Data security in local network using distributed firewall ppt
- 1. Data Security in LAN using Distributed Firewall 1 Presented by Sabreen Irfana GMIT Guided by: Mr. Santosh Kumar B.E ,M Tech Asst prof ,Dept ISE GMIT
- 2. Abstract Computer and networking have become inseparable now . A number of confidential transaction occur every second and today computers are used mostly for transaction rather than processing of data, so Data security is needed to prevent hacking of data and to provide authenticated data transfer 2
- 3. .Contd Data security can be achieved by Firewall Conventional firewall relay on the notion of restricted topology and controlled entry point Restricting the network topology difficult in filtering certain protocols, expanding network and few more problems leads to the evolution of DISTRIBUTED FIREWALL 3
- 4. Contents Introduction to Security and Firewalls Problems with traditional Firewalls Distributed Firewall Concept Distributed Firewall Implementation Conclusions 4
- 5. Firewalls Firewall is a device or set of instruments designed to permit or deny network transmissions based upon a set of rules and regulations which are frequently used to protect networks from unauthorized access In most systems today, the firewall is the software that implements the “security policy” for a system A firewall is typically placed at the edge of a system and acts as a filter for unauthorized traffic 5
- 6. Security Policy A “security policy” defines the security rules of a system. Without a defined security policy, there is no way to know what access is allowed or disallowed An example policy: (simple) ◦ Allow all connections to the web server ◦ Deny all other access 6
- 7. Firewall Example 7 Internet Company 2 Company 4 Company 1 Company 3 Firewall FirewallFirewall Firewall
- 8. Firewall Drawbacks Traditional Firewalls uses restricted topology of the network Donot protect networks from internal attack Certain protocols (FTP, Real-Audio) are difficult for firewalls to process Assumes inside users are “trusted” single points of access make firewalls hard to manage 8
- 10. .contd 2 .Assumes inside users are trusted 10
- 11. .contd 3.Single point of failure or access 11
- 12. .Data security Threats IP Spoofing or IP masquerading 12 A 10.10.10.1 B 134.117.1.60 B 10.10.10.1 Src_IP 134.117.1.60 dst_IP Any (>1024) Src_port 80 dst_port 11.11.11.1 Src_IP 134.117.1.60 dst_IP Any (>1024) Src_port 80 dst_port spoofed
- 13. .cont IP spoofing 13 sender victim partner Oh, my partner sent me a packet. I’ll process this. impersonation
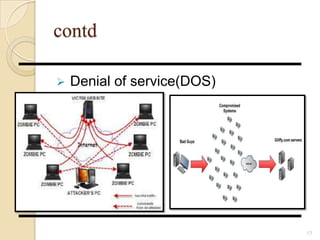
- 15. contd Denial of service(DOS) 15
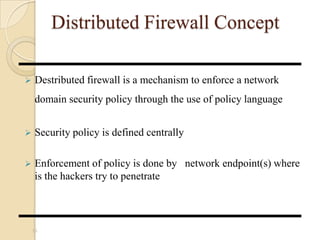
- 16. Distributed Firewall Concept Destributed firewall is a mechanism to enforce a network domain security policy through the use of policy language Security policy is defined centrally Enforcement of policy is done by network endpoint(s) where is the hackers try to penetrate 16
- 17. .contd It filters traffic from both the internal and internet network They overcome the single point of failure concept 17
- 18. 18
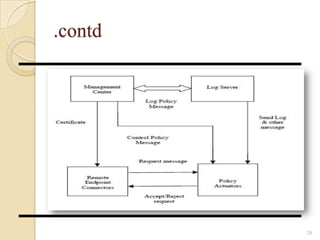
- 19. Architecture of Distributed Firewalls The whole distributed firewall system consists of four main parts: I. The management center II. Policy actuator: III. Remote endpoint connectors IV. Log server 19
- 20. .contd 20
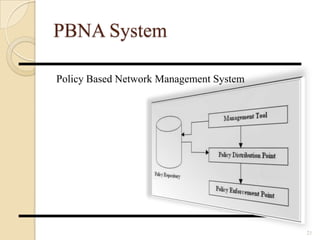
- 21. PBNA System Policy Based Network Management System 21
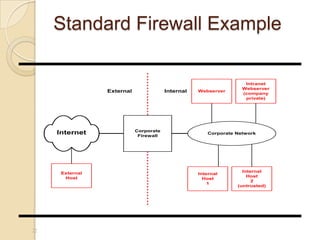
- 22. Standard Firewall Example 22 Corporate Network Corporate Firewall Internet InternalExternal External Host Internal Host 1 Internal Host 2 (untrusted) Webserver Intranet Webserver (company private)
