Computer Networking and Internet Protocols A Comprehensive Introduction 1st Edition by Raj Jain
- 1. Computer Networking and Internet Protocols A Comprehensive Introduction 1st Edition by Raj Jain install download https://ebookball.com/product/computer-networking-and-internet- protocols-a-comprehensive-introduction-1st-edition-by-raj- jain-15742/ Explore and download more ebooks or textbooks at ebookball.com
- 2. Get Your Digital Files Instantly: PDF, ePub, MOBI and More Quick Digital Downloads: PDF, ePub, MOBI and Other Formats The TCP IP Guide A Comprehensive Illustrated Internet Protocols Reference 1st Edition by Charles Kozierok ISBN 159327047X 9781593270476 https://ebookball.com/product/the-tcp-ip-guide-a-comprehensive- illustrated-internet-protocols-reference-1st-edition-by-charles- kozierok-isbn-159327047x-9781593270476-16842/ The TCP IP Guide A Comprehensive Illustrated Internet Protocols Reference 1st Edition by Charles Kozierok ISBN 9781593270957 159327095X https://ebookball.com/product/the-tcp-ip-guide-a-comprehensive- illustrated-internet-protocols-reference-1st-edition-by-charles- kozierok-isbn-9781593270957-159327095x-20212/ The Internet Book Everything You Need to Know About Computer Networking and How the Internet Works 5th Edition by Douglas Comer ISBN 9780429824449 0429824440 https://ebookball.com/product/the-internet-book-everything-you- need-to-know-about-computer-networking-and-how-the-internet- works-5th-edition-by-douglas-comer- isbn-9780429824449-0429824440-15736/ Networking for Beginners Simple Guide to Study Basic Advanced Computer Network Hardware Wireless and Cabling LTE Internet and Cyber Security 1st edition by Jack Mathew 1712954016 978-1712954010 https://ebookball.com/product/networking-for-beginners-simple- guide-to-study-basic-advanced-computer-network-hardware-wireless- and-cabling-lte-internet-and-cyber-security-1st-edition-by-jack- mathew-1712954016-978-1712954010-20034/
- 3. Medical and Dental Space Planning A Comprehensive Guide to Design Equipment and Clinical Procedures 3rd Edition by Jain Malkin ISBN 9780471385745 https://ebookball.com/product/medical-and-dental-space-planning- a-comprehensive-guide-to-design-equipment-and-clinical- procedures-3rd-edition-by-jain-malkin-isbn-9780471385745-7320/ Computer Networking and Cybersecurity A Guide to Understanding Communications Systems Internet Connections and Network Security Along with Protection from Hacking and Cyber Security Threats 1st edition by Quinn Kiser 1952559790‎ 978-1952559792 https://ebookball.com/product/computer-networking-and- cybersecurity-a-guide-to-understanding-communications-systems- internet-connections-and-network-security-along-with-protection- from-hacking-and-cyber-security-threats-1st-editio/ Medical and Dental Space Planning A Comprehensive Guide to Design Equipment and Clinical Procedures 4th Edition by Jain Malkin ISBN 1118896564 9781118896563 https://ebookball.com/product/medical-and-dental-space-planning- a-comprehensive-guide-to-design-equipment-and-clinical- procedures-4th-edition-by-jain-malkin- isbn-1118896564-9781118896563-5244/ Internet Infrastructure Networking Web Services and Cloud Computing 1st Edition by Richard Fox, Wei Hao ISBN 9781351707169 1351707167 https://ebookball.com/product/internet-infrastructure-networking- web-services-and-cloud-computing-1st-edition-by-richard-fox-wei- hao-isbn-9781351707169-1351707167-15734/ Computer Hacking A Beginners Guide to Computer Hacking How to Hack Internet Skills Hacking Techniques and More 1st Edition by Joe Benton ISBN B00W0S29N6 https://ebookball.com/product/computer-hacking-a-beginners-guide- to-computer-hacking-how-to-hack-internet-skills-hacking- techniques-and-more-1st-edition-by-joe-benton- isbn-b00w0s29n6-15696/
