Cloud Computing Basics - https://youtu.be/ohK8Nd8Jq_o
- 1. Pla Virtual u d tfo ization rm C lo xaa S elco T r id Hyb G ri d nts e C li Broker ure s tr uct Inf ra What is Cloud Computing ?
- 2. I Virtualization am... Utility Computing Software As a Service Cluster of Packaging loosely of Capable of coupled computer self computers resources management for a as a common metered cause service
- 3. What is a cloud ? A cloud is a computing service that charges you based only on the amount of computing service that you use .
- 4. Key Characteristics of Cloud Device location Cost Agility Independance Multi Tenancy Reliability Scalability Security Sustainability Virtualizaton
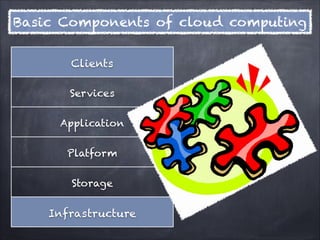
- 5. Basic Components of cloud computing Clients Services Application Platform Storage Infrastructure
- 6. Cloud Computing Architecture SaaS PaaS IaaS Software as a service Platform as a service Infrastructure as a service These three services encapsulate the Basic 6 cloud computing components.
- 7. Software as a Service (SaaS) # Software as a Service (SaaS): In this model, a complete application is offered to the customer, as a service on demand. A single instance of the service runs on the cloud & multiple end users are serviced. On the customers‟ side, there is no need for upfront investment in servers or software licenses, while for the provider, the costs are lowered, since only a single application needs to be hosted & maintained.
- 8. Platform as a Service (PaaS) # Platform as a Service (Paas): Here, a layer of software, or development environment is encapsulated & offered as a service, upon which other higher levels of service can be built. The customer has the freedom to build his own applications, which run on the provider‟s infrastructure. To meet manageability and scalability requirements of the applications, PaaS providers offer a predefined combination of OS and application servers, such as LAMP platform (Linux, Apache, MySql and PHP), restricted J2EE, Ruby etc.
- 9. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) # Infrastructure as a Service (Iaas): IaaS provides basic storage and computing capabilities as standardized services over the network. Servers, storage systems, networking equipment, data centre space etc. are pooled and made available to handle workloads. The customer would typically deploy his own software on the infrastructure.
- 10. How is it different ??? Cloud API # One of the key Characteristics that distinguish cloud computing from standard enterprise computing is that the infrastructure itself is programmable. # Instead of physically deploying servers,storage and network resources to support applications, developers specify how the same virtual components are configured and inter connected. # Including how virtual machine images and application data are stored and retrieved from a storage cloud. # Developers specify how and when components are deployed through an API that is specified by the cloud provider
- 12. Public Cloud Public clouds are owned and operated by third parties; they deliver superior economies of scale to customers, as the infrastructure costs are spread among a mix of users, giving each individual client an attractive low-cost, “Pay-as-you-go” model. All customers share the same infrastructure pool with limited configuration, security protections, and availability variances. These are managed and supported by the cloud provider. One of the advantages of a Public cloud is that they may be larger than an enterprises cloud, thus providing the ability to scale seamlessly, on demand
- 13. Private Cloud Private clouds are built exclusively for a single enterprise. They aim to address concerns on data security and offer greater control, which is typically lacking in a public cloud. There are two variations to a private cloud:On-premise Private Cloud: # On-premise private clouds: , also known as internal clouds are hosted within one‟s own data center. # Externally hosted Private Cloud: This type of private cloud is hosted externally with a cloud provider, where the provider facilitates an exclusive cloud environment with full guarantee of privacy. This is best suited for enterprises that don‟t prefer a public cloud due to sharing of physical resources.
- 14. Hybrid Cloud Hybrid Clouds combine both public and private cloud models. With a Hybrid Cloud, service providers can utilize 3rd party Cloud Providers in a full or partial manner thus increasing the flexibility of computing. The Hybrid cloud environment is capable of providing on-demand, externally provisioned scale. The ability to augment a private cloud with the resources of a public cloud can be used to manage any unexpected surges in workload.
- 15. Cloud Computing Economics # Avoid Capital Expenditure . # Billed on utility/subscription. # Terminate contract anytime. # Lower cost of entry.
- 16. Clients in Cloud Computing Architecture Clients are the devices that the end users interact with, to manage their information on the cloud Thin Client Mobile Thick Client
- 17. Importance of telco in Cloud computing Telecom operators have a unique opportunity to position themselves to capitalise on the growth of cloud services – both as providers and adopters of the technology.
- 18. Cloud and the Telecom Advantage #. Seen as a trusted partner, telecom operators with cloud offerings become a natural choice for enterprises taking advantage IP Internet Protocol of the technology. #. Telecom networks, is providing a synergistic platform for operators to realise new revenues and improve bottom lines. And those investing in the capability LTE Long Term Evolution to provide cloud services are opening the doors to holding an elevated position in the Networked Society.
- 19. Cloud and the Telecom Advantage ..... #. As providers of cloud services, telecom operators can manage connectivity,deliver cloudCapabilities and leverage network assets to enhance cloud offerings. #.Telecom operators also benefit from cloud computing as users by transferring selected business functions to the cloud just as any large enterprise would.
- 20. Grid computing Grid computing is often confused with cloud computing, but they are quite different. Grid computing applies the resources of numerous computers in a network to work on a single problem at the same time. - Cost effective way to use a given amt of computer resource. - Way to solve problems that need tremendous computing power. - The resource of several computers can be shared cooperatively, without one computer managing the other.
- 21. Cloud Broker “The future of cloud computing will be permeated with the notion of brokers negotiating relationships between providers of cloud services and the service customers” “In this context, a broker might be software, appliances, platforms or suites of technologies that enhance the base services available through the cloud. Enhancement will include managing access to these services, providing greater security or even creating completely new services.”
- 22. Cloud Broker - Types The cloud broker creates a layer of abstraction b/w user and providers so that the end users can see one cohesive view of all of the services #. Cloud Service Intermediation: Building services atop an existing cloud platform, such additional security or management capabilities. #.Aggregation: Deploying customer services over multiple cloud platforms. #. Cloud Service Arbitrage: Brokers supply flexibility and "opportunistic choices" - and foster competition between clouds .