Database management system by Gursharan singh
- 1. Database Management System by Gursharan Singh Database is a organised collection of related data of an organisatioin and data is a collection of facts and figures that can be processed to produce information. Database Management System or DBMS in short refers to the technology of storing and retrieving users’ data with utmost efficiency along with appropriate security measures. Advantages of DBMS Reduced Data Redundancy Redundancy means having multiple copies of the same data. In computer file-based processing system, each application program has its own data files. The same data may be duplicated in more than one file. The duplication of data may create many problems such as: 1. To update a specific data/record, the same data must be updated in all files, otherwise different file may have different information about a specific item. 2. A valuable storage space is wasted. In DBMS, all data of an organization is integrated into a single database file. The data is recorded in only one place in the database and it is not duplicated. Reduced Data consistency Data inconsistency mean that different files may contain different information of a particular object or person. By controlling the data redundancy, the data consistency is obtained. If a data item appears only once, any update to its value has to be performed only once and the updated value is immediately available to all users Data Isolation In computer file-based system, data is isolated in separate files. It is difficult to update and to access particular information from data files.Dbms solved this problem by saving all data in the same database table. Data Dependence In computer file-based processing systems, the data stored in file depends upon the application program through which the file was created. It means that the structure of data files is coupled with application program. It is difficult to change the structure of data files or records. If you want to change the structure of data file (or format of file), then you have to modify the application program. Program Maintenance
- 2. In computer file-based processing system, the structure of data file is coupled with the individual application programs. Therefore, any modification to a data file such as size of a data field, its type etc. requires the modification of the application program also. This process of modifying the program is referred to as program maintenance. Data Sharing In computer file-based processing systems, each application program uses its own private data files. The computer file-based processing systems do not provide the facility to share data of a data file among multiple users on the network. Data Security The computer file-based processing system do not provide the proper security system against illegal access of data. Anyone can easily change or delete valuable data stored in the data file. It is the most complicated problem of file-processing system. Incompatible File Format In computer file-based processing systems, the structure of data file is coupled with the application program and the structure of data file is dependent on the programming languages in which the application program was developed. Characteristics Traditionally, data was organized in file formats. DBMS was a new concept then, and all the research was done to make it overcome the deficiencies in traditional style of data management. A modern DBMS has the following characteristics − Real-world entity − A modern DBMS is more realistic and uses real-world entities to design its architecture. It uses the behavior and attributes too. For example, a school database may use students as an entity and their age as an attribute. Relation-based tables − DBMS allows entities and relations among them to form tables. A user can understand the architecture of a database just by looking at the table names. Isolation of data and application − A database system is entirely different than its data. A database is an active entity, whereas data is said to be passive, on which the database works and organizes. DBMS also stores metadata, which is data about data, to ease its own process. Less redundancy − DBMS follows the rules of normalization, which splits a relation when any of its attributes is having redundancy in values. Normalization is a mathematically rich and scientific process that reduces data redundancy.
- 3. Consistency − Consistency is a state where every relation in a database remains consistent. There exist methods and techniques, which can detect attempt of leaving database in inconsistent state. A DBMS can provide greater consistency as compared to earlier forms of data storing applications like file-processing systems. Query Language − DBMS is equipped with query language, which makes it more efficient to retrieve and manipulate data. A user can apply as many and as different filtering options as required to retrieve a set of data. Traditionally it was not possible where file-processing system was used. ACID Properties − DBMS follows the concepts of Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (normally shortened as ACID). These concepts are applied on transactions, which manipulate data in a database. ACID properties help the database stay healthy in multi- transactional environments and in case of failure. Multiuser and Concurrent Access − DBMS supports multi-user environment and allows them to access and manipulate data in parallel. Though there are restrictions on transactions when users attempt to handle the same data item, but users are always unaware of them. Users A typical DBMS has users with different rights and permissions who use it for different purposes. Some users retrieve data and some back it up. The users of a DBMS can be broadly categorized as follows − Administrators − Administrators maintain the DBMS and are responsible for administrating the database. They are responsible to look after its usage and by whom it should be used. They create access profiles for users and apply limitations to maintain isolation and force security. Administrators also look
- 4. after DBMS resources like system license, required tools, and other software and hardware related maintenance. Designers − Designers are the group of people who actually work on the designing part of the database. They keep a close watch on what data should be kept and in what format. They identify and design the whole set of entities, relations, constraints, and views. End Users − End users are those who actually reap the benefits of having a DBMS. End users can range from simple viewers who pay attention to the logs or market rates to sophisticated users such as business analysts. 3-tier Architecture A 3-tier architecture separates its tiers from each other based on the complexity of the users and how they use the data present in the database. It is the most widely used architecture to design a DBMS. Database (Data) Tier − At this tier, the database resides along with its query processing languages. We also have the relations that define the data and their constraints at this level.
