Data stax webinar cassandra and titandb insights into datastax graph strategy v3 wc
- 1. Cassandra and TitanDB Insights into DataStax's Graph Strategy Robin Schumacher – VP Products Dr. Matthias Broecheler – Director of Engineering
- 2. Agenda • Overview of DataStax • Introduction to Graph • Comparing Graph to an RDBMS • A Look at DataStax’s Graph Strategy • Next Steps ©2015 DataStax
- 3. Founded in April 2010 450+ Santa Clara, Austin, New York, London, Paris, Tokyo, Sydney 410+ Employees Customers 30 Percent Overview
- 4. 1970s 1990s Client-ServerMainframe Evolution of Data Management 4 Monolithic hardware Centralized workloads Vendor lock-in General purpose databases (one size fits all) Isolated / semi-connected Commodity hardware Distributed workloads Massive scalability Radically connected Today Cloud Mobile Social Infrastructure centric Application / data centric
- 5. Cassandra – NoSQL for Modern Enterprise Workloads Always on Fully distributed Best in scale and performance 80%+ contributions -> DataStax Free tools and drivers Free training ©2015 DataStax San Francisco Stockholm New York
- 6. Enabling The Internet Enterprise with DataStax Enterprise ©2015 DataStax
- 8. What is a Graph Database? ©2015 DataStax High Level Used to manage highly connected or complex data User Level Used to support traversal and analytic queries against a data model that uses vertices, edges and properties to represent and store data Technical Level Uses specialized index structures, data partitioning techniques, and query optimizers to efficiently traverse large graphs
- 9. What is a Graph Database? ©2015 DataStax DataStax DataBricks Spark DSE CassandraJonathan Ellis Robin Schumacher Billy Bosworth worksFor title: VP Product develops uses uses reportsTo worksFor title: CTO worksFor title: CEO
- 10. What is a Graph Database? ©2015 DataStax DataStax DataBricks Spark DSE CassandraJonathan Ellis Robin Schumacher Billy Bosworth worksFor title: VP Product develops uses uses reportsTo worksFor title: CTO worksFor title: CEO Property Edge Vertex
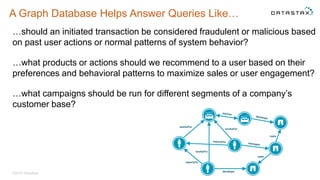
- 11. A Graph Database Helps Answer Queries Like… …should an initiated transaction be considered fraudulent or malicious based on past user actions or normal patterns of system behavior? …what products or actions should we recommend to a user based on their preferences and behavioral patterns to maximize sales or user engagement? …what campaigns should be run for different segments of a company’s customer base? ©2015 DataStax
- 12. Comparing Graph DB to RDBMS
- 13. Key Difference Between Graph DB and RDBMS ©2015 DataStax RDBMS Graph DB Process to query data elements (joins) is inefficient on large data sets or many relationships Better performance for relationship queries due to specialized index structures Expressing JOIN-intensive queries in SQL is time-consuming and error- prone Intuitive query language enabling faster application development
- 14. RDBMS vs. Graph DB: Query Complexity ©2015 DataStax SELECT TOP (5) [t14].[ProductName] FROM (SELECT COUNT(*) AS [value], [t13].[ProductName] FROM [customers] AS [t0] CROSS APPLY (SELECT [t9].[ProductName] FROM [orders] AS [t1] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t2] INNER JOIN [products] AS [t3] ON [t3].[ProductID] = [t2].[ProductID] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t4] INNER JOIN [orders] AS [t5] ON [t5].[OrderID] = [t4].[OrderID] LEFT JOIN [customers] AS [t6] ON [t6].[CustomerID] = [t5].[CustomerID] CROSS JOIN ([orders] AS [t7] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t8] INNER JOIN [products] AS [t9] ON [t9].[ProductID] = [t8].[ProductID]) WHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY] FROM [orders] AS [t10] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t11] INNER JOIN [products] AS [t12] ON [t12].[ProductID] = [t11].[ProductID] WHERE [t9].[ProductID] = [t12].[ProductID] AND [t10].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID] AND [t11].[OrderID] = [t10].[OrderID]) AND [t6].[CustomerID] <> [t0].[CustomerID] AND [t1].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID] AND [t2].[OrderID] = [t1].[OrderID] AND [t4].[ProductID] = [t3].[ProductID] AND [t7].[CustomerID] = [t6].[CustomerID] AND [t8].[OrderID] = [t7].[OrderID]) AS [t13] WHERE [t0].[CustomerID] = N'ALFKI' GROUP BY [t13].[ProductName]) AS [t14] ORDER BY [t14].[value] DESC g.V('customerId','ALFKI').as('customer') .out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').as('products') .in('is').in('contains').in('ordered').except('customer') .out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').except('products') .groupCount().cap().orderMap(T.decr)[0..<5].productNa me VS.