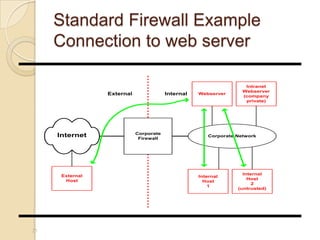
- 23. Standard Firewall Example Connection to web server 23 Corporate Network Corporate Firewall Internet InternalExternal External Host Internal Host 1 Internal Host 2 (untrusted) Webserver Intranet Webserver (company private)
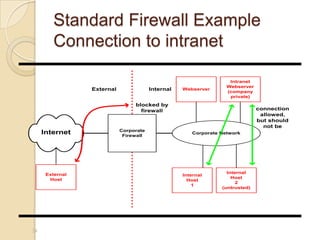
- 24. Standard Firewall Example Connection to intranet 24 Corporate Network Corporate Firewall Internet InternalExternal External Host Internal Host 1 Internal Host 2 (untrusted) Webserver Intranet Webserver (company private) blocked by firewall connection allowed, but should not be
- 25. Distributed Firewall Example 25 Corporate NetworkInternet InternalExternal External Host Internal Host 1 Internal Host 2 (untrusted) Webserver Intranet Webserver (company private) Internal Host (telecommuting)
- 26. Distributed Firewall Example to web server 26 Corporate NetworkInternet InternalExternal External Host Internal Host 1 Internal Host 2 (untrusted) Webserver Intranet Webserver (company private) Internal Host (telecommuting)
- 27. Distributed Firewall Example to intranet 27 Corporate NetworkInternet InternalExternal External Host Internal Host 1 Internal Host 2 (untrusted) Webserver Intranet Webserver (company private) Internal Host (telecommuting)
- 28. Components of Distributed Firewalls 28 A Distributed Firewall is a mechanism to enforce a network domain security policy through the use of the following: Policy Language Policy Distributed Scheme Certificates
- 29. .contd 29 Policy language The Policy language is used to create policies for each firewall. These policies are the collection of rules, which guides the firewall for evaluating the network traffic. It also defines which inbound and outbound connections on any component of the network policy domain are allowed.
- 30. .contd 30 Policy Distribution Scheme The policy distribution scheme should guarantee the integrity of the policy during transfer. This policy is consulted before processing the incoming or outgoing messages. The distribution of the policy can be different and varies with the implementation. It can be either directly pushed to end systems , or pulled when necessary
- 31. .contd 31 Certificates There may be the chance of using IP address for the host identification by the distributed firewalls. But a mechanism of security is more important. It is preferred to use certificate to identify hosts. IPSec provides cryptographic certificates. Unlike IP address, which can be easily spoofed, the digital certificate is much more secure and the authentication of the certificate is not easily forged. Policies are distributed by means of these
- 32. Advantages 32 1. Provides security for internet and intranet 2. Multiple access points 3. Insiders are no longer trusted 4. Security policy rules are distributed and established on needed basis 5 End to End can be easily done and filtering packets is easy
- 33. Disadvantage 33 1. Compliance of the security policy for insiders is one of the major issues of the distributed firewalls. This problem especially occurs when each ending host have the right of changing security policy. There can be some techniques to make modifying policies harder but it is not totally impossible to prevent it. 2 It is not so easy to implement an intrusion detection system in a distributed firewall environment. It is possible to log suspicious connections on local server but these logs need to be collected and analyzed by security experts in central service
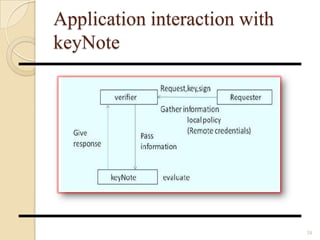
- 34. Distributed Firewall implementation.. Language to express policies and resolving requests (KeyNote system) Using keynode and Ipsec allows control of mixed level policies where authentication mechanism is applied through public key cryptography 34
- 35. KeyNote A language to describe security policies (RFC 2704) Fields : ◦ KeyNote Version – Must be first field, if present ◦ Authorizer – Mandatory field, identifies the issuer of the assertion ◦ Comment ◦ Conditions – The conditions under which the Authorizer trusts the Licensee ◦ Licensees – Identifies the authorized, should be public key, but can be IP address ◦ Signature – Must be last, if present All field names are case-insensitive 35
- 37. KeyNote Example 2 37 KeyNote-Version: 2 Authorizer: “rsa-hex:1023abcd” Licensee: “IP:158.130.6.141” Conditions: (@remote_port < 1024 && @local_port == 22 ) -> “true”; Signature: “rsa-sha1-hex:bee11984” Note that this credential delegates to an IP address,
- 39. Example of Connection to a Distributed Firewall local host security policy: KeyNote-Version: 2 Authorizer: “POLICY” Licensees: ADMINISTRATIVE_KEY Assumes an IPSEC SA between hosts 39
- 40. Example of Connection to a Distributed Firewall KeyNote-Version: 2 Authorizer: ADMINISTRATIVE_KEY Licensees: USER_KEY Conditions: (app_domain == "IPsec policy" && encryption_algorithm == “yes" && local_address == "158.130.006.141") -> "true"; (app_domain == "Distributed Firewall" && @local_port == 23 && encrypted == "yes" && authenticated == "yes") -> "true"; Signature: ... 40
- 41. Example of Connection to a Distributed Firewall 41 source local host 158.130.6.141 (running Policy Daemon) IPSEC SA TCP connect (23) context created local port=23 encrypted="yes" authenticated="yes" Policy Daemon checks context vs. credential continue TCP session Returns TRUE
- 42. Conclusions Distributed firewalls allows the network security policy to remain under control of the system administrators Insiders may no longer be unconditionally treated as “trusted” Does not completely eliminate the need for traditional firewalls More research is needed in this area to increase robustness, efficiency, 42
- 43. Future Work High quality administration tools NEED to exist for distributed firewalls to be accepted Allow per-packet scanning as opposed to per-connection scanning Policy updating 43
- 44. References [1] Sotiris Ioannidis, Angelos D. Keromytis, Steve M. Bellovin, Jonathan M. Smith, “Implementing a Distributed Firewall”, CCS ’00,Athens, Greece. [2] Steven M. Bellovin, “Distributed Firewalls”, November 1999 issue of; login: pp. 37-39. [3] W. R. Cheswick and S. M. Bellovin. “Firewalls and Internet Security”: Repelling the Wily Hacker. Addison-Wesley, 1994. [4] [Robert Stepanek, “Distributed Firewalls”, [email protected], T-110.501 Seminar on Network Security, HUT TML 2001. [5] Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan “Security and Internet Protocol”, Computer Engineering 44
- 45. 45


































![References
[1] Sotiris Ioannidis, Angelos D. Keromytis, Steve M. Bellovin, Jonathan
M. Smith, “Implementing a Distributed Firewall”, CCS ’00,Athens,
Greece.
[2] Steven M. Bellovin, “Distributed Firewalls”, November 1999 issue of;
login: pp. 37-39.
[3] W. R. Cheswick and S. M. Bellovin. “Firewalls and Internet Security”:
Repelling the Wily Hacker. Addison-Wesley, 1994.
[4] [Robert Stepanek, “Distributed Firewalls”, rost@cc.hut.fi, T-110.501
Seminar on Network Security, HUT TML 2001.
[5] Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan “Security and Internet Protocol”,
Computer Engineering
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datasecurityinlocalnetworkusingdistributedfirewall-140330025100-phpapp02/85/Data-security-in-local-network-using-distributed-firewall-ppt-44-320.jpg)
