Control flow statements in java
- 1. Control Flow Statements Branching Statements Looping Statements Jump Statemetns
- 2. Branching Statements • If statement • If else Statement • If..else…if statement • Nest if…else statement • Switch Statement <<goTo first slide>>
- 3. If Statement • An if statement consists of a Boolean expression followed by one or more statements. If the Boolean expression evaluates to true then the block of code inside the if statement will be executed. If not the first set of code after the end of the if statement (after the closing curly brace) will be executed. if(Boolean expression) { //Some code should be work } public static void main(String[] y) { int my_int=25; if(my_int==25) { System.out.println("the condition is true"); } } Go to branch statement slide
- 4. If else Statement • An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the Boolean expression is false. if(Boolean expression) { //some code excut } else { //some code excut } public static void main(String[] y) { int my_int=25; if(my_int<25) { System.out.println("the condition is true"); } else { System.out.println("the condition is not true"); } } • Go to branch statement slide
- 5. If…else…if statement • An if statement can be followed by an optional else if...else statement, which is very useful to test various conditions using single if...else if statement. When using if , else if , else statements there are few points to keep in mind. • An if can have zero or one else's and it must come after any else if's. • An if can have zero to many else if's and they must come before the else. • Once an else if succeeds, none of the remaining else if's or else's will be tested. if(Boolean Expression 1) { //some code } else if (Boolean Expression 2) { //some code } else if (Boolean Expression 2) { //some code } else { //some code }
- 6. public static void main(String[] y) { int my_int=25; if(my_int<25) { System.out.println("the condition is true"); } else if(my_int>25) {System.out.println("the else if condition is true for 25 > 25"); } else if(my_int==25) { System.out.println("the condition is true for 25==25"); } else { System.out.println("any of the condition is not ture"); } } Go to branch statement slides
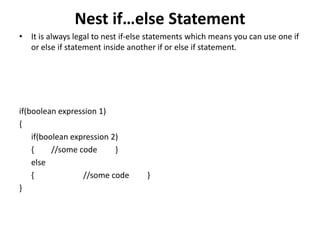
- 7. Nest if…else Statement • It is always legal to nest if-else statements which means you can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement. if(boolean expression 1) { if(boolean expression 2) { //some code } else { //some code } }
- 8. public static void main(String[] y) { int course_value=90; String course_name="java"; String Course_type="core & advanced"; if(course_value==90) { if(course_name=="java") { if(Course_type=="core & advanced") { System.out.println("the nested condition is true"); } } } else { System.out.println("the nested conditions are not true"); } } Go to Branch statement slide
- 9. Switch Statement • Switch case statements are a substitute for long if statements that compare a variable to several "integral" values.. The value of the variable given into switch is compared to the value following each of the cases, and when one value matches the value of the variable, the computer continues executing the program from that point. switch(expression) { case value1: {//some code}break; case value2: {//some code}break; default: {//some code}break; }
- 10. public static void main(String[] y) { int x=10; /* * x value is compared with case values */ switch(x) { case 10:{System.out.println("the x value is 10");}break; case 30:{System.out.println("the x value is 30");}break; case 40:{System.out.println("the x value is 40");}break; } } Go to branch statement slide
- 11. LOOP control Statements • loop is a sequence of instruction s that is continually repeated until a certain condition is reached. There are four types of loops: • For loop • For each loop • While loop • Do..While loop <<goto first slide>>
- 12. For loop • The for is an entry-entrolled loop and is used when an action is to repeated for a predetermined number of times for(initial value; test condition; increment) { //some code } public static void main(String[] y) { for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {System.out.println("hello world "+i);} } Go to loop slide
- 13. Foreach Statement • A ForEach style loop is designed to cycle through a collection of objects,such as an array, in strictly sequential fashion, from start to finish.Implement a foreach loop by using the keyword foreach, java adds the foreach compability by enhancing the for statement. • for(type itr-var:collection)statement-block int[] a={1,2,3,4}; for(int x:a) { System.out.println("array of a["+x+"] "+a[x]); } Go to loop slide