- 5. Application (Middle) Tier − At this tier reside the application server and the programs that access the database. For a user, this application tier presents an abstracted view of the database. End-users are unaware of any existence of the database beyond the application. At the other end, the database tier is not aware of any other user beyond the application tier. Hence, the application layer sits in the middle and acts as a mediator between the end-user and the database. User (Presentation) Tier − End-users operate on this tier and they know nothing about any existence of the database beyond this layer. At this layer, multiple views of the database can be provided by the application. All views are generated by applications that reside in the application tier. Data Models Entity-Relationship Model Entity-Relationship (ER) Model is based on the notion of real-world entities and relationships among them. While formulating real-world scenario into the database model, the ER Model creates entity set, relationship set, general attributes and constraints. ER Model is best used for the conceptual design of a database. ER Model is based on − Entities and their attributes. Relationships among entities. These concepts are explained below.
- 6. Entity − An entity in an ER Model is a real-world entity having properties called attributes. Every attribute is defined by its set of values called domain. For example, in a school database, a student is considered as an entity. Student has various attributes like name, age, class, etc. Relationship − The logical association among entities is called relationship. Relationships are mapped with entities in various ways. Mapping cardinalities define the number of association between two entities. Mapping cardinalities − o one to one o one to many o many to one o many to many Relational Model The most popular data model in DBMS is the Relational Model. It is more scientific a model than others. This model is based on first-order predicate logic and defines a table as an n-ary relation.
- 7. The main highlights of this model are − Data is stored in tables called relations. Relations can be normalized. In normalized relations, values saved are atomic values. Each row in a relation contains a unique value. Each column in a relation contains values from a same domain. Database Schema A database schema is the skeleton structure that represents the logical view of the entire database. It defines how the data is organized and how the relations among them are associated. It formulates all the constraints that are to be applied on the data. A database schema defines its entities and the relationship among them. It contains a descriptive detail of the database, which can be depicted by means of schema diagrams. It’s the database designers who design the schema to help programmers understand the database and make it useful.
