Corrib.org - OpenSource and Research
- 1. Corrib.org group OpenSource and Research Adam Gzella Sebastian Ryszard Kruk
- 2. Outline Corrib.org and DERI SemanticWeb Corrib.org achievements and interests JeromeDL notitio.us OpenSource in Reasearch and Academia
- 3. Goals for this presentation Show how open source supports research Present corrib.org tools and solutions I nvite to cooperate with us
- 4. Digital Enterprise Research Institute DERI is a Centre for Science, Engineering and Technology (CSET) established in 2003 with funding from the Science Foundation Ireland. As National University of Ireland, Galway institute More than 120 people now from 27 countries Funding: SFI, EI, EU projects. The biggest SemanticWeb institute on the planet.
- 5. Corrib.org Corrib.org - informal group run within DERI. E stablished to manage the collaboration with GUT (Gdańsk University of Technology). T urn ed into ecosystem for research and open source development on semantic digital libraries and semantic infrastructure Delivered 11 Masters Another 5 in progress 2 PhD coming up
- 6. Corrib.org 8 core members About 10 supporting members and students Profesional advisors, including prof. Stefan Decker (DERI), prof. Henryk Krawczyk (GUT), prof. Hong-Gee Kim (DERI Korea) Leader – Sebastian Kruk
- 7. Corrib.org Corrib.org – vast number of different projects 2 characteristics stays the same: Domain: SemanticWeb Open Source Main technology that we are using: Java (JSE and JEE) Open Source - fast research dissemination channel
- 8. SemanticWeb – short introduction Current Web vs. Semantic Web? An extension of the current Web in which information is given well-defined meaning, better enabling computers and people to work in cooperation. [Tim Berners-Lee] Current Web was designed for humans, and there is little information usable for machines Was the Web meant to be more? Objects with well defined attributes as opposed to untyped hyperlinks between Internet resources A network of relationships amongst named objects, yielding unified information management tasks What do you mean by “Semantic”? the semantics of something is the meaning of something Semantic Web is able to describe things in a way that computers can understand
- 9. SemanticWeb - RDF Describing things on the Semantic Web RDF (Resource Description Framework) a data format for describing information and resources, the fundamental data model for the Semantic Web Using RDF, we can describe relationships between things like: A is a part of B or Y is a member of Z and their properties ( size , weight , age , price …) in a machine-understandable format RDF graph-based model delivers straightforward machine processing Putting information into RDF files makes it possible for “scutters” or RDF crawlers to search , discover , pick up , collect , analyse and process information from the Web
- 10. SemanticWeb - RDF How RDF can help us? identify objects establish relationships express a new relationship just add a new RDF statement integrate information from different sources copy all the RDF data together RDF allows many points of view
- 11. SemanticWeb - Ontologies What is an Ontology? „ An ontology is a specification of a conceptualization.“ Tom Gruber, 1993 Ontologies are social contracts Agreed, explicit semantics Understandable to outsiders (Often) derived in a community process Ontology markup and representation languages: RDF and RDF Schema OWL Other: DAML+OIL, EER, UML, Topic Maps, MOF, XML Schemas
- 12. SemanticWeb – RDFS and OWL RDF Schema - small vocabulary for RDF: Class, subClassOf, type Property, subPropertyOf domain, range OWL – The Web Ontology Language provides a vocabulary for defining classes, their properties and their relationships among classes. Based on Description Logics OWL is a W3C Recommendation
- 13. SemanticWeb and KOS KOS – Knowledge Organisation System tools that present the organized interpretation of knowledge structures semantic tools - meaning of words and other symbols as well as (semantic) relations between symbols and concept organize information and promote knowledge management Examples: classification and categorization schemata (organize materials at a general level) subject headings (provide more detailed access) authority files (control variant versions of key information such as geographic names and personal names) highly structured vocabularies, such as thesauri traditional schemes, such as semantic networks and ontologies
- 14. Understanding KOS controlled vocabulary - a list of terms that have been enumerated explicitly taxonomy - a collection of controlled vocabulary terms organized into a hierarchical structure. formal ontology – a controlled vocabulary expressed in an ontology representation language. This language has a grammar for using vocabulary terms to express something meaningful within a specified domain of interest. meta-model - an explicit model of the constructs and rules needed to build specific models within a domain of interest. A valid meta-model is an ontology, but not all ontologies are modeled explicitly as meta-models. as a set of building blocks and rules used to build models as a model of a domain of interest, and as an instance of another model.
