Data Communication & Computer network: Bipolar codes
- 1. Introduction to Data communication Topic : Bipolar Codes Lecture #7 Dr Rajiv Srivastava Director Sagar Institute of Research & Technology (SIRT) Sagar Group of Institutions, Bhopal http://www.sirtbhopal.ac.in
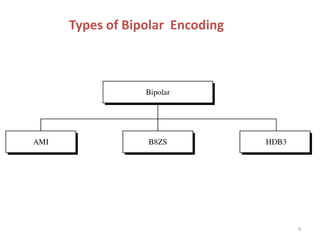
- 3. Bipolar Encoding • Bipolar encoding, like RZ, uses three voltage levels: positive, negative and zero. • Unlike RZ, however, the zero level in bipolar encoding is used to represent binary 0. The 1s are represented by alternating positive and negative voltages. If the first 1 bit is represented by the positive amplitude, the second will be represented by the negative amplitude, the third by the positive amplitude, and so on. This alteration occurs even when the 1 bits are not consecutive. • Three types of bipolar encoding are in popular use by the data communications industry : 1. AMI 2. B8ZS & 3. HDB3 3
- 4. Types of Bipolar Encoding 4
- 5. In bipolar encoding, we use three levels: positive, zero & negative. Tip 5
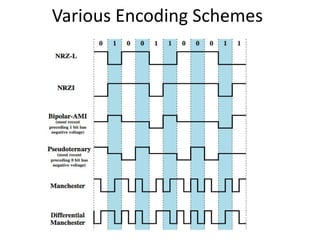
- 6. Bipolar AMI • Bipolar alternate mark inversion (AMI) is the simplest type of bipolar encoding. In the name alternate mark inversion, the word mark comes from telegraphy and means 1. – So AMI means alternate 1 inversion. – A neutral, zero voltage represents binary 0. • Binary 1s are represented by alternating positive and negative voltages. Figure gives an example. 6
- 7. Figure : Bipolar AMI encoding 7
- 8. AMI with Pseudoternary variation • A variation of bipolar AMI is called Pseudoternary, in which binary 0 alternates between positive and negative voltages. • By inverting on each occurrence of a 1, bipolar AMI accomplishes two things : 1. first, the DC component is zero, and 2. second, a long sequence of 1s stays synchronized • However, there is no mechanism to ensure the synchronization of a long string of 0s. 8
- 9. Figure: Bipolar schemes: AMI and pseudoternary In Bipolar AMI encoding, we use three levels: positive, zero & negative Pseudoternary AMI 1 represented by absence of signals 0 represented by alternating positive & negative Used in DS1 & E1 lines
- 11. • Two variations of bipolar AMI have been developed to solve the problem of synchronizing sequential 0s, especially for long-distance transmission. 1. The first, used in North America, is called bipolar 8-zero substitution (B8ZS). 2. The second, used in Europe and Japan, is called high-density bipolar 3 (HDB3). • Both are adaptations of bipolar AMI that modify the original pattern only in the case of multiple consecutives 0s. 11
- 12. Bipolar 8-Zero Substitution (B8ZS) • B8ZS is the convention adopted in North America to provide synchronization of long strings of 0s. • In this technique. Eight consecutive zero-level voltages are replaced by the sequence 000VB0VB. • The V is the sequence denotes violation; this is non- zero voltage that breaks the AMI rule of encoding(opposite polarity from the previous). • The B in the sequence denotes bipolar, which means a non zero level voltage in accordance with the AMI rule. • The two cases are shown in the figure. 12
- 13. Figure: Two cases of B8ZS scrambling technique - V means the same polarity as the polarity of previous non zero pulse - B means the polarity opposite to the polarity of previous non zero pulse
- 14. Example : Using B8ZS, encode the bit stream 10000000000100. Assume that the polarity of the first 1 is positive. • Solution • 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 v B 0 0 0 0 B V Polarity changes on every next 1 using AMI Amplitude time
- 15. High-Density Bipolar3 (HDB3) • The problem of synchronizing strings of consecutive 0s is solved differently in Europe and Japan than in the United States. This convention, called HDB3, introduces changes into the bipolar AMI pattern every time four consecutive 0s are encountered instead of waiting for the eight expected by B8ZS in North America. • Although the name is HDB3, the pattern changes whenever there are four 0s in succession. 15
- 16. • This technique is more conservative than B8ZS • The 4 consecutive zero level voltages are replaced with a sequence of 000V or B00V • The reason for two different substitutions is to maintain the even no of non zero pulses after each substitution. • The two rules can be stated below: 1. If the no of non zero pulses after the last substitution is odd, the substitution pattern will be 000V, which makes the total no of non zero pulses even. 2. If the no of non zero pulses after the last substitution is even, the substitution pattern will be B00V, which makes the total no of non zero pulses even. • Figure shows the example. 16
- 17. Figure: Different situations in HDB3 scrambling technique Important : After the first substitution the polarity of 1 is changed as per AMI scheme. Which is followed after each substitution.
- 18. Example : Using HDB3, encode the bit stream 10000000000100. Assume that the number of 1s so far is odd and the first 1 is positive. • Solution • 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 v 0 0 0 0 0 B V Amplitude time
- 19. Combined Look At Bipolar AMI, B8ZS and HDB3
- 20. Thank You Dr Rajiv Srivastava Director Sagar Institute of Research & Technology (SIRT) Sagar Group of Institutions, Bhopal http://www.sirtbhopal.ac.in