- 8. A database schema can be divided broadly into two categories − Physical Database Schema − This schema pertains to the actual storage of data and its form of storage like files, indices, etc. It defines how the data will be stored in a secondary storage. Logical Database Schema − This schema defines all the logical constraints that need to be applied on the data stored. It defines tables, views, and integrity constraints. Database Instance It is important that we distinguish these two terms individually. Database schema is the skeleton of database. It is designed when the database doesn't exist at all. Once the database is operational, it is very difficult to make any changes to it. A database schema does not contain any data or information. A database instance is a state of operational database with data at any given time. It contains a snapshot of the database. Database instances tend to change with time. A DBMS ensures that its every instance (state)
- 9. is in a valid state, by diligently following all the validations, constraints, and conditions that the database designers have imposed. Data Independence A database system normally contains a lot of data in addition to users’ data. For example, it stores data about data, known as metadata, to locate and retrieve data easily. It is rather difficult to modify or update a set of metadata once it is stored in the database. But as a DBMS expands, it needs to change over time to satisfy the requirements of the users. If the entire data is dependent, it would become a tedious and highly complex job. Metadata itself follows a layered architecture, so that when we change data at one layer, it does not affect the data at another level. This data is independent but mapped to each other. Logical Data Independence Logical data is data about database, that is, it stores information about how data is managed inside. For example, a table (relation) stored in the database and all its constraints, applied on that relation. Logical data independence is a kind of mechanism, which liberalizes itself from actual data stored on the disk. If we do some changes on table format, it should not change the data residing on the disk. Physical Data Independence
- 10. All the schemas are logical, and the actual data is stored in bit format on the disk. Physical data independence is the power to change the physical data without impacting the schema or logical data. For example, in case we want to change or upgrade the storage system itself − suppose we want to replace hard-disks with SSD − it should not have any impact on the logical data or schemas. ER Data Model The ER model defines the conceptual view of a database. It works around real-world entities and the associations among them. At view level, the ER model is considered a good option for designing databases. Entity An entity can be a real-world object, either animate or inanimate, that can be easily identifiable. For example, in a school database, students, teachers, classes, and courses offered can be considered as entities. All these entities have some attributes or properties that give them their identity. An entity set is a collection of similar types of entities. An entity set may contain entities with attribute sharing similar values. For example, a Students set may contain all the students of a school; likewise a Teachers set may contain all the teachers of a school from all faculties. Entity sets need not be disjoint. Attributes Entities are represented by means of their properties, called attributes. All attributes have values. For example, a student entity may have name, class, and age as attributes. There exists a domain or range of values that can be assigned to attributes. For example, a student's name cannot be a numeric value. It has to be alphabetic. A student's age cannot be negative, etc.
- 11. Types of Attributes Simple attribute − Simple attributes are atomic values, which cannot be divided further. For example, a student's phone number is an atomic value of 10 digits. Composite attribute − Composite attributes are made of more than one simple attribute. For example, a student's complete name may have first_name and last_name. Derived attribute − Derived attributes are the attributes that do not exist in the physical database, but their values are derived from other attributes present in the database. For example, average_salary in a department should not be saved directly in the database, instead it can be derived. For another example, age can be derived from data_of_birth. Single-value attribute − Single-value attributes contain single value. For example − Social_Security_Number. Multi-value attribute − Multi-value attributes may contain more than one values. For example, a person can have more than one phone number, email_address, etc. These attribute types can come together in a way like − simple single-valued attributes simple multi-valued attributes composite single-valued attributes composite multi-valued attributes Entity-Set and Keys Key is an attribute or collection of attributes that uniquely identifies an entity among entity set. For example, the roll_number of a student makes him/her identifiable among students. Super Key − A set of attributes (one or more) that collectively identifies an entity in an entity set. Candidate Key − A minimal super key is called a candidate key. An entity set may have more than one candidate key. Primary Key − A primary key is one of the candidate keys chosen by the database designer to uniquely identify the entity set.
- 12. Relationship The association among entities is called a relationship. For example, an employee works_at a department, a student enrolls in a course. Here, Works_at and Enrolls are called relationships. Relationship Set A set of relationships of similar type is called a relationship set. Like entities, a relationship too can have attributes. These attributes are called descriptive attributes. Degree of Relationship The number of participating entities in a relationship defines the degree of the relationship. Binary = degree 2 Ternary = degree 3 n-ary = degree Mapping Cardinalities Cardinality defines the number of entities in one entity set, which can be associated with the number of entities of other set via relationship set. One-to-one − One entity from entity set A can be associated with at most one entity of entity set B and vice versa. One-to-many − One entity from entity set A can be associated with more than one entities of entity set B however an entity from entity set B, can be associated with at most one entity.
- 13. Many-to-one − More than one entities from entity set A can be associated with at most one entity of entity set B, however an entity from entity set B can be associated with more than one entity from entity set A. Many-to-many − One entity from A can be associated with more than one entity from B and vice versa.
