tells us that the total energy of the system must be conserved, meaning that the energy of the system is the same at the end of the cyclical process as it was at the beginning. This can be expressed as: E2 = E1 or E2 - E1 = ∆E = 0
- 12. Important Aspects of the Energy Balance The instantaneous time rate form of the energy balance is: OR: OR: All the above are convenient forms of the energy balance to start the analysis of closed systems.
- 13. Choices for System Boundaries Figures show a gas or liquid in a rigid, well- insulated container: In Fig. a, the gas itself is the system. As current flows through the copper plate, energy transfers from the copper plate to the gas due to the temperature difference between the plate & the gas, & this is called heat transfer. In Fig. b, the boundary is drawn to include the copper plate. Thus, from the thermodynamic definition of work that the energy transfer that occurs as current crosses the boundary of this system must be regarded as work.
- 14. Choices for System Boundaries Figure show a gas or liquid in a rigid, well-insulated container: In Fig. c, the boundary is located so that no energy is transferred across it by heat or work. The next two examples illustrate the use of the energy balance for processes of closed systems.
- 15. Example-Cooling a Gas in a Piston-Cylinder Four-tenths kilogram of a certain gas is contained within a piston–cylinder assembly. The gas undergoes a process for which the pressure–volume relationship is pV1.5 = constant The initial pressure is 3 bar, the initial volume is 0.1 m3, and the final volume is 0.2 m3. The change in specific internal energy of the gas in the process is u2 - u1 = -55 kJ/kg. There are no significant changes in kinetic or potential energy. Determine the net heat transfer for the process, in kJ.
- 16. Example-Cooling a Gas in a Piston-Cylinder SOLUTION Known: A gas within a piston–cylinder assembly undergoes an expansion process for which the pressure–volume relation and the change in specific internal energy are specified. Find: Determine the net heat transfer for the process.
- 17. Example-Cooling a Gas in a Piston-Cylinder Analysis: An energy balance for the closed system takes the form where the kinetic and potential energy terms drop out by assumption 3. Then, writing ΔU in terms of specific internal energies, the energy balance becomes where m is the system mass. Solving for Q The value of the work for this process is determined in the solution to part (a) of Example 2.1: W = +17.6 kJ. The change in internal energy is obtained using given data as Substituting values
- 18. Example-Cooling a Gas in a Piston-Cylinder Solve on Your Own
- 19. Using the Energy Balance: Steady-State Operation A system is at steady state if none of its properties change with time. Many devices operate at steady state or nearly at steady state, so that property variations with time are small enough to ignore. The two examples to follow illustrate the application of the energy rate equation to closed systems at steady state.
- 20. Example-Evaluating Energy Transfer Rates of a Gearbox at Steady State During steady-state operation, a gearbox receives 60 kW through the input shaft and delivers power through the output shaft. For the gearbox as the system, the rate of energy transfer by convection is where h = 0.171 kW/m2·K is the heat transfer coefficient, A = 1.0 m2 is the outer surface area of the gearbox, Tb = 300 K (27°C) is the temperature at the outer surface, and Tf = 293 K (20°C) is the temperature of the surrounding air away from the immediate vicinity of the gearbox. For the gearbox, evaluate the heat transfer rate and the power delivered through the output shaft, each in kW.
- 21. Example-Evaluating Energy Transfer Rates of a Gearbox at Steady State SOLUTION Known: A gearbox operates at steady state with a known power input. An expression for the heat transfer rate from the outer surface is also known. Find: Determine the heat transfer rate & the power delivered through the output shaft, each in kW. Engineering Model: 1. The gearbox is a closed system at steady state. 2. For the gearbox, convection is the dominant heat transfer mode.
- 22. Example-Evaluating Energy Transfer Rates of a Gearbox at Steady State Analysis: Using the given expression for 𝑄 together with known data, the rate of energy transfer by heat is ❶ The minus sign for 𝑄 signals that energy is carried out of the gearbox by heat transfer. The energy rate balance, Eq. 2.37, reduces at steady state to ❷ The symbol 𝑊 represents the net power from the system. The net power is the sum of 𝑊1 and the output power 𝑊2
- 23. Example-Evaluating Energy Transfer Rates of a Gearbox at Steady State With this expression for 𝑊, the energy rate balance becomes Solving for 𝑊2, inserting 𝑄= -1.2 kW, and 𝑊1 = -60 kW, where the minus sign is required because the input shaft brings energy into the system, we have ❸ ❹ The positive sign for 𝑊2 indicates that energy is transferred from the system through the output shaft, as expected.
