Data design and analysis of computing tools
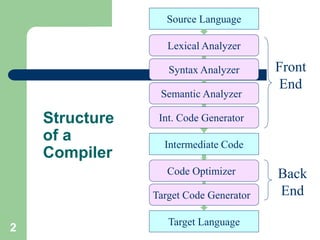
- 2. 2 Structure of a Compiler Source Language Target Language Semantic Analyzer Syntax Analyzer Lexical Analyzer Front End Code Optimizer Target Code Generator Back End Int. Code Generator Intermediate Code
- 3. 3 Today! Source Language Target Language Semantic Analyzer Syntax Analyzer Lexical Analyzer Front End Code Optimizer Target Code Generator Back End Int. Code Generator Intermediate Code
- 4. 4 The Role of Lexical Analyzer The lexical analyzer is the first phase of a compiler.The main task of lexical Analyzer(Scanner) is to read a stream of characters as an input and produce a sequence of tokens that the parser(Syntax Analyzer) uses for syntax analysis.
- 5. 5 Read Character Token Symbol Table Parser Lexical Analyzer input Push back character Get Next Token The Role of Lexical Analyzer (cont’d)
- 6. 6 The Role of Lexical Analyzer (cont’d) For example,a lexical analyzer for Pascal must read ahead after it sees the character >.If the next character is = ,then the character sequence >= is the lexeme forming the token for the “Greater than or equal to ” operator.Other wise > is the lexeme forming “Greater than ” operator ,and the lexical analyzer has read one character too many.
- 7. 7 The Role of Lexical Analyzer (cont’d) The extra character has to be pushed back on to the input,because it can be the beginning of the next lexeme in the input.The lexical analyzer and parser form a producer- Consumer pair. The lexical analyzer produces tokens and the parser consumes them.Produced tokens can be held in a token buffer until they are consumed.
- 8. 8 The Role of Lexical Analyzer (cont’d) The interaction b/w the two is constrained only by the size of the buffer,because the lexical analyzer can not proceed when the buffer is full and the parser can not proceed when the buffer is empty.Commonly ,the buffer holds just one token.In this case,the interaction can be implemented simply by making the lexical analyzer be a procedure called by the parser,returning tokens on demand.
- 9. 9 The Role of Lexical Analyzer (cont’d) The implementation of reading and pushing back character is usually done by setting up an input buffer.A block of character is read into the buffer at a time; a pointer keeps track of the portion of the input that has been analyzed.Pushing back a character is implemented by moving the pointer.
- 10. 10 The Role of Lexical Analyzer (cont’d) Some times lexical analyzer are divided into two phases,the first is called Scanning and the second is called Lexical Analysis.The scanning is responsible for doing simple tasks ,while the lexical analyzer does the more complex operations.For example, a Fortran might use a scanner to eliminate blanks from the input.
- 11. 11 Issues in Lexical Analysis There are several reasons for separating the analysis phase of compiling into lexical analysis and parsing. Simpler design is perhaps the most important consideration.The separation of lexical analysis from syntax analysis often allows us to simply one or the other of these phases.For example,a parser embodying the conventions for comments and white space is significantly more complex---
- 12. 12 Issues in Lexical Analysis (cont’d) --then one that can assume comments and white space have already been removed by a lexical analyzer.If we are designing a new language,separating the lexical and syntactic conventions can lead to a cleaner over all language design.
- 13. 13 Issues in Lexical Analysis (cont’d) 2) Compiler efficiency is improved. A separate lexical analyzer allows us to construct a specialized and potentially more efficient processor for the task.A large amount of time is spent reading the source program and partitioning it into tokens.Specialized buffering techniques for reading in put characters and processing tokens can significantly speed up the performance of a compiler.
- 14. 14 Issues in Lexical Analysis (cont’d) 3) Compiler portability is enhanced. Input alphabet peculiarities and other device-specific anomalies can be restricted to the lexical analyzer.The representation of special or non- standard symbols,such as ↑ in Pascal ,can be isolated in the lexical analyzer.