- 14. Representation of ER diagram Let us now learn how the ER Model is represented by means of an ER diagram. Any object, for example, entities, attributes of an entity, relationship sets, and attributes of relationship sets, can be represented with the help of an ER diagram. Entity Entities are represented by means of rectangles. Rectangles are named with the entity set they represent. Attributes Attributes are the properties of entities. Attributes are represented by means of ellipses. Every ellipse represents one attribute and is directly connected to its entity (rectangle). If the attributes are composite, they are further divided in a tree like structure. Every node is then connected to its attribute. That is, composite attributes are represented by ellipses that are connected with an ellipse.
- 15. Multivalued attributes are depicted by double ellipse. Derived attributes are depicted by dashed ellipse.
- 16. Relationship Relationships are represented by diamond-shaped box. Name of the relationship is written inside the diamond-box. All the entities (rectangles) participating in a relationship, are connected to it by a line. Binary Relationship and Cardinality A relationship where two entities are participating is called a binary relationship. Cardinality is the number of instance of an entity from a relation that can be associated with the relation. One-to-one − When only one instance of an entity is associated with the relationship, it is marked as '1:1'. The following image reflects that only one instance of each entity should be associated with the relationship. It depicts one-to-one relationship. One-to-many − When more than one instance of an entity is associated with a relationship, it is marked as '1:N'. The following image reflects that only one instance of entity on the left and more than one instance of an
- 17. entity on the right can be associated with the relationship. It depicts one-to- many relationship. Many-to-one − When more than one instance of entity is associated with the relationship, it is marked as 'N:1'. The following image reflects that more than one instance of an entity on the left and only one instance of an entity on the right can be associated with the relationship. It depicts many-to-one relationship. Many-to-many − The following image reflects that more than one instance of an entity on the left and more than one instance of an entity on the right can be associated with the relationship. It depicts many-to-many relationship. Participation Constraints Total Participation − Each entity is involved in the relationship. Total participation is represented by double lines.
- 18. Partial participation − Not all entities are involved in the relationship. Partial participation is represented by single lines.
- 19. Codd's 12 Rules Dr Edgar F. Codd, after his extensive research on the Relational Model of database systems, came up with twelve rules of his own, which according to him, a database must obey in order to be regarded as a true relational database. These rules can be applied on any database system that manages stored data using only its relational capabilities. This is a foundation rule, which acts as a base for all the other rules. Rule 1: Information Rule The data stored in a database, may it be user data or metadata, must be a value of some table cell. Everything in a database must be stored in a table format. Rule 2: Guaranteed Access Rule Every single data element (value) is guaranteed to be accessible logically with a combination of table-name, primary-key (row value), and attribute-name (column value). No other means, such as pointers, can be used to access data. Rule 3: Systematic Treatment of NULL Values The NULL values in a database must be given a systematic and uniform treatment. This is a very important rule because a NULL can be interpreted as one the following − data is missing, data is not known, or data is not applicable. Rule 4: Active Online Catalog The structure description of the entire database must be stored in an online catalog, known as data dictionary, which can be accessed by authorized users. Users can use the same query language to access the catalog which they use to access the database itself. Rule 5: Comprehensive Data Sub-Language Rule A database can only be accessed using a language having linear syntax that supports data definition, data manipulation, and transaction management operations. This language can be used directly or by means
- 20. of some application. If the database allows access to data without any help of this language, then it is considered as a violation. Rule 6: View Updating Rule All the views of a database, which can theoretically be updated, must also be updatable by the system. Rule 7: High-Level Insert, Update, and Delete Rule A database must support high-level insertion, updation, and deletion. This must not be limited to a single row, that is, it must also support union, intersection and minus operations to yield sets of data records. Rule 8: Physical Data Independence The data stored in a database must be independent of the applications that access the database. Any change in the physical structure of a database must not have any impact on how the data is being accessed by external applications. Rule 9: Logical Data Independence The logical data in