- 24. Example-Evaluating Energy Transfer Rates of a Gearbox at Steady State Solve on Your Own
- 25. Example-Determining Surface Temperature of a Silicon Chip at Steady State A silicon chip measuring 5 mm on a side & 1 mm in thickness is embedded in a ceramic substrate. At steady state, the chip has an electrical power input of 0.225 W. The top surface of the chip is exposed to a coolant whose temperature is 20°C. The heat transfer coefficient for convection between the chip and the coolant is 150 W/m2·K. If heat transfer by conduction between the chip and the substrate is negligible, determine the surface temperature of the chip, in °C.
- 26. Example-Determining Surface Temperature of a Silicon Chip at Steady State SOLUTION Known: A silicon chip of known dimensions is exposed on its top surface to a coolant. The electrical power input and convective heat transfer coefficient are known. Find: Determine the surface temperature of the chip at steady state. Engineering Model: 1. The chip is a closed system at steady state. 2. There is no heat transfer between the chip and the substrate.
- 27. Example-Determining Surface Temperature of a Silicon Chip at Steady State Analysis: The surface temperature of the chip, Tb, can be determined using the energy rate balance, Eq. 2.37, which at steady state reduces as follows ❶ With assumption 2, the only heat transfer is by convection to the coolant. In this application, Newton’s law of cooling, Eq. 2.34, takes the form ❷ Collecting results Solving for Tb
- 28. Example-Determining Surface Temperature of a Silicon Chip at Steady State Solve on Your Own
- 29. Using the Energy Balance: Transient Operation Many devices undergo periods of transient operation where the state changes with time. (Observed during startup & shutdown periods) The next example illustrates the application of the energy rate balance to an electric motor during startup. The example also involves both electrical work and power transmitted by a shaft.
- 30. Example-Investigating Transient Operation of a Motor The rate of heat transfer between a certain electric motor and its surroundings varies with time as where t is in seconds and 𝑄 is in kW. The shaft of the motor rotates at a constant speed of ω = 100 rad/s (about 955 revolutions per minute, or RPM) and applies a constant torque of τ = 18 N·m to an external load. The motor draws a constant electric power input equal to 2.0 kW. For the motor, plot 𝑄 and 𝑊, each in kW, and the change in energy ΔE, in kJ, as functions of time from t = 0 to t = 120 s. Discuss.
- 31. Example-Investigating Transient Operation of a Motor SOLUTION Known: A motor operates with constant electric power input, shaft speed, and applied torque. The time-varying rate of heat transfer between the motor and its surroundings is given. Find: Plot 𝑄, 𝑊, and ΔE versus time. Discuss. Engineering Model: The system shown in the Accompanying sketch is a closed system.
- 32. Example-Investigating Transient Operation of a Motor Analysis: The time rate of change of system energy is 𝑊represents the net power from the system: the sum of the power associated with the rotating shaft,𝑊𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑓𝑡, and the power associated with the electricity flow, 𝑊𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐: The rate is known from the problem statement: 𝑊𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 = -2.0 kW, where the negative sign is required because energy is carried into the system by electrical work. The term 𝑊𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑓𝑡 can be evaluated with Eq. 2.20 as Because energy exits the system along the rotating shaft, this energy transfer rate is positive. In summary, where the minus sign means that the electrical power input is greater than the power transferred out along the shaft.
- 33. Example-Investigating Transient Operation of a Motor With the foregoing result for 𝑊 and the given expression for 𝑄, the energy rate balance becomes Integrating ❶ The accompanying plots, Figs. E2.6b and c, are developed using the given expression for 𝑄 and the expressions for 𝑊 and ΔE obtained in the analysis. Because of our sign conventions for heat and work, the values of 𝑄and 𝑊 are negative. In the first few seconds, the net rate that energy is carried in by work greatly exceeds the rate that energy is carried out by heat transfer. Consequently, the energy stored in the motor increases rapidly as the motor “warms up.” As time elapses, the value of Q approaches 𝑊, and the rate of energy storage diminishes. After about 100 s, this transient operating mode is nearly over, and there is little further change in the amount of energy stored, or in any other property. We may say that the motor is then at steady state. ❷
- 34. Example-Investigating Transient Operation of a Motor Solve on Your Own