- 4. 1 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Computer Networking and Internet Protocols: Computer Networking and Internet Protocols: A Comprehensive Introduction A Comprehensive Introduction Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis [email protected] http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/ OSPF IP Gigabit Ethernet RSVP MPLS ? TCP
- 5. 2 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis ! IP: Addressing, forwarding, IPv6, TCP ! Ethernet ! Quality of Service (QoS): RSVP ! Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS) ! Route Discovery Protocols : RIP, OSPF, BGP ! Wireless networking ! Optical networking Overview Overview
- 6. 3 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 1. Introduction to TCP/IP 1. Introduction to TCP/IP ! TCP/IP Reference Model ! Internet Protocol (IP) ! Forwarding an IP Datagram ! IP Datagram Format ! IPv6 Enhancements ! Domain Name Service ! TCP: Key Features ! User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- 7. 4 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 2. Ethernet 2. Ethernet ! Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) ! IEEE 802 Address Format ! Interconnection Devices ! Distance-B/W Principle ! Gigabit Ethernet ! Spanning Tree ! 10Gbps Ethernet PHYs ! Metro Ethernet Services
- 8. 5 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 3. Quality of Service (QoS) 3. Quality of Service (QoS) ! ATM QoS and Issues ! Integrated Services and RSVP ! Differentiated Services: Expedited and Assured Forwarding ! Subnet Bandwidth Manager (SBM) ! COPS Protocol for Policy ! IEEE 802.1D Model
- 9. 6 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 4. MPLS 4. MPLS ! Routing vs Switching ! Label Stacks ! Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) ! RSVP Extensions ! Traffic Engineering ! Traffic Trunks ! Traffic Engineering Extensions to OSPF and IS-IS
- 10. 7 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 5. Routing Protocols 5. Routing Protocols ! Building Routing Tables ! Routing Information Protocol Version 1 (RIP V1) ! RIP V2 ! OSPF ! BGP and IDRP.
- 11. 8 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 6. Wireless Networks 6. Wireless Networks ! Recent advances in wireless PHY ! WiMAX Broadband Wireless Access ! Cellular Telephony Generations ! WiMAX vs LTE ! 4G: IMT-Advanced ! 700 MHz
- 12. 9 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 7. Optical Networks 7. Optical Networks ! Recent DWDM Records ! OEO vs OOO Switches ! More Wavelengths ! Ultra-Long Haul Transmission ! Passive Optical Networks ! IP over DWDM: MPλS, GMPLS ! Free Space Optical Comm ! Optical Packet Switching
- 13. 10 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Day 1: Schedule (Tentative) Day 1: Schedule (Tentative) ! 10:00-10:15 Course Introduction ! 10:15-11:30 Internet Protocol (IP), IPv6 ! 11:30-11:45 Coffee Break ! 11:45-1:15 DNS, TCP ! 1:15-2:00 Lunch Break ! 2:00-3:15 Metro Ethernet ! 3:15-3:30 Coffee Break ! 3:30-5:00 Quality of Service
- 14. 11 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Day 2: Schedule (Tentative) Day 2: Schedule (Tentative) ! 10:00-11:00 MPLS, MPLS-TE ! 11:00-11:15 Coffee Break ! 11:15-12:15 Routing Protocols ! 12:15-1:00 Lunch Break ! 1:00-2:15 Wireless Networking ! 2:15-2:30 Coffee Break ! 2:30-4:00 Optical Networking
- 15. 12 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Pre Pre- -Test Test ! Check if you know the difference between: " Private addresses and public addresses " Class C vs Class A addresses " Extension header vs base header " Distance vector vs link state routing " Inter-domain vs intra-domain routing " Universal vs multicast bit " Spanning tree vs IS-IS " UBR vs ABR " DiffServ vs IntServ " RSVP vs LDP " CDMA vs OFDMA " OOO vs OEO optical switching " MPLS vs GMPLS " Routing vs switching
- 16. 13 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Pre Pre- -Test (Cont) Test (Cont) ! If you checked more than 7 items, you may not gain much from this course. ! If you checked only a few or none, don’t worry. This course will cover all this and much more.