a database must be independent of its user’s view (application). Any change in logical data must not affect the applications using it. For example, if two tables are merged or one is split into two different tables, there should be no impact or change on the user application. This is one of the most difficult rule to apply. Rule 10: Integrity Independence A database must be independent of the application that uses it. All its integrity constraints can be independently modified without the need of any change in the application. This rule makes a database independent of the front-end application and its interface. Rule 11: Distribution Independence The end-user must not be able to see that the data is distributed over various locations. Users should always get the impression that the data is located at one site only. This rule has been regarded as the foundation of distributed database systems. Rule 12: Non-Subversion Rule
- 21. If a system has an interface that provides access to low-level records, then the interface must not be able to subvert the system and bypass security and integrity constraints. Generalization As mentioned above, the process of generalizing entities, where the generalized entities contain the properties of all the generalized entities, is called generalization. In generalization, a number of entities are brought together into one generalized entity based on their similar characteristics. For example, pigeon, house sparrow, crow and dove can all be generalized as Birds. Specialization Specialization is the opposite of generalization. In specialization, a group of entities is divided into sub- groups based on their characteristics. Take a group ‘Person’ for example. A person has name, date of birth, gender, etc. These properties are common in all persons, human beings. But in a company, persons can be identified as employee, employer, customer, or vendor, based on what role they play in the company. Similarly, in a school database, persons can be specialized as teacher, student, or a staff, based on what role they play in school as entities. Inheritance
- 22. We use all the above features of ER-Model in order to create classes of objects in object-oriented programming. The details of entities are generally hidden from the user; this process known as abstraction. Inheritance is an important feature of Generalization and Specialization. It allows lower-level entities to inherit the attributes of higher-level entities. For example, the attributes of a Person class such as name, age, and gender can be inherited by lower- level entities such as Student or Teacher. Relational data model Relational data model is the primary data model, which is used widely around the world for data storage and processing. This model is simple and it has all the properties and capabilities required to process data with storage efficiency. Concepts Tables − In relational data model, relations are saved in the format of Tables. This format stores the relation among entities. A table has rows and columns, where rows represents records and columns represent the attributes.
- 23. Tuple − A single row of a table, which contains a single record for that relation is called a tuple. Relation instance − A finite set of tuples in the relational database system represents relation instance. Relation instances do not have duplicate tuples. Relation schema − A relation schema describes the relation name (table name), attributes, and their names. Relation key − Each row has one or more attributes, known as relation key, which can identify the row in the relation (table) uniquely. Attribute domain − Every attribute has some pre-defined value scope, known as attribute domain. Properties of relations Properties of database relations are: • relation name is distinct from all other relations • each cell of relation contains exactly one atomic (single) value • each attribute has a distinct name • values of an attribute are all from the same domain • order of attributes has no significance each tuple is distinct; there are no duplicate tuples • order of tuples has no significance, theoretically. Keys Types of keys in DBMS Primary Key – A primary is a column or set of columns in a table that uniquely identifies tuples (rows) in that table. Super Key – A super key is a set of one of more columns (attributes) to uniquely identify rows in a table. Candidate Key – A super key with no redundant attribute is known as candidate key
- 24. Alternate Key – Out of all candidate keys, only one gets selected as primary key, remaining keys are known as alternate or secondary keys. Composite Key – A key that consists of more than one attribute to uniquely identify rows (also known as records & tuples) in a table is called composite key. Foreign Key – Foreign keys are the columns of a table that points to the primary key of another table. They act as a cross-reference between tables. Primary key in DBMS BY CHAITANYA SINGH | FILED UNDER: DBMS Definition: A primary is a column or set of columns in a table that uniquely identifies tuples (rows) in that table. Example: Student Table Stu_Id Stu_Name Stu_Age 101 Steve 23 102 John 24 103 Robert 28 104 Carl 22