- 14. While loop(Entry Control loop) • It repeates a statement or block while its controlling expression(any boolean Expression) is true • The body of the loop will be executed as long as the conditional expression is true. while(condition) { //body of code } public static void main(String[] y) { while(x<5) { /*x++ increment value of x;*/ System.out.println("the value of x is "+x); x++; } } Go to loop slide
- 15. Do-while loop • A while loop is initially false then the body of the loop will not be executed at all .The do-while loop always executes its body at least once because its conditional expression is at the bottom of the loop do { //body of code }while(boolean expression); System.out.println("the do While loop"); int x=1; do { /*x++ increment value of x; */ System.out.println("the value of x is "+x); x++; }while(x<5); Go to loop slided
- 16. Jump Statements • Break • Continue • Return <<goto first slide>>
- 17. Jump Statements • Break • In java the break statement has 3 uses • Terminates a statement sequence in a switch statement • It can be used to exit loop • It can be used more civilized form of goto statement • Using Break to exit the loop By using break, you can force immediate termination of a loop .when break statement is encountered inside a loop the loop is terminated and program control resumes at the next statement following loop
- 18. public static void main(String[] y) { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { if(i==5) { System.out.println("condition break"); break; } System.out.println("the value of i is::"+i); } }
- 19. • Using break in the form of GOTO • Syntax Break label_name; public static void main(String[] y) { first:{ secound:{ third:{ System.out.println("third block"); if(true) { break secound; } } System.out.println("secound block"); } System.out.println("first block"); } } go to jump statements
- 20. Continue • A continue statement causes control to be transferred directly to the conditional expression that controls the loop public static void main(String[] y) { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { if(true) { System.out.println("the if block"); continue; } System.out.println("the for loop"); } }
- 21. Using continue with labels • Specify the labels with continue statement public static void main(String[] y) { outer:for(int i=0;i<=2;i++){ for(int j=0;j<=1;j++) { System.out.println("value of J is::"+j); continue outer; } System.out.println("the value of i is::"+i); } /* for continue labels it should be used with loops only not for blocks */ } Go to jump statements
- 22. Return • The return statement is used to explicitly return from a method.That is,it causes program control to transfer back to the caller of the method.At any time in a method the return statement can be used to cause execution to branch back to the caller of the method.Thus,the return statement can be used to cause execution to branch back to the caller ot the method.Thus, the return statement immediately terminates the method in which it is executed. public static void main(String[] y) { System.out.println("before return statement"); if(true) { return; } System.out.println("after return statement"); /* here return causes execution to return to the java run-time system */ }
- 23. class Demo_break { int demo() { return(1); } public static void main(String[] y) { Demo_break d=new Demo_break(); System.out.println("the return value is"+d.demo()); } } • goto jump statement
- 24. • Find the errors in the following 1. If(x+y=z&&y>0) 2. If(x>0); A=b+c; Else A=a*b; 3. If(x<0)||(q<0)
- 25. Class ifelse { int result=55; char grade; if(result>90) grade=‘A’; else if(result>80)grade=“B”; else if(result>70) grade=“c”; else grade=“F”; else grade=“g”; System.out.println(“the grade is “+grade); } See the output
- 26. • Correct the code to print the output “correct value” public static void main(String[] args) { int i=2; if(i=2) { System.out.println("correct value"); } else { System.out.println("not correct value"); }



![If Statement
• An if statement consists of a Boolean expression followed by one or more
statements. If the Boolean expression evaluates to true then the block of
code inside the if statement will be executed. If not the first set of code
after the end of the if statement (after the closing curly brace) will be
executed.
if(Boolean expression)
{
//Some code should be work
}
public static void main(String[] y)
{
int my_int=25;
if(my_int==25)
{
System.out.println("the condition is true");
}
}
Go to branch statement slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-3-320.jpg)
![If else Statement
• An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement,
which executes when the Boolean expression is false.