- 17. 14 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Disclaimers Disclaimers ! This course covers a lot of topics ! These topics are normally taught in 3 quarter-courses ! Fundamental and basics will be covered ! You will need to read RFC’s for detailed info ! This course has been designed specifically for you. Please feel free to ask questions, make comments, agree or disagree. ! More discussion ⇒ More relevant topics
- 18. 15 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Student Questionnaire Student Questionnaire ! Name (Optional): _________________________ ! Computer networking courses taken: ________________________________________________ ! Telecom Networking background: _________________________________________________ ! What do you want covered in this course: _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________
- 19. 16 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Introduction to Introduction to TCP/IP TCP/IP Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO, USA [email protected] http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/
- 20. 17 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis 1. TCP/IP Reference Model 2. Internet Protocol (IP) 3. Forwarding an IP Datagram 4. IP Datagram Format 5. IPv6 Enhancements 6. Domain Name Service 7. TCP: Key Features 8. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Overview Overview
- 21. 18 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis TCP/IP Reference Model TCP/IP Reference Model ! TCP = Transport Control Protocol ! IP = Internet Protocol (Routing) Application Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical Application Transport Internetwork Host to Network FTP TCP IP Ether net Telnet HTTP UDP Packet Radio Point-to- Point TCP/IP Ref Model OSI Ref Model TCP/IP Protocols
- 22. 19 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Layered Packet Format Layered Packet Format ! Nth layer control info is passed as N-1th layer data. FTP Data FTP Header TCP Data TCP Header IP Data IP Header Ethernet Data Ethernet Header Ethernet Trailer
- 23. 20 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Internetworking Internetworking ! Inter-network = Collection of networks Connected via routers Network Network Network Network Router Router
- 24. 21 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Internet = Collection of Networks Internet = Collection of Networks ! Any computer can talk to any other computer Net 2 Net 1 Net 3 Net 4
- 25. 22 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Internet Protocol (IP) Internet Protocol (IP) ! Layer 3 protocol that forwards datagrams across internet ! Uses routing tables prepared by routing protocols, e.g., Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Routing Information Protocol (RIP) ! Connectionless service vs connection-oriented (circuits)
- 26. 23 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IP Address IP Address ! Class A: (1+3 bytes) Network Local 0 7 1 24 bits Network Local 10 14 2 16 bits ! Class B: (2+2 bytes) Network Local 110 21 3 8 bits ! Class C: (3+1 bytes) ! Local = Subnet + Host (Variable length) Router Router Subnet Host Group (Multicast) 1110 28 4 bits ! Class D:
- 27. 24 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Subnetting Subnetting ! All hosts on a subnetwork have the same prefix. Position of the prefix is indicated by a “subnet mask” ! Example: First 23 bits = subnet Address: 10010100 10101000 00010000 11110001 Mask: 11111111 11111111 11111110 00000000 .AND. 10010100 10101000 00010000 00000000 Subnet 1 Subnet 2 Subnet n Network
- 28. 25 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis An Addressing Example An Addressing Example ! All hosts on a network have the same network prefix Fig 14.6 128.10 128.10 192.5.48 192.5.48 128.10.0.1 Router Router Router Router 128.211 128.211 10 10 Router Router 128.10.0.2 128.211.6.115 192.5.48.3 10.0.0.37 10.0.0.49
- 29. 26 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis ! All-0 host suffix ⇒ Network Address ! All-0s ⇒ This computer (In some old networks: 0.0.0.0 = broadcast. Not used.) ! All-0s network ⇒ This network. E.g., 0.0.0.2 = Host 2 on this network ! All-1 host suffix ⇒ All hosts on the destination net (directed broadcast), All-0 host suffix ⇒ Berkeley directed broadcast address ! All-1s ⇒ All hosts on this net (limited broadcast) ⇒ Subnet number cannot be all 1 ! 127.*.*.* ⇒ Looback through IP layer Special IP Addresses Special IP Addresses
- 30. 27 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Private Addresses Private Addresses ! Any organization can use these inside their network Can’t go on the internet. [RFC 1918] ! 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix) ! 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix) ! 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix) Network Address Translator Private Network Internet Private Addresses Public Addresses
- 31. 28 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Forwarding an IP Datagram Forwarding an IP Datagram ! Delivers datagrams to destination network (subnet) ! Routers maintain a “routing table” of “next hops” ! Next Hop field does not appear in the datagram Table at R2: Fig 16.2 Net 1 Forward to R1 Net 2 Deliver Direct Net 3 Deliver Direct Net 4 Forward to R3 Net 1 Net 1 R1 R1 Net 2 Net 2 R2 R2 Net 3 Net 3 R3 R3 Net 4 Net 4 Destination Next Hop