- 25. In the above Student table, the Stu_Id column uniquely identifies each row of the table. Note: We denote the primary key by underlining the column name. The value of primary key should be unique for each row of the table. Primary key column cannot contain duplicate values. Primary key column should not contain nulls. Primary keys are not necessarily to be a single column; more than one column can also be a primary key for a table. For e.g. {Stu_Id, Stu_Name} collectively can play a role of primary key in the above table, but that does not make sense because Stu_Id alone is enough to uniquely identifies rows in a table then why to make things complex. Having that said, we should choose more than one columns as primary key only when there is no single column that can play the role of primary key. Super key in DBMS BY CHAITANYA SINGH | FILED UNDER: DBMS Definition: A super key is a set or one of more columns (attributes) to uniquely identify rows in a table. Often people get confused between super key and candidate key, so we will also discuss a little about candidate key here. How candidate key is different from super key? Answer is simple – Candidate keys are selected from the set of super keys, the only thing we take care while selecting candidate key is: It should not have any redundant attribute. That’s the reason they are also termed as minimal super key. Let’s take an example to understand this: Employee table Emp_SSN Emp_Number Emp_Name
- 26. 123456789 226 Steve 999999321 227 Ajeet 888997212 228 Chaitanya 777778888 229 Robert Super keys: {Emp_SSN} {Emp_Number} {Emp_SSN, Emp_Number} {Emp_SSN, Emp_Name} {Emp_SSN, Emp_Number, Emp_Name} {Emp_Number, Emp_Name} All of the above sets are able to uniquely identify rows of the employee table. Candidate Keys: As I stated above, they are the minimal super keys with no redundant attributes. {Emp_SSN} {Emp_Number} Only these two sets are candidate keys as all other sets are having redundant attributes that are not necessary for unique identification. Foreign key in DBMS BY CHAITANYA SINGH | FILED UNDER: DBMS Definition: Foreign keys are the columns of a table that points to the primary key of another table. They act as a cross-reference between tables.
- 27. For example: In the below example the Stu_Id column in Course_enrollment table is a foreign key as it points to the primary key of the Student table. Course_enrollment table: Course_Id Stu_Id C01 101 C02 102 C03 101 C05 102 C06 103 C07 102 Student table: Stu_Id Stu_Name Stu_Age
- 28. 101 Chaitanya 22 102 Arya 26 103 Bran 25 104 Jon 21 Note: Practically, the foreign key has nothing to do with the primary key tag of another table, if it points to a unique column (not necessarily a primary key) of another table then too, it would be a foreign key. So, a correct definition of foreign key would be: Foreign keys are the columns of a table that points to the candidate key of another table. Candidate Key in DBMS BY CHAITANYA SINGH | FILED UNDER: DBMS A super key with no redundant attribute is known as candidate key. Candidate keys are selected from the set of super keys, the only thing we take care while selecting candidate key is: It should not have any redundant attributes. That’s the reason they are also termed as minimal super key. For example: Emp_Id Emp_Number Emp_Name
- 29. E01 2264 Steve E22 2278 Ajeet E23 2288 Chaitanya E45 2290 Robert There are two candidate keys in above table: {Emp_Id} {Emp_Number} Composite key in DBMS BY CHAITANYA SINGH | FILED UNDER: DBMS A key that consists of more than one attribute to uniquely identify rows (also known as records & tuples) in a table is called composite key. It is also known as compound key. Example: Table – Sales cust_Id order_Id product_code product_count C01 O001 P007 23
- 30. C02 O123 P007 19 C02 O123 P230 82 C01 O001 P890 42 Key in above table: {cust_id, order_id} This is a composite key as it consists of more than one attribute. Alternate key in DBMS BY CHAITANYA SINGH | FILED UNDER: DBMS Out of all candidate keys, only one gets selected as primary key, remaining keys are known as alternative or secondary keys. For example: Consider the below table Emp_Id Emp_Number Emp_Name E01 2264 Steve E22 2278 Ajeet E23 2288 Chaitanya
- 31. E45 2290 Robert There are two candidate keys in above table: {Emp_Id} {Emp_Number} Constraints Every relation has some conditions that must hold for it to be a valid relation. These conditions are called Relational Integrity Constraints. There are three main integrity constraints − Key constraints Domain constraints Referential integrity constraints Primary Key Constraints There must be at least one minimal subset of attributes in the relation, which can identify a tuple uniquely. This minimal subset of attributes is called keyfor that relation. If there are more than one such minimal subsets, these are called candidate keys. Key constraints force that − in a relation with a key attribute, no two tuples can have identical values for key attributes. a key attribute can not have NULL values. Key constraints are also referred to as Entity Constraints. Domain Constraints Attributes have specific values in real-world scenario. For example, age can only be a positive integer. The same constraints have been tried to employ on the attributes of a relation. Every attribute is bound to have a specific range of values. For example, age cannot be less than zero and telephone numbers cannot contain a digit outside 0-9.