- 15. RDBMS vs. Graph DB: Data Modeling ©2015 DataStax SELECT TOP (5) [t14].[ProductName] FROM (SELECT COUNT(*) AS [value], [t13].[ProductName] FROM [customers] AS [t0] CROSS APPLY (SELECT [t9].[ProductName] FROM [orders] AS [t1] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t2] INNER JOIN [products] AS [t3] ON [t3].[ProductID] = [t2].[ProductID] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t4] INNER JOIN [orders] AS [t5] ON [t5].[OrderID] = [t4].[OrderID] LEFT JOIN [customers] AS [t6] ON [t6].[CustomerID] = [t5].[CustomerID] CROSS JOIN ([orders] AS [t7] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t8] INNER JOIN [products] AS [t9] ON [t9].[ProductID] = [t8].[ProductID]) WHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY] FROM [orders] AS [t10] CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t11] INNER JOIN [products] AS [t12] ON [t12].[ProductID] = [t11].[ProductID] WHERE [t9].[ProductID] = [t12].[ProductID] AND [t10].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID] AND [t11].[OrderID] = [t10].[OrderID]) AND [t6].[CustomerID] <> [t0].[CustomerID] AND [t1].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID] AND [t2].[OrderID] = [t1].[OrderID] AND [t4].[ProductID] = [t3].[ProductID] AND [t7].[CustomerID] = [t6].[CustomerID] AND [t8].[OrderID] = [t7].[OrderID]) AS [t13] WHERE [t0].[CustomerID] = N'ALFKI' GROUP BY [t13].[ProductName]) AS [t14] ORDER BY [t14].[value] DESC VS.
- 16. Comparing Graph DB to NoSQL
- 17. Key Difference Between Graph DB and NoSQL ©2015 DataStax NoSQL Graph DB Data model can’t represent relationships between rows or documents requiring application developers to maintain those inside the application which is cumbersome, inefficient, and error prone Natively supports relationships in the data model and provides a query language to efficiently retrieve them
- 18. NoSQL vs. Graph DB: Query Expressivity ©2015 DataStax g.V('customerId','ALFKI').as('customer') .out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').as('products') .in('is').in('contains').in('ordered').except('customer') .out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').except('products') .groupCount().cap().orderMap(T.decr)[0..<5].productNam e VS.? (requires application code)
- 19. A Look at DataStax’s Graph Strategy
- 20. Product Strategy for 2015 © 2015 DataStax, All Rights Reserved. 20 • Part of DataStax’s product strategy in 2015 will be to support multiple data models in DataStax Enterprise (DSE) • Support for multi-model will occur across several releases of DSE in 2015
- 21. Why Multi-Model in DataStax Enterprise? 21 Transactions Analytics Search Mixed Workload Needed? Solved in DSE Wide Row Graph JSON Mixed Model Needed? Solved in DSE DSE Analytics Search Transactions DSE Wide Row JSON Graph
- 23. Why Graph? • Best answer for applications having highly connected data • Key enabler of systems of engagement and systems of insight applications • Use cases include: • Personalization • Social engagement systems (e.g. matchmaking services, contacts catalogs, etc.) • Fraud detection • Financial analysis • Security analysis • Communication • Supply chain management ©2015 DataStax
- 24. ©2015 DataStax
- 25. Titan – the Foundation for DSE Graph • Titan is a scalable, distributed graph database that is optimized for storing, traversing and querying complex graph data in real time • Titan is open source and licensed under the Apache 2 • Current technical benefits include: • Built on top of Cassandra, Hbase, and BerkeleyDB • Scale-out and multi-data center capable • Able to support thousands of concurrent users and billions of graph data points • Analytics on graph data supported via Hadoop integration • Search enabled via support for Solr, Lucene, and Elasticsearch ©2015 DataStax
- 26. What is DataStax Enterprise Graph? DSE Graph is a scalable graph database solution for modern Web and mobile applications that need to manage highly connected data DSE Graph will be deeply integrated into the DSE platform: • Tight Cassandra integration • Graph analytics powered by Spark • DSE Search support • OpsCenter monitoring ©2015 DataStax
- 27. 2015 Plans for Titan / DSE Graph • DataStax will contribute to TinkerPop and is dedicated to making it the #1 open source graph framework • Release Titan 1.0 (TP3 compatible; a prerequisite coming out 1-2 months before) • First release of DSE Graph to occur in DSE 5.0. EAP builds will be available for interested customer • Recommendations for customer are to continue to develop using TinkerPop to ensure seamless compatibility with DSE Graph • DataStax to provide utilities/instructions for moving existing Titan databases to DSE Graph ©2015 DataStax
- 28. Next Steps • Check DataStax blog for updates on DSE Graph • If a current DSE customer, contact us about participating in upcoming Early Adopter Program (EAP) releases of DSE Graph • If haven’t tried DSE yet, download it from http://www.datastax.com/download and follow our getting started guide in your own environment (or use the DataStax Sandbox) ©2015 DataStax
Editor's Notes
- #4: We were founded in April 2010, so we are almost 5 years old. On December 1st, 2013, we were 150 employees, we are now over 380. That’s about a 250% growth in little over 12 months - impressive growth by any standards. We are headquartered in Santa Clara, California with offices in Austin, New York, London, Paris, Tokyo and Sydney, and we have transacted business in over 50 countries around the world. We have over 400 customers that span many different verticals and use cases. As you can see here, we have decided to show our customer logos on an iPhone. That is not because it’s the done thing in presentations today but rather to impress upon you that if you are using an iPhone, IOS or Android device, the chances are you are already using our technology as you move through your day. Currently 29 of the Fortune 100 use DataStax as their database technology of choice and this number is rising. We are on a remarkable journey and this rate and trajectory of growth is nt letting up. So why have we been experiencing such incredible growth and success.
- #5: Describe the evolution of various transactional database technologies from mainframe to todays distributed databases.
- #15: http://sql2gremlin.com/#complex/recommendation
- #16: http://sql2gremlin.com/#complex/recommendation
- #19: http://sql2gremlin.com/#complex/recommendation
- #28: Titan 1.0 in Summer. DSE Graph in Winter.













![RDBMS vs. Graph DB: Query Complexity
©2015 DataStax
SELECT TOP (5) [t14].[ProductName]
FROM (SELECT COUNT(*) AS [value],
[t13].[ProductName]
FROM [customers] AS [t0]
CROSS APPLY (SELECT [t9].[ProductName]
FROM [orders] AS [t1]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t2]
INNER JOIN [products] AS [t3]
ON [t3].[ProductID] = [t2].[ProductID]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t4]
INNER JOIN [orders] AS [t5]
ON [t5].[OrderID] = [t4].[OrderID]
LEFT JOIN [customers] AS [t6]
ON [t6].[CustomerID] = [t5].[CustomerID]
CROSS JOIN ([orders] AS [t7]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t8]
INNER JOIN [products] AS [t9]
ON [t9].[ProductID] = [t8].[ProductID])
WHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY]
FROM [orders] AS [t10]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t11]
INNER JOIN [products] AS [t12]
ON [t12].[ProductID] = [t11].[ProductID]
WHERE [t9].[ProductID] = [t12].[ProductID]
AND [t10].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID]
AND [t11].[OrderID] = [t10].[OrderID])
AND [t6].[CustomerID] <> [t0].[CustomerID]
AND [t1].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID]
AND [t2].[OrderID] = [t1].[OrderID]
AND [t4].[ProductID] = [t3].[ProductID]
AND [t7].[CustomerID] = [t6].[CustomerID]
AND [t8].[OrderID] = [t7].[OrderID]) AS [t13]
WHERE [t0].[CustomerID] = N'ALFKI'
GROUP BY [t13].[ProductName]) AS [t14]
ORDER BY [t14].[value] DESC
g.V('customerId','ALFKI').as('customer')
.out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').as('products')
.in('is').in('contains').in('ordered').except('customer')
.out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').except('products')
.groupCount().cap().orderMap(T.decr)[0..<5].productNa
me
VS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastaxwebinarcassandraandtitandbinsightsintodatastaxgraphstrategyv3wc-150312121827-conversion-gate01/85/Data-stax-webinar-cassandra-and-titandb-insights-into-datastax-graph-strategy-v3-wc-14-320.jpg)
![RDBMS vs. Graph DB: Data Modeling
©2015 DataStax
SELECT TOP (5) [t14].[ProductName]
FROM (SELECT COUNT(*) AS [value],
[t13].[ProductName]
FROM [customers] AS [t0]
CROSS APPLY (SELECT [t9].[ProductName]
FROM [orders] AS [t1]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t2]
INNER JOIN [products] AS [t3]
ON [t3].[ProductID] = [t2].[ProductID]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t4]
INNER JOIN [orders] AS [t5]
ON [t5].[OrderID] = [t4].[OrderID]
LEFT JOIN [customers] AS [t6]
ON [t6].[CustomerID] = [t5].[CustomerID]
CROSS JOIN ([orders] AS [t7]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t8]
INNER JOIN [products] AS [t9]
ON [t9].[ProductID] = [t8].[ProductID])
WHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY]
FROM [orders] AS [t10]
CROSS JOIN [order details] AS [t11]
INNER JOIN [products] AS [t12]
ON [t12].[ProductID] = [t11].[ProductID]
WHERE [t9].[ProductID] = [t12].[ProductID]
AND [t10].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID]
AND [t11].[OrderID] = [t10].[OrderID])
AND [t6].[CustomerID] <> [t0].[CustomerID]
AND [t1].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID]
AND [t2].[OrderID] = [t1].[OrderID]
AND [t4].[ProductID] = [t3].[ProductID]
AND [t7].[CustomerID] = [t6].[CustomerID]
AND [t8].[OrderID] = [t7].[OrderID]) AS [t13]
WHERE [t0].[CustomerID] = N'ALFKI'
GROUP BY [t13].[ProductName]) AS [t14]
ORDER BY [t14].[value] DESC
VS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastaxwebinarcassandraandtitandbinsightsintodatastaxgraphstrategyv3wc-150312121827-conversion-gate01/85/Data-stax-webinar-cassandra-and-titandb-insights-into-datastax-graph-strategy-v3-wc-15-320.jpg)


![NoSQL vs. Graph DB: Query Expressivity
©2015 DataStax
g.V('customerId','ALFKI').as('customer')
.out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').as('products')
.in('is').in('contains').in('ordered').except('customer')
.out('ordered').out('contains').out('is').except('products')
.groupCount().cap().orderMap(T.decr)[0..<5].productNam
e
VS.?
(requires application code)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastaxwebinarcassandraandtitandbinsightsintodatastaxgraphstrategyv3wc-150312121827-conversion-gate01/85/Data-stax-webinar-cassandra-and-titandb-insights-into-datastax-graph-strategy-v3-wc-18-320.jpg)










