Database introduction
- 1. Introduction Database integral part of our day to day life Collection of related database Database Management System : software managing and controlling access to the database. Database system : collection of application interracting with database
- 2. Example of use of database systems A database is accessed when : Purshasing in a supermarket ( item price) Purchase using credit cards ( valid cards) Inquiries about a holliday (flight details) Make a loan (library) Rent video ( detail info on each video) Online bookstore( book details)
- 3. Sample data
- 4. Dtabase in the dev cycle Project Identifcation and Selection Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Implementation Maintenance
- 5. Database A repository of data simultaneously used by many users (a shared ressource). Collection of logically related data. Description of this data (data dictionary) BDMS Software interracting with : Users Application programs database
- 6. BDMS Software interracting with : Users Application programs Database DBMS allows users (using a query language): Insert Update Delete Retrive data from DB
- 7. Database application programs Computer program that allow users to interact with the DB through DBMS.
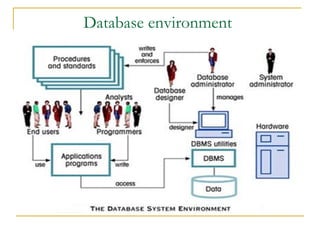
- 8. DBMS environment Hardware :Computer systems that DBMS and application programs run on. Software: DBMS,application programs, operating system, network software(if DBMS used over network). Data ( operational data and meta-data) Procedures: instruction and rules that govern use of database People: DB designer, administrators , programmers and end users
- 10. DBMS architecture 2 layer architecture Client-Server The client that runs the application and the server that handles the database back-end Multiple users able to access the DB simultanousely. Server is processing data while the client for business logic and presentation.
- 12. DBMS architecture 3 layer architecture User Interface layer ( runs on the user´s client) Business logic (middle layer) and data processing layer. Runs on a server called ”application server”. DBMS ( store data ) , may run on a separate server called ”database server”
- 14. 3 layer architecture advantages Thin client (less hardware) , client only handling presentation logic.This means a little communication needed between the client(browser) and the middle tier. Separating the core business logic from the database functions Modularity : Easy to modify or replace one tier without affecting the other tiers Easier load balancing Maps quite naturally to the web environment Security : middle tier protecting the DB. Scalabale : add as many middle tier as needed
- 15. Functions of a DBMS Data storage , retrieval and update A user-accessible Catalog Hold data about the structure of database , users , applications and so on Transaction support Ensure that all the updates are made or that none of them are made Concurrency control services Enable many users to access shared data concurrently Recovery services When transaction fails, DB revovered to a consistent state
- 16. Functions of a DBMS Autorization services Only special part could have access to info Support for data communication Terminal at remote locations can communicate with host of DBMS through network Integrity Services Stored data are consistent and correct Services to promote Data Independence Utility Services Utility program help manage the DB effectively
- 17. Advantages of DBMS Control of data redundancy (duplication) Eliminate redundency where possible , Data consistency Data stored in more than once , system can ensure that all copies of the data are kept consistent Sharing of data By all authorized users Improved data integrity Rules that DB is not permitted to violate User define data and DBMS enforce it Improved maintenance through data independence Make application immune to changes in data description