- 32. Referential integrity Constraints Referential integrity constraints work on the concept of Foreign Keys. A foreign key is a key attribute of a relation that can be referred in other relation. Referential integrity constraint states that if a relation refers to a key attribute of a different or same relation, then that key element must exist. Relational languages A relational languageisanabstract language whichprovidesthe database userwithan interface throughwhichtheycanspecifydatato be retrievedaccordingtocertainselection criteria.The twomain relational languagesare relational algebraandrelational calculus. Relational Algebra Relational algebra is a procedural query language, which takes instances of relations as input and yields instances of relations as output. It uses operators to perform queries. The fundamental operations of relational algebra are as follows − Select Project Union Set different Cartesian product Rename We will discuss all these operations in the following sections. Select Operation (σ) It selects tuples that satisfy the given predicate from a relation. Notation − σp(r) Where σ stands for selection predicate and r stands for relation. p is prepositional logic formula which may use connectors like and, or, and not. These terms may use relational operators like − =, ≠, ≥, < , >, ≤.
- 33. For example − σsubject = "database"(Books) Output − Selects tuples from books where subject is 'database'. σsubject = "database" and price = "450"(Books) Output − Selects tuples from books where subject is 'database' and 'price' is 450. σsubject = "database" and price = "450" or year > "2010"(Books) Output − Selects tuples from books where subject is 'database' and 'price' is 450 or those books published after 2010. Project Operation (∏) It projects column(s) that satisfy a given predicate. Notation − ∏A1, A2, An (r) Where A1, A2 , An are attribute names of relation r. Duplicate rows are automatically eliminated, as relation is a set. For example − ∏subject, author (Books) Selects and projects columns named as subject and author from the relation Books. Union Operation (∪) It performs binary union between two given relations and is defined as − r ∪ s = { t | t ∈ r or t ∈ s} Notation − r U s Where r and s are either database relations or relation result set (temporary relation). For a union operation to be valid, the following conditions must hold − r, and s must have the same number of attributes. Attribute domains must be compatible. Duplicate tuples are automatically eliminated. ∏ author (Books) ∪ ∏ author (Articles)
- 34. Output − Projects the names of the authors who have either written a book or an article or both. Set Difference (−) The result of set difference operation is tuples, which are present in one relation but are not in the second relation. Notation − r − s Finds all the tuples that are present in r but not in s. ∏ author (Books) − ∏ author (Articles) Output − Provides the name of authors who have written books but not articles. Cartesian Product (Χ) Combines information of two different relations into one. Notation − r Χ s Where r and s are relations and their output will be defined as − r Χ s = { q t | q ∈ r and t ∈ s} σauthor = 'tutorialspoint'(Books Χ Articles) Output − Yields a relation, which shows all the books and articles written by tutorialspoint. Rename Operation (ρ) The results of relational algebra are also relations but without any name. The rename operation allows us to rename the output relation. 'rename' operation is denoted with small Greek letter rho ρ. Notation − ρ x (E) Where the result of expression E is saved with name of x. Additional operations are − Set intersection Assignment Natural join
- 35. Database Joins is a combination of a Cartesian product followed by a selection process. A Join operation pairs two tuples from different relations, if and only if a given join condition is satisfied. We will briefly describe various join types in the following sections. Theta (θ) Join Theta join combines tuples from different relations provided they satisfy the theta condition. The join condition is denoted by the symbol θ. Notation R1 ⋈θ R2 R1 and R2 are relations having attributes (A1, A2, .., An) and (B1, B2,.. ,Bn) such that the attributes don’t have anything in common, that is R1 ∩ R2 = Φ. Theta join can use all kinds of comparison operators. Student SID Name Std 101 Alex 10 102 Maria 11 Subjects Class Subject