- 15. SemanticWeb - Appliacations Semantic Web cannot be and is not only a set of recommendations Semantic Web is becoming reality by applications that support it and are based on it Enabling technologies: RDF Storages: Sesame, Jena, YARS Reasoners: KAON, Racer Editors: Protege, SWOOP, MarcOnt Portal End-User applications: Semantic wikis: Makna, SemperWiki Semantic blogs Semantic digital librarie s
- 16. SemanticWeb - Applications The challenge for the Semantic Web The Semantic Web can’t work all by itself For example, it is not very likely that you will be able to sell your car just by putting your RDF file on the Web Need society-scale applications: Semantic Web agents and/or services, consumers and processors for semantic data, more advanced collaborative applications
- 17. Corrib.org mission Help SemanticWeb to emerge b y providing suitable infrastructure , tools and by building SemanticWeb applications.
- 18. FOAFRealm User management system based on FOAF metadata. FOAF (Friend-Of-A-Friend) a Web of machine-readable pages describing people, the links between them and the things they create and do. Standard for describing persons. Important extensions to FOAF friendshipLevel – allows us to specify how good someone knows someone First goals of the project: Quick registration with FOAF profile Plugin to Apache Tomcat server that would allow to authenticate users using FOAF profiles.
- 19. FOAFRealm Current role of FOAFRealm Providing social network features for other applications Providing flexible access rights control based on the social network. Based on the distance and friendship level in the social graph Full-fledged REST SOA build for the system.
- 20. HyperCuP Scalable P2P communication protocol. Our approach was to deliver more lightweight implementation than these delivered in the Edutella project Supports P2P network based on hypercube Provides most efficient P2P broadcast algorithm We have delivered prototype Java implementation http:// hypercup.corrib.org /
- 21. MarcOnt Initiative Motivation: Build a bibliographic ontology for Semantic Digital Libraries MarcOnt Initiative goals: Deliver a set of tools for collaborative ontology development Collaboration Tools for domain experts Enable mediation between formats (MMS)
- 22. MarcOnt Marcont Ontology Central point of MarcOnt Initiative Translation and mediation format Continuous collaborative ontology improvement Knowledge from the domain experts Community influence and evaluation MarcOnt Portal Collaborative ontology development. Portal provides: Suggestions Annotations Versioning Ontology editor with diff and visualisations and on-line editing
- 23. MarcOnt Format translation Interoperability MarcOnt Mediation Services RDF Translator
- 24. Didaskon Didaskon delivers components for composing suggestion of elearning course based on learning objects coming from both courseware and informal learning. Architecture of the future e-Learning system Ontology for user model – delivering personalised content Ontology for content - ensuring cooperation of heterogeneous environments which use different formats
- 25. Didaskon Content sources: Formal: e-Learning courses (LOM standard), books, articles (data provided by digital library) Informal: Internet, social networks, Web2.0 portals Informal knowledge – 80% of whole learning process! How to capture informal knowledge and use it toghether with formal sources? -> Maybe utilise SemanticWeb interoperability -> IKHarvester
- 26. IKHarvester Informal Knowledge Harvester Harvesting RDF data and Creating LOM objects from the informal sources If page provided reach information –> IKH a llows to read RDF from a given resource If there is no RDF data on the page (most of the pages) -> T ranslate given resource to RDF (Wikipedia pages, blogs and foras Blade- architecture to support new types of sources
- 28. S 3 B - Social Semantic Search and Browsing M iddleware that deliver s searching, browsing, filtering, and sharing information with support of RDF storage and full text index. C onsists of a number of component s
- 29. S 3 B – SQE SQE – Semantic Query Expansion Why simple full-text search is not enough? Too many results (low precision) One needs to specify the exact keyword (low recall) How to distinguish between: Python and python? (high fall-out) How ? Disambiguation through a context Query context Short-term context ( User’s goal , Location , Time ) Long-term context ( User’s interest , Search engine specific )
- 30. S 3 B – SQE Techniques Query refinement Spread activation Types mapping Pruning Acquiring the context information: Previous searches of the user Semantically annotated user’s bookmarks Community profile Manual query refinement “ Tell me why” button and the transcript of refinement process Continue to faceted navigation
- 31. S 3 B – MBB MBB – MultiBeeBrowse faceted navigation solution, which allows to access current browsing context, history of browsing. keeps the track of relations between performed queries adaptive hypermedia techniques to improve usability
- 32. S 3 B – MBB - Motivations The search does not end on a (long) list of results The results are not a list (!) but a graph „ Lost in hyperspace” A need for unified UI and services for filter/narrow and browse/expand services Share browsing experience – navigate collaboratively
- 33. S 3 B – MBB - Solutions Defines REST access to services and their composition Basic services: access, search, filter, similar, browse, combine Meta services : RDF serialization, subscription channels, service ID generation, Context services : manage contexts, manage service calls/compositions in the context, lists contexts Statistics services : properties, values, token s
- 34. S 3 B – MBB Helping users with different problems Finding results Going back and forth in the refinement process Overview of current browsing context Replaying previous queries 4 views: Basic browsing view Structured history view HoneyComb view Life-long history view
- 35. S 3 B – MBB
- 36. S 3 B – TTM TagsTreeMaps filtering based on clustered tags using treemaps to present the tag space zoomable interface paradigm
- 37. S 3 B – TTM Problems with Tag Clouds: information overload (for large tag clouds) cannot carry structure and/or semantics querying model: only conjunctive queries Solution: limits the information overload clustering tagging space limiting popularity range zoomable browser on the tagging space selecting multiple tags fulltext filtering - easy highlight matching tags optional conjunctive (AND) and union (OR) mode defined interfaces for delivering processors in the pipeline (e.g., clustering, filtering, coloring )
- 38. S 3 B – TTM
- 39. S 3 B – NLQ Natural Language Query Templates allows to perform complex queries using natural language can be created and modified based on the needs of users easily internationalized
- 40. Find articles related to mission in the context of aerospace ... Query Templates (Regular Expressions) English Portuguese Aerospace mission skos:related results marcont:hasKeyword marcont:hasDomain SELECT * FROM ....