- 15. 15 Issues in Lexical Analysis (cont’d) Specialized tools have been designed to help automate the construction of lexical analyzers and parsers when they are separated.
- 16. 16 What exactly is lexing? Consider the code: if (i==j); z=1; else; z=0; endif; This is really nothing more than a string of characters: if_( i==j);ntz=1;nels e;ntz=0;nendif; During our lexical analysis phase we must divide this string into meaningful sub- strings.
- 17. 17 Tokens The output of our lexical analysis phase is a streams of tokens. A token is a syntactic category. In English this would be types of words or punctuation, such as a “noun”, “verb”, “adjective” or “end-mark”. In a program, this could be an “identifier”, a “floating-point number”, a “math symbol”, a “keyword”, etc…
- 18. 18 Identifying Tokens A sub-string that represents an instance of a token is called a lexeme. The class of all possible lexemes in a token is described by the use of a pattern. For example, the pattern to describe an identifier (a variable) is a string of letters, numbers, or underscores, beginning with a non-number. Patterns are typically described using regular expressions.
- 19. 19 Implementation A lexical analyzer must be able to do three things: 1. Remove all whitespace and comments. 2. Identify tokens within a string. 3. Return the lexeme of a found token, as well as the line number it was found on.
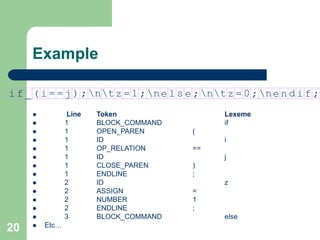
- 20. 20 Example if_ ( i= = j);ntz=1;nels e;ntz=0 ;nendif; Line Token Lexeme 1 BLOCK_COMMAND if 1 OPEN_PAREN ( 1 ID i 1 OP_RELATION == 1 ID j 1 CLOSE_PAREN ) 1 ENDLINE ; 2 ID z 2 ASSIGN = 2 NUMBER 1 2 ENDLINE ; 3 BLOCK_COMMAND else Etc…
- 21. 21 Lookahead Lookahead will typically be important to a lexical analyzer. Tokens are typically read in from left-to-right, recognized one at a time from the input string. It is not always possible to instantly decide if a token is finished without looking ahead at the next character. For example… Is “i” a variable, or the first character of “if”? Is “=” an assignment or the beginning of “==”?
- 22. 22 TOKENS The output of our lexical analysis phase is a streams of tokens.A token is a syntactic category. “A name for a set of input strings with related structure” Example: “ID,” “NUM”, “RELATION“,”IF” In English this would be types of words or punctuation, such as a “noun”, “verb”, “adjective” or “end-mark”. In a program, this could be an “identifier”, a “floating-point number”, a “math symbol”, a “keyword”, etc…
- 23. 23 Tokens (cont’d) As an example,consider the following line of code,which could be part of a “ C ” program. a [index] = 4 + 2
- 24. 24 Tokens (cont’d) a ID [ Left bracket index ID ] Right bracket = Assign 4 Num + plus sign 2 Num
- 25. 25 Attributes For Tokens (cont’d) < ID , pointer to symbol-table entry for E > < assign_op , > < ID , pointer to symbol entry for M > < add_op , > < ID , pointer to symbol entry for C > < mult_op , > < num ,integer value 2 >
- 26. 26 THANKS




















![23
Tokens (cont’d)
As an example,consider the following line of
code,which could be part of a “ C ” program.
a [index] = 4 + 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect-04-240402014957-b76c92e5/85/Data-design-and-analysis-of-computing-tools-23-320.jpg)
![24
Tokens (cont’d)
a ID
[ Left bracket
index ID
] Right bracket
= Assign
4 Num
+ plus sign
2 Num](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect-04-240402014957-b76c92e5/85/Data-design-and-analysis-of-computing-tools-24-320.jpg)