- 36. 10 Math 10 English 11 Music 11 Sports Student_Detail − STUDENT ⋈Student.Std = Subject.Class SUBJECT Student_detail SID Name Std Class Subject 101 Alex 10 10 Math 101 Alex 10 10 English 102 Maria 11 11 Music 102 Maria 11 11 Sports Equijoin When Theta join uses only equality comparison operator, it is said to be equijoin. The above example corresponds to equijoin. Natural Join (⋈) Natural join does not use any comparison operator. It does not concatenate the way a Cartesian product does. We can perform a Natural Join only if there is at least one common attribute that exists between two relations. In addition, the attributes must have the same name and domain.
- 37. Natural join acts on those matching attributes where the values of attributes in both the relations are same. Courses CID Course Dept CS01 Database CS ME01 Mechanics ME EE01 Electronics EE HoD Dept Head CS Alex ME Maya EE Mira Courses ⋈ HoD Dept CID Course Head CS CS01 Database Alex ME ME01 Mechanics Maya EE EE01 Electronics Mira
- 38. Outer Joins Theta Join, Equijoin, and Natural Join are called inner joins. An inner join includes only those tuples with matching attributes and the rest are discarded in the resulting relation. Therefore, we need to use outer joins to include all the tuples from the participating relations in the resulting relation. There are three kinds of outer joins − left outer join, right outer join, and full outer join. Left Outer Join(R S) All the tuples from the Left relation, R, are included in the resulting relation. If there are tuples in R without any matching tuple in the Right relation S, then the S-attributes of the resulting relation are made NULL. Left A B 100 Database 101 Mechanics 102 Electronics Right A B 100 Alex 102 Maya 104 Mira
- 39. Courses HoD A B C D 100 Database 100 Alex 101 Mechanics --- --- 102 Electronics 102 Maya Right Outer Join: ( R S ) All the tuples from the Right relation, S, are included in the resulting relation. If there are tuples in S without any matching tuple in R, then the R-attributes of resulting relation are made NULL. Courses HoD A B C D 100 Database 100 Alex 102 Electronics 102 Maya --- --- 104 Mira Full Outer Join: ( R S) All the tuples from both participating relations are included in the resulting relation. If there are no matching tuples for both relations, their respective unmatched attributes are made NULL. Courses HoD A B C D
- 40. 100 Database 100 Alex 101 Mechanics --- --- 102 Electronics 102 Maya --- --- 104 Mira SQL Overview SQL is Structured Query Language, which is a computer language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data stored in a relational database. SQL is the standard language for Relational Database System. All the Relational Database Management Systems (RDMS) like MySQL, MS Access, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, Postgres and SQL Server use SQL as their standard database language. Advantages of SQL:- Allows users to access data in the relational database management systems. Allows users to describe the data. Allows users to define the data in a database and manipulate that data. Allows to embed within other languages using SQL modules, libraries & pre- compilers. Allows users to create and drop databases and tables. Allows users to create view, stored procedure, functions in a database. Allows users to set permissions on tables, procedures and views. Data Definition Language
- 41. The Data Definition Language (DDL) part of SQL permits database tables to be created or deleted. We can also define indexes (keys), specify links between tables, and impose constraints between database tables. SQL uses the following set of commands to define database schema − CREATE Creates new databases, tables and views from RDBMS. For example − CREATE TABLE User (FirstName TEXT, LastