data and addressing for internet having new
- 3. What is an IP Address? An IP Address is a 32-bit sequence of 1s and 0s. A way to identify machines on a network. A unique identifier. A numerical label. 101010001111000011101010100111011
- 4. IP Usage Used to connect to another computer. Allows transfers of files and e-mail.
- 5. What is an internet protocol? Protocol used for communicating data.
- 6. Services provided by IP Addressing Fragmentation
- 7. Part of IP Address Network Part Local or Host Part
- 8. IP Structure IP Addresses consist of four sections. Each section is 8 bits long. Each section can range from 0 to 255. Written, for example, 128.35.0.72
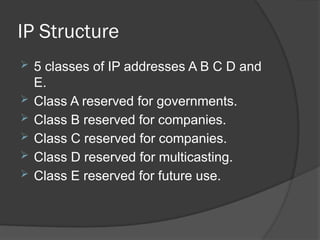
- 9. IP Structure 5 classes of IP addresses A B C D and E. Class A reserved for governments. Class B reserved for companies. Class C reserved for companies. Class D reserved for multicasting. Class E reserved for future use.
- 10. IP ranges Class Address Range Supports Class A 1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254 Supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks. Class B 127.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254 Supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks. Class C 192.0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254 Supports 254 hosts on each of 2 million networks. Class D 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 Reserved for multicast group. Class E 224.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254 Reserved for future use, or research and development purposes
- 11. network Host Host Host Class A 24 Bits Network Network Host Host Class B 16 Bits Network Network Network Host Class C 8 Bits
- 12. Address Class High-Order Bits First Octal Address Range Number of Bits in the Network Address Number of Networks Number of Hosts per Network Class A 0 0-127 8 126 16,777,216 Class B 10 128-191 16 16,384 65,536 Class C 110 192-223 24 2,097,152 254 Class D 1110 224-255 28 N/A N/A
- 13. EXAMPLE Network Host 32 Bits Network Network Host Host 8 bits 1 byte 8 bits 1 byte 8 bits 1 byte 8 bits 1 byte 176 10 0 0 Network Address (host bits = all zeros) N N N N 176 10 255 255 Broadcast Address (host bits = all ones)
- 14. How to Calculate Historical classful network architecture Class First Octal Binary Range of first Octal Networ k ID Host ID Number of Networ ks Number Of Addres ses A 0XXXX XXX 0-127 a b.c.d 27=128 224=16,7 77,214 B 10XXXX XX 128-191 a.b c.d 214=16,3 84 216=65,5 34 C 110XXX XX 192-223 a.b.c d 221=2,09 7,152 28=254
- 15. IP versions IPv4: 32-bit* number: Written in Dotted Decimal Notation 205.150.58.7 4 billion different host addresses IPv6: 128-bit* number: Written in Hex Decimal Notation 2001:0503:0C27:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000 16 billion network addresses
- 16. Types of IP Address Static address Dynamic address
- 17. Types of IP Address Static IP Address Manually input by network administrator Manageable for small networks Requires careful checks to avoid duplication
- 18. Types of IP Address Dynamic IP Address. Examples – BOOTP, DHCP. Assigned by server when host boots. Derived automatically from a range of addresses. Duration of `lease` negotiated, then address released back to server.
- 19. Public and Private IP Address A public IP Address will be issued by an ISP and will have number ranges from 1 to 191 in first octal with the exception of the private address ranges that starts at 10.0.0 for class A private networks and 172.16.0 for the class B private addresses.
- 20. THANKS FOR YOUR TIME