Computerized System Validation : Understanding basics
- 1. Mail : [email protected] Phone : +91 8000656594
- 2. A computerized system is a function integrated with a computer system . Generation, measurement, calculation, assessment, transfer, processing, storage or archiving of data Intended for regulatory submission or to support regulatory decisions .
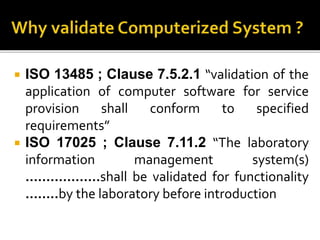
- 3. ISO 13485 ; Clause 7.5.2.1 “validation of the application of computer software for service provision shall conform to specified requirements” ISO 17025 ; Clause 7.11.2 “The laboratory information management system(s) ………………shall be validated for functionality ……..by the laboratory before introduction
- 4. OECD No.1 GLP : “ensure that computerized systems used in the study have been validated” ICH E6(R2), GCP : “A process of establishing and documenting that the specified requirements of a computerized system ……… of the system or transition to a new system. ICH Q7 (R2), GMP-related computerized systems should be validated. A NEED FOR EVERY REGULATED SYSTEM …!!!
- 5. Lets understand the responsibilities …!!!
- 6. IT Personnel : purchase, installation and maintenance of a computerized system. Supplier : Third parties, vendors, internal IT departments, service providers including hosted service providers . User : The personnel operating the computerized system. System Owner / IT Owner :The individual who is responsible for the availability, support and maintenance of a system and for the security of the data residing on that system. The System Owner acts on behalf of the management.
- 7. Validation Director: A delegated person responsible for a validation project. Facility Management person(s) who has the authority and formal responsibility for the organization and functioning of the test facility according to these Principles of Good Laboratory Practice. Quality Assurance (QA) has to review the validation documentation and inspect the validation activities for regulatory compliance. Personnel are responsible for performing activities with computerized systems in accordance with the GLP Principles and recognized technical standards
- 9. Acceptance Criteria : The documented criteria that should be met to successfully complete a test phase or to meet delivery requirements. Acceptance testing Formal testing of a computerized system in its anticipated operating environment to determine whether all acceptance criteria of the test facility have been met .
- 10. Authorization concept : A formal procedure to define and control access rights to and privileges in a computerized system. Back-up Provision made as a part of contingency plan for the recovery of data files or software or to restart processing, or for the use of alternative computer equipment.
- 11. Change Control: Evaluation and documentation to determine whether a validation process is necessary following any changes to the computerized system. Change Management : Change management is the process for the life cycle of changes.
- 12. Configuration: A configuration is an arrangement of functional units and pertains to the choice of hardware, software and documentation that affects function and performance of the system.
- 13. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) The concept of corrective and preventive actions focuses on the systematic investigation of the root causes of identified problems or risks in an attempt to prevent their recurrence or to prevent occurrence.
- 14. Data migration Data migration is the activity of transporting electronic data from one system (computer) to another, transferring data between storage media or simply the transition of data from one state to another
- 16. Data approval Data approval means locking data after collection and verification and e.g. transformation to make data suitable for use in records. Data capture Data capture are actions that typically take place to plan, collect, and verify data .
- 17. Electronic record Any combination of text, graphics, data, audio, pictorial, or other information representation in digital form. Electronic Signature An electronic measure that can be substituted for a handwritten signature or initials for the purpose of signifying approval, authorization or verification of specific data entries.
- 18. Hybrid system : Co-existence of paper and electronic record and signature components.
- 19. Life cycle : An approach to computerized system development that begins with identification of the user’s requirements, continues through design, integration, qualification, user validation, control and maintenance, and ends when use of the system is retired. Life cycle model : A life cycle model describes the phases or activities of a project from conception until the product is retired.
- 20. Risk: Combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm. Risk analysis: Estimation of the risk associated with the identified hazards. Risk assessment : Risk assessment consists of the identification of hazards and the analysis and evaluation of risks associated with exposure to those hazards .
- 22. Security: The protection of computer hardware and software from accidental or malicious access, use, modification, destruction or disclosure. Software A programme acquired for or developed, adapted or tailored to the facility requirements for the purpose of controlling processes, data collection, data manipulation, data reporting and/or archiving.
- 24. Views Expressed and errors , if any are attributable to author. If you rely on the above views without a personalize opinion or study and if you have benefits you are free to keep it for yourself without any ACKNOWLEDGEMENT !!!! It is a nutshell presentation for training and understanding purpose only . For training session please mail at [email protected] or contact +91 8000656594