- 41. S 3 B – Recommendations Resource-based Recommendations customizable view of recommendations extensible with new similarity plugins
- 42. S 3 B – Recommendations Library resource hasKeyword hasDomain hasCreator A C D E F Step 1: Find similar resources Step 2: Rank and filter according to user’s settings G ... by keyword (max. 2) by author (max. 2) by domain (max. 2) E C B A summary (max. 3)
- 43. JOnto and Tagging Unified Java and REST API for accessing KOS Representing complete KOS in RDF SKOS WordNet in OWL/RDF TagOntology Support for: taxonomies (UDC, DDC, LoC, ACM, DMoz, PKT) thesauri (WordNet, OpenThesaurus) free tagging Easily extensible: with new taxonomies (RDF or flat file source) thesauri in RDF (WordNet in OWL/RDF ontology) Fulltext indexing for faster filtering and retrieval
- 44. Tagging Support for semantic tagging Using ontology based on Toms Gruber tagging ontology
- 45. S 3 B – Social Semantic Collaborative Filtering Why? The bottom-line of acquiring knowledge: informal communication (“word of mouth”) How? Everyone classifies (filters) the information in bookmark folders ( user-oriented taxonomy ) Peers share (collaborate over) the information ( community-driven taxonomy ) Result? Knowledge “flows“ from the expert through the social network to the user System amass a lot of information on user/community profile (context)
- 46. S 3 B – SSCF Problems? The horizon of a social network (2-3 degrees of separation) How to handle fine-grained information (blogs, wikis, etc.) Solutions? Inference engine to suggest knowledge from the outskirts of the social network Support for SIOC metadata: SIOC browser in SSCF Annotations and evaluations of “local” resources
- 47. S 3 B – SSCF Goal: to enhance individual bookmarks with shared knowledge within a community Users annotate catalogues of bookmarks with semantic information taken from DMoz or WordNet vocabularies Catalogs can include (transclusion) friend's catalogues Access to catalogues can be restricted with social networking-based polices SSCF delivers: Community-oriented, semantically-rich taxonomies Information about a user's interest Flows of expertise from the domain expert Recommendations based on users previous actions Support for SIOC metadata
- 48. S 3 B – SSCF Annotated directories Taxonomies Semantic Tags Using JOnto API Tagged resources Recommendations based on users’ profile/interest Prolog engine Directory Keyword A Taxonomy A Keyword B Resource R1 Resource R2 Resource R3 Prolog Engine Resource R3 Resource R2 Tag 1 Tag 2 Tag 3 Tag 2
- 49. JeromeDL and notitio.us Two main corrib.org projects Utylises aforementioned technologies to provide and delivers innovative: Digital Library – JeromeDL Knowledge Management System – notitio.us
- 50. Jerome Digital Library Joint effort of DERI, National University of Ireland, Galway Gdansk University of Technology (GUT) Distributed under BSD Open Source license Instances all over the world Ireland Poland Brazil Italy Mexico Korea
- 51. JeromeDL – Semantic Digital Library Semantic digital libraries integrate information based on different metadata, e.g.: resources, user profiles, bookmarks, taxonomies – high quality semantics = highly and meaningfully connected information provide interoperability with other systems (not only digital libraries) on either metadata or communication level or both – RDF as common denominator between digital libraries and other services delivering more robust, user friendly and adaptable search and browsing interfaces empowered by semantics (legacy, formal, and social annotations)
- 52. JeromeDL – Motivation use cases Librarians support for rich metadata (MARC21) in uploading resources, accessing bibliographic information and searching persistent identifiers Scientists easy publishing (designed as a institute/university digital library) creating hierarchical networks of digital libraries support for accessing, sharing and searching using bibliography metadata (BibTeX) Everyone simple search (incl. natural language queries) community-aware information sharing and browsing, support for internationalization
- 53. JeromeDL - Motivation Support for different kinds of bibliographic metadata, like: DublinCore, BibTeX and MARC21 at the same time making use of existing rich sources of bibliographic descriptions (like MARC21) created by human Support users and communities users have control over their profile information community-aware profiles are integrated with bibliographic descriptions support for community generated knowledge Deliver communication between instances P2P mode for searching and users authentication hierarchical model for browsing
- 54. JeromeDL JeromeDL is the semantic digital library that provides integrated social networking with user profiling. enhanced personalized search facility. interconnects meaningful description of resources with social media. extensible access control based on social networks. collaborative browsing and filtering. dynamic collections . integration with Web 2.0 services.