if(Boolean expression)
{ //some code excut }
else
{ //some code excut }
public static void main(String[] y)
{
int my_int=25;
if(my_int<25)
{ System.out.println("the condition is true"); }
else
{ System.out.println("the condition is not true"); }
}
• Go to branch statement slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-4-320.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] y)
{
int my_int=25;
if(my_int<25)
{
System.out.println("the condition is true");
}
else if(my_int>25)
{System.out.println("the else if condition is true for 25 >
25");
}
else if(my_int==25)
{
System.out.println("the condition is true for 25==25");
}
else
{
System.out.println("any of the condition is not ture");
}
}
Go to branch statement slides](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-6-320.jpg)
![public static void main(String[] y)
{
int course_value=90;
String course_name="java";
String Course_type="core & advanced";
if(course_value==90)
{
if(course_name=="java")
{
if(Course_type=="core & advanced")
{
System.out.println("the nested condition is
true");
}
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("the nested conditions are not true");
}
}
Go to Branch statement slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-8-320.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] y)
{
int x=10;
/*
* x value is compared with case values
*/
switch(x)
{
case 10:{System.out.println("the x value is 10");}break;
case 30:{System.out.println("the x value is 30");}break;
case 40:{System.out.println("the x value is 40");}break;
}
}
Go to branch statement slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-10-320.jpg)

![For loop
• The for is an entry-entrolled loop and is used when an action is to
repeated for a predetermined number of times
for(initial value; test condition; increment)
{ //some code }
public static void main(String[] y)
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{System.out.println("hello world "+i);}
}
Go to loop slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-12-320.jpg)
![Foreach Statement
• A ForEach style loop is designed to cycle through a collection of
objects,such as an array, in strictly sequential fashion, from start to
finish.Implement a foreach loop by using the keyword foreach, java adds
the foreach compability by enhancing the for statement.
• for(type itr-var:collection)statement-block
int[] a={1,2,3,4};
for(int x:a)
{
System.out.println("array of a["+x+"] "+a[x]);
}
Go to loop slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-13-320.jpg)
![While loop(Entry Control loop)
• It repeates a statement or block while its controlling expression(any boolean
Expression) is true
• The body of the loop will be executed as long as the conditional expression is
true.
while(condition)
{
//body of code
}
public static void main(String[] y)
{
while(x<5)
{ /*x++ increment value of x;*/
System.out.println("the value of x is "+x);
x++;
}
}
Go to loop slide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-14-320.jpg)



![public static void main(String[] y)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if(i==5)
{
System.out.println("condition break");
break;
}
System.out.println("the value of i is::"+i);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-18-320.jpg)
![• Using break in the form of GOTO
• Syntax Break label_name;
public static void main(String[] y)
{
first:{
secound:{
third:{
System.out.println("third block");
if(true)
{
break secound;
}
}
System.out.println("secound block");
}
System.out.println("first block");
}
}
go to jump statements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-19-320.jpg)
![Continue
• A continue statement causes control to be transferred directly to the
conditional expression that controls the loop
public static void main(String[] y)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
if(true)
{
System.out.println("the if block");
continue;
}
System.out.println("the for loop");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-20-320.jpg)
![Using continue with labels
• Specify the labels with continue statement
public static void main(String[] y)
{
outer:for(int i=0;i<=2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=1;j++)
{
System.out.println("value of J is::"+j);
continue outer;
}
System.out.println("the value of i is::"+i);
}
/*
for continue labels it should be used with loops only not for blocks
*/
}
Go to jump statements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-21-320.jpg)
![Return
• The return statement is used to explicitly return from a method.That is,it
causes program control to transfer back to the caller of the method.At any
time in a method the return statement can be used to cause execution to
branch back to the caller of the method.Thus,the return statement can be
used to cause execution to branch back to the caller ot the method.Thus, the
return statement immediately terminates the method in which it is executed.
public static void main(String[] y)
{
System.out.println("before return statement");
if(true)
{
return;
}
System.out.println("after return statement");
/*
here return causes execution to return to the java run-time system
*/
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-22-320.jpg)
![class Demo_break
{
int demo()
{
return(1);
}
public static void main(String[] y)
{
Demo_break d=new Demo_break();
System.out.println("the return value
is"+d.demo());
}
}
• goto jump statement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-23-320.jpg)


![• Correct the code to print the output “correct
value”
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=2;
if(i=2)
{
System.out.println("correct value");
}
else
{
System.out.println("not correct value");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlflowstatements-160413034140/85/Control-flow-statements-in-java-26-320.jpg)
