Distributed RDBMS: Data Distribution Policy: Part 1 - What is a Data Distribution Policy
- 1. Distributed RDBMS Data Distribution Policy: Part 1 What is a data distribution policy? October 2014
- 2. 2 Data Distribution Policy: Part 1 Distributed RDBMSs provide many scalability, availability and performance advantages. But how do you “distribute” data? This presentation gives you a practical understanding of key issues to a successful distributed RDBMS. The presentation explores: • What a data distribution policy is • The challenges faced when data is distributed via sharding • What defines a good data distribution policy • The best way to distribute data for your application and workload
- 3. 3 Why is a Distributed Relational Database Good? Distributed relational databases are a perfect match for Cloud computing models and distributed Cloud infrastructure. They are the way forward for delivering web scale applications and keeping ACID properties. • Social apps • Games • Many concurrent users • High transaction throughput • Very large data volumes
- 4. 4 What Is a Data Distribution Policy? A data distribution policy describes the rules under which data is distributed. A policy that matches your application’s unique workflow will give you critical web scale benefits, including: • Endless scalability • High availability • Geo-location of data near user populations • Multi-tenancy • Archiving capabilities • Data tiering
- 5. NOTE: A poorly conceived data distribution policy will: • Degrade system performance • Use more system resources • Cause you maintenance problems This presentation outlines attributes of good data distribution policies. 5 Data Distribution Must Match App Workflow
- 6. 3 Key Questions about a Distributed RDBMS 1. How is data distributed in a distributed RDBMS? 2. What is the best way to distribute data for “my unique 6 application”? 3. How do I retune my distributed database for optimal performance as my application evolves and usage patterns change? Answer: This is all managed through your data distribution policy.
- 7. What about Sharding? Sharding is the old way to create a distributed database. In the past, developers needed to program data distribution logic into their actual applications in order to distribute data across an array of linked databases. Consequently, sharding was born, which entailed: • Splitting up databases into slices of data • Running every read or write through new custom-built 7 application code in order to place and locate bits of data
- 8. 8 Sharding Challenges Some great work was accomplished using sharding, but it’s slow and detailed work, and it creates major challenges, including: 1. Increasingly difficult operational issues, such as backup, adding indexes, and changing schemas 2. Checking that query paths actually yield accurate results Explore more details on sharding challenges: • “Top 10 DIY MySQL Sharding Challenges” • “Database Scalability: The Sharding Conflict”
- 9. So, What Makes a Good Data Distribution Policy? 1. Even and predictable workload 9 distribution across the clusters in your distributed database 2. Immense scalability and availability 3. The ability to handle more concurrent users, higher transaction throughput, and bigger volumes of data All benefits are all lost with a poorly conceived data distribution policy that does not align to your application’s unique usage and workloads.
- 10. Problem: When a Single Instance Database Reaches Its Limit Imagine we have a single database that is starting to exhibit signs of reaching its capacity limits. Its throughput becomes unpredictable and users become frustrated waiting for queries to be processed. 10
- 11. Solution: Evolving to a Distributed Database The best way to improve the situation is to evolve to a distributed RDBMS, which would result in: • Evenly dividing the total workload across an array of 11 database clusters • A decreased number of queries that any particular database cluster (or shard) receives • Minimizing the cross-database chatter (from cluster to cluster, or shard to shard), so that each transaction can be completed within a single cluster in a single fetch/trip Recommended reading: • “Challenges in Querying a Distributed Relational Database” for more information.
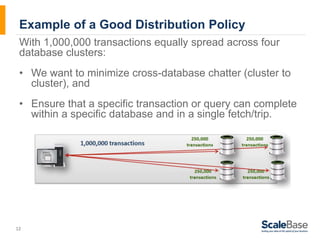
- 12. Example of a Good Distribution Policy With 1,000,000 transactions equally spread across four database clusters: • We want to minimize cross-database chatter (cluster to 12 cluster), and • Ensure that a specific transaction or query can complete within a specific database and in a single fetch/trip.
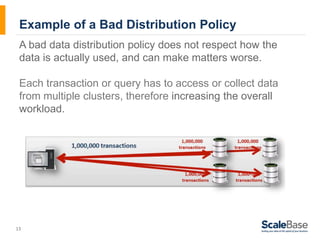
- 13. Example of a Bad Distribution Policy A bad data distribution policy does not respect how the data is actually used, and can make matters worse. Each transaction or query has to access or collect data from multiple clusters, therefore increasing the overall workload. 13
- 14. Data Distribution Policy Summary 14 Data Distribution Policy Bad Data Distribution Policy Good Data Distribution Policy The load isn't distributed – it’s multiplied! Distributes the workload evenly across available resources Doesn’t scale Distributes the sessions Adding an additional DB does NOT reduce the overall workload Delivers linear scalability The limitation of a single DB becomes the limitation of the entire array Adding another database, increases the overall scale potential of the distributed database When queries need data from multiple DBs, transactions must commit multiple separate DBs (2PC) before completing. This adds a lot of overhead to each Commit. Queries complete using data from a single, smaller database. This reduces a lot of overhead to any Commits.
- 15. What Is the Best Way to Distribute Data for Your Applications and Workloads? Unless we distribute data intelligently and aligned to application requirements, we will not achieve any benefit. Actually, things can become worse than before. Data must be distributed across a cluster of smaller databases in a way that maintains relational integrity, two-phase 15 commit and rollback. The natural question we are lead to ask is: “OK, So what is the best way to distribute data for my applications and my workloads?” This is answered in PART 2 of this Distributed RDBMS Data Distribution Policy slide presentation.
- 16. Additional Distributed RDBMS Resources To develop a custom made data distribution policy for your RDBMS and application, look for Part 2 of this slide presentation. We also recommend the following resources: • Four table Types You Need To Know To Scale Your 16 Relational Database • Distributed Databases and Cascading Tables • Discover your Application Scalability Score with ScaleBase Analysis Genie • Optimizing Sharding Policies to Scale Out MySQL – Choosing the Best Data Distribution Policy (whitepaper)
- 17. ScaleBase Software • ScaleBase is a distributed database built on MySQL and 17 optimized for the cloud. It deploys in minutes so your database can handle an unlimited number of users, humongous volumes of data, and faster transactions. • It dynamically optimizes workloads and availability by logically distributing data across public, private, and geo-distributed clouds.
- 18. ScaleBase Software 18 “What differentiates ScaleBase is its ability to add scalability without the need to migrate to new database architecture or make any changes to existing applications” - Matt Aslett, The 451 Group “ScaleBase allows us to effectively scale, without downtime, and without having to rewrite our application.” - Sheeri Cabral, Mozilla
- 19. Try ScaleBase Today ScaleBase software is available for free: • ScaleBase Website • Amazon Marketplace • Rackspace Marketplace • IBM Cloud marketplace • ScaleBase’s free online Analysis Genie service AWS Marketplace Guide and a AWS Getting Started Tutorial are available from the documentation section of the ScaleBase website. 19 Contact ScaleBase [email protected]
- 20. Data Distribution Policy: Part 2 and 3 Data Distribution Policy Part 2: • The different approaches to data distribution • How to create your own data distribution policy, whether you 20 are scaling an existing application or creating a new app. • How ScaleBase can help you create your policy Data Distribution Policy Part 3: • Three stages of your data distribution policy’s lifecycle. • Adapting the distributed RDBMS to match application changes. • Ensuring that your distributed relational database is flexible and elastic enough to accommodate endless growth and change.
- 21. Distributed RDBMS Data Distribution Policy: Part 1 October 2014