- 32. 29 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IP Addresses and Routing Table Entries IP Addresses and Routing Table Entries ! IF ((Mask[i] & Destination Addr) = = Destination[i]) Forward to NextHop[i] Destination Mask Next Hop 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.7 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Deliver direct 128.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 Deliver direct 192.4.10.0 255.255.255.0 128.1.0.9 30.0.0.0 30.0.0.0 40.0.0.0 40.0.0.0 128.1.0.0 128.1.0.0 192.4.0.0 192.4.0.0 30.0.0.7 40.0.0.7 128.1.0.8 192.4.10.9 40.0.0.8 128.1.0.9 Fig 16.3
- 33. 30 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Sample Routing Table Sample Routing Table Network-Address Netmask Gateway-Address Interface Metric 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 24.93.104.1 24.93.107.238 1 24.93.104.0 255.255.248.0 24.93.107.238 24.93.107.238 1 24.93.107.238 255.255.255.255 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 24.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 24.93.107.238 24.93.107.238 1 127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 128.146.0.0 255.255.0.0 164.107.61.254 164.107.61.210 1 164.107.61.0 255.255.255.0 164.107.61.210 164.107.61.210 1 164.107.61.210 255.255.255.255 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 164.107.255.255 255.255.255.255 164.107.61.210 164.107.61.210 1 224.0.0.0 224.0.0.0 24.93.107.238 24.93.107.238 1 224.0.0.0 224.0.0.0 164.107.61.210 164.107.61.210 1 255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 164.107.61.210 164.107.61.210 1 Host 164.107.61/24 24.93.104/21 Router Router 24.93.104.238 24.93.104.1 164.107.61.254 164.107.61.210
- 34. 31 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IP Datagram Format IP Datagram Format Vers H. Len Service Type Total Length Identification Flags Time to live Protocol Header Checksum Fragment Offset Source IP Address Destination IP Address IP Options (May be omitted) Padding Data Fig 16.4
- 35. 32 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IP Header Format IP Header Format ! Version (4 bits) ! Internet header length (4 bits): in 32-bit words. Min header is 5 words or 20 bytes. ! Type of service (8 bits): Reliability, precedence, delay, and throughput ! Total length (16 bits): header + data in bytes Total must be less than 64 kB. ! Identifier (16 bits): Helps uniquely identify the datagram during its life for a given source, destination address
- 36. 33 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IP Header (Cont) IP Header (Cont) ! Flags (3 bits): More flag - used for fragmentation No-fragmentation Reserved ! Fragment offset (13 bits): In units of 8 bytes ! Time to live (8 bits): Specified in router hops ! Protocol (8 bits): Next level protocol to receive the data ! Header checksum (16 bits): 1’s complement sum of all 16-bit words in the header
- 37. 34 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IP Header (Cont) IP Header (Cont) ! Source Address (32 bits): Original source. Does not change along the path. ! Destination Address (32 bits): Final destination. Does not change along the path. ! Options (variable): Security, source route, record route, stream id (used for voice) for reserved resources, timestamp recording ! Padding (variable): Makes header length a multiple of 4 ! Data (variable): Data + header < 65,535 bytes
- 38. 35 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Maximum Transmission Unit Maximum Transmission Unit ! Each subnet has a maximum frame size Ethernet: 1518 bytes FDDI: 4500 bytes Token Ring: 2 to 4 kB ! Transmission Unit = IP datagram (data + header) ! Each subnet has a maximum IP datagram length: MTU Fig 17.3 S S R R Net 1 MTU=1500 Net 1 MTU=1500 Net 2 MTU=1000 Net 2 MTU=1000 R R
- 39. 36 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis IPv6 Enhancements IPv6 Enhancements 1. Expanded address space: 128 bit 2. Address auto-configuration: Dynamic assignment 3. Increased addressing flexibility: Anycast + Multicast 4. Improved option mechanism: Extension Headers " Improved speed and simplified router processing 5. Support for resource allocation " Replaces type of service " Labeling of packets to particular traffic flow
- 40. 37 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Colon Colon- -Hex Notation Hex Notation ! Dot-Decimal: 127.23.45.88 ! Colon-Hex: FEDC:0000:0000:0000:3243:0000:0000:ABCD " Can skip leading zeros of each word " Can skip one sequence of zero words, e.g., FEDC::3243:0000:0000:ABCD ::3243:0000:0000:ABCD " Can leave the last 32 bits in dot-decimal, e.g., ::127.23.45.88 " Can specify a prefix by /length, e.g., 2345:BA23:0007::/50
- 41. 38 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Local Local- -Use Addresses Use Addresses ! Link Local: Not forwarded outside the link, FE:80::xxx 0 Interface ID 1111 1110 10 10 bits n bits 118-n ! Site Local: Not forwarded outside the site, FE:C0::xxx ! Provides plug and play 0 Subnet ID 1111 1110 11 10 bits n bits m bits Interface ID 118-n-m bits
- 42. 39 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Extension Headers Extension Headers Most extension headers are examined only at destination 1. Hop-by-Hop Options 2. Fragmentation: All IPv6 routers can carry 536 Byte payload 3. Routing: Loose or tight source routing 4. Destination Options Base Header Extension Header 1 Extension Header n Data
- 43. 40 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Extension Header (Cont) Extension Header (Cont) Base Header Next = Routing Route Header Next = TCP TCP Segment Base Header Next = Hop Hop Header Next = Routing Routing Header Next = TCP TCP Segment Base Header Next = TCP TCP Segment # Only Base Header: # Only Base Header and One Extension Header: # Only Base Header and Two Extension Headers:
- 44. 41 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Domain Name Service Domain Name Service ! Computers use addresses ! Humans cannot remember IP addresses ⇒ Need names Example, Liberia for 164.107.51.28 ! Simplest Solution: Each computer has a unique name and has a built in table of name to address translation ! Problem: Not scalable ! Solution: DNS (Adopted in 1983) ! Hierarchical Names: Liberia.cse.wustl.edu
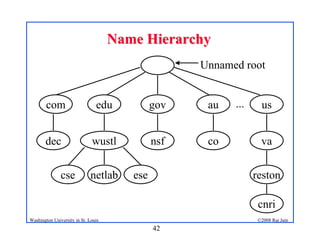
- 45. 42 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Name Hierarchy Name Hierarchy reston com edu gov au us dec wustl nsf co va cse netlab ese cnri Unnamed root ...
- 46. 43 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Name Hierarchy Name Hierarchy ! Unique domain suffix is assigned by Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) ! The domain administrator has complete control over the domain ! No limit on number of sub-domains or number of levels ! computer.site.division.company.com computer.site.subdivision.division.company.com ! Name space is not related to physical interconnection, e.g., math.wustl and cse.wustl could be on the same floor or in different cities
- 47. 44 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Name Resolution Name Resolution User Name Resolver Name Server Name Server Cache Cache Cache Query Referral Query Response Query Response Data- base Data- base Name Server Cache Data- base Query Response
- 48. 45 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Name Resolution (Cont) Name Resolution (Cont) ! Each computer has a name resolver routine, e.g., gethostbyname in UNIX ! Each resolver knows the name of a local DNS server ! Resolver sends a DNS request to the server ! DNS server either gives the answer, forwards the request to another server, or gives a referral ! Referral = Next server to whom request should be sent ! Servers respond to a full name only However, humans may specify only a partial name Resolvers may fill in the rest of the suffix, e.g., Liberia.cis = Liberia.cis.wustl.edu
- 49. 46 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis TCP: Key Features TCP: Key Features ! Point-to-point communication: Two end-points ! Connection oriented. Full duplex communication. ! Reliable transfer: Data is delivered in order Lost packets are retransmitted. ! Stream interface: Continuous sequence of octets
- 50. 47 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis Transport Control Protocol (TCP) Transport Control Protocol (TCP) ! Key Services: " Send: Please send when convenient " Data stream push: Please send it all now, if possible. " Urgent data signaling: Destination TCP! please give this urgent data to the user (Urgent data is delivered in sequence. Push at the should be explicit if needed.) " Note: Push has no effect on delivery. Urgent requests quick delivery
- 51. 48 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis TCP Header Format TCP Header Format 16 16 32 32 6 Source Port Dest Port Seq No Ack No Data Offset Control Window Resvd 4 6 16 16 16 x y Size in bits Check- sum Urgent Options Pad Data FTP HTTP SMTP
- 52. 49 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis TCP Header TCP Header ! Source Port (16 bits): Identifies source user process 20 = FTP, 23 = Telnet, 53 = DNS, 80 = HTTP, ... ! Destination Port (16 bits) ! Sequence Number (32 bits): Sequence number of the first byte in the segment. ! Ack number (32 bits): Next byte expected ! Data offset (4 bits): # of 32-bit words in the header ! Reserved (6 bits) ! Window (16 bits): Will accept [Ack] to [Ack]+[window]
- 53. 50 ©2008 Raj Jain Washington University in St. Louis User Datagram Protocol (UDP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ! Connectionless end-to-end service ! Unreliable: No flow control. No error recovery (No acks. No retransmissions.) ! Used by network management and Audio/Video. ! Provides port addressing ! Error detection (Checksum) optional. Source Port Dest Port Check- sum Length 16 16 16 Size in bits 16 Data
- 54. Other documents randomly have different content
- 55. links and up to date contact information can be found at the Foundation’s website and official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation Project Gutenberg™ depends upon and cannot survive without widespread public support and donations to carry out its mission of increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be freely distributed in machine-readable form accessible by the widest array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations ($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt status with the IRS. The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate. While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who approach us with offers to donate. International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
- 56. Please check the Project Gutenberg web pages for current donation methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate. Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg™ electronic works Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg™ concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and distributed Project Gutenberg™ eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support. Project Gutenberg™ eBooks are often created from several printed editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition. Most people start at our website which has the main PG search facility: www.gutenberg.org. This website includes information about Project Gutenberg™, including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.
