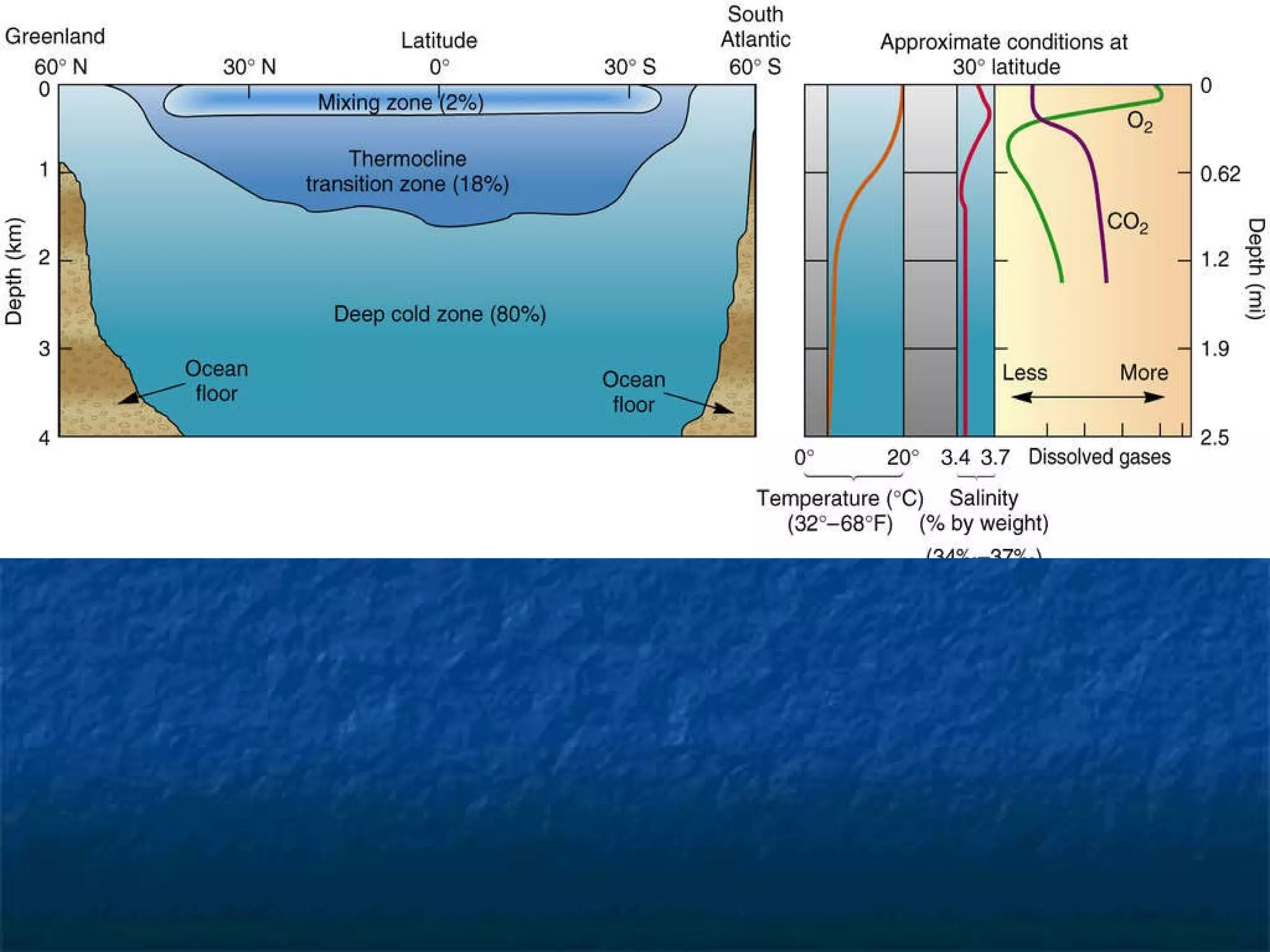
The document discusses coastal systems and their components, processes, and landforms. It describes how oceans are composed of salts dissolved in water and atmospheric gases. Coastal systems are influenced by solar energy, winds, tides, waves, and longshore currents which cause erosion, sediment transport, and deposition. This shapes various coastal landforms like wave-cut platforms, beaches, barrier islands, and reefs. It also describes biological factors like coral reefs and coastal wetlands that provide habitat but are threatened by climate change and development.