- 55. Metadata and Services in JeromeDL
- 56. JeromeDL – Dynamic Collections Dynamic Collections specified with triples filter or RDF query can be arranged in a tree structure easily extensible
- 58. JeromeDL – flexible access control Identity management based on social networks support for social networking metadata standard (FOAF) users and authors are part of a community Access control module apply access control licenses to resources and services defines atomic protections based on IP or position in the social network easily extensible
- 59. JeromeDL – access to semantics Exposing underlying semantics rendering RDF in various flavors exposing semantics in JSON and SIOC syndication feeds (RSS) Querying semantic database RDF query (SPARQL) endpoint OAI-PMH Open Search Delivering metadata to other services MarcOnt Mediation Services
- 60. JeromeDL – search beyond one JDL Distributed search Extensible Library Protocol based on HyperCuP P2P infrastructure Federated Search hierarchical order of JeromeDL instances exposing resources bottom-up OAI-PMH harvesting other libraries exposing resources to other libraries
- 61. Towards Library 2.0 Users become active producers of the content and metadata JeromeDL turns a single resources into a blog post users can annotate it users can rank it metadata about user annotations is exported in SIOC Community annotations for multimedia (alpha) region of interest (ROI) tagging in photos time-tagging of video streams
- 62. JeromeDL – Conclusions JeromeDL is a semantically enhanced DL based on semantic web and social networking technologies enhances users experience through the social interactions exploits the social networks for recommendations offers extensible access control delivers semantics for other services improves user experience of the information discovery process (confirmed by evaluation)
- 63. notitio.us Provide knowledge management solutions for the enterprises and the communities of users Build upon solution of the Semantic Web research
- 64. notitio.us service that enables the aggregation of metadata-rich information from various types of social semantic information sources. allows users to easily discover and share their knowledge. advanced solution to further information browsing, using either faceted navigation or tags-based filtering capable of exporting information in a standard way so that its data can be used by other semantically- enabled applications.
- 65. notitio.us – main modules SSCF – social bookmarking system with recomendations MBB – browsing on unstructured metadata TTM – browsing resources by tags IKHarvester – providing Semantic information
- 66. notitio.us – information flow Information discovery Information browsing and sharing Information exporting
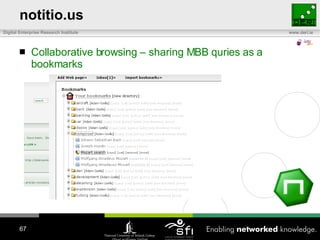
- 67. notitio.us Collaborative browsing – sharing MBB quries as a bookmarks
- 68. notitio.us distinctive features (compared to del.icio.us and similar) Reacher resources organisation. Well annotated directories and self created hierarchy Instant access to social network benefits Recommendation system that takes into account your resources and your characteristic Innavative browsing features including collaborative browsing
- 69. Summary – OpenSource in Research On the corrib.org example you can see how the OpenSource works in Academia. openSource != freeSource utilise the scale effect of people using the Open Source solutions for further research and for commercialisation efforts ,
- 70. Future JeromeDL and notitio.us future – commercialisations and further research
- 71. We invite everyone interested to contact and cooperate with us! Adam Gzella – [email_address] Sebastian Kruk – [email_address] http ://www.corrib.org http://www.jeromedl.org http://notitio.us http://www.deri.org
Editor's Notes
- #2: In other words – how open source can work in academia se







![SemanticWeb – short introduction Current Web vs. Semantic Web? An extension of the current Web in which information is given well-defined meaning, better enabling computers and people to work in cooperation. [Tim Berners-Lee] Current Web was designed for humans, and there is little information usable for machines Was the Web meant to be more? Objects with well defined attributes as opposed to untyped hyperlinks between Internet resources A network of relationships amongst named objects, yielding unified information management tasks What do you mean by “Semantic”? the semantics of something is the meaning of something Semantic Web is able to describe things in a way that computers can understand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconf2-1214600793569246-9/85/Corrib-org-OpenSource-and-Research-8-320.jpg)





























































![We invite everyone interested to contact and cooperate with us! Adam Gzella – [email_address] Sebastian Kruk – [email_address] http ://www.corrib.org http://www.jeromedl.org http://notitio.us http://www.deri.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconf2-1214600793569246-9/85/Corrib-org-OpenSource-and-Research-71-320.jpg)