- 57. Welcome to Our Bookstore - The Ultimate Destination for Book Lovers Are you passionate about books and eager to explore new worlds of knowledge? At our website, we offer a vast collection of books that cater to every interest and age group. From classic literature to specialized publications, self-help books, and children’s stories, we have it all! Each book is a gateway to new adventures, helping you expand your knowledge and nourish your soul Experience Convenient and Enjoyable Book Shopping Our website is more than just an online bookstore—it’s a bridge connecting readers to the timeless values of culture and wisdom. With a sleek and user-friendly interface and a smart search system, you can find your favorite books quickly and easily. Enjoy special promotions, fast home delivery, and a seamless shopping experience that saves you time and enhances your love for reading. Let us accompany you on the journey of exploring knowledge and personal growth! ebookball.com





























![27
©2008 Raj Jain
Washington University in St. Louis
Private Addresses
Private Addresses
! Any organization can use these inside their network
Can’t go on the internet. [RFC 1918]
! 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix)
! 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix)
! 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix)
Network
Address
Translator
Private
Network
Internet
Private
Addresses
Public
Addresses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2817-250503213549-8c3ff2e4/85/Computer-Networking-and-Internet-Protocols-A-Comprehensive-Introduction-1st-Edition-by-Raj-Jain-30-320.jpg)

![29
©2008 Raj Jain
Washington University in St. Louis
IP Addresses and Routing Table Entries
IP Addresses and Routing Table Entries
! IF ((Mask[i] & Destination Addr) = = Destination[i])
Forward to NextHop[i]
Destination Mask Next Hop
30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.7
40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Deliver direct
128.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 Deliver direct
192.4.10.0 255.255.255.0 128.1.0.9
30.0.0.0
30.0.0.0 40.0.0.0
40.0.0.0 128.1.0.0
128.1.0.0 192.4.0.0
192.4.0.0
30.0.0.7
40.0.0.7 128.1.0.8 192.4.10.9
40.0.0.8 128.1.0.9
Fig 16.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2817-250503213549-8c3ff2e4/85/Computer-Networking-and-Internet-Protocols-A-Comprehensive-Introduction-1st-Edition-by-Raj-Jain-32-320.jpg)


















![49
©2008 Raj Jain
Washington University in St. Louis
TCP Header
TCP Header
! Source Port (16 bits): Identifies source user process
20 = FTP, 23 = Telnet, 53 = DNS, 80 = HTTP, ...
! Destination Port (16 bits)
! Sequence Number (32 bits): Sequence number of the
first byte in the segment.
! Ack number (32 bits): Next byte expected
! Data offset (4 bits): # of 32-bit words in the header
! Reserved (6 bits)
! Window (16 bits): Will accept [Ack] to
[Ack]+[window]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2817-250503213549-8c3ff2e4/85/Computer-Networking-and-Internet-Protocols-A-Comprehensive-Introduction-1st-Edition-by-Raj-Jain-52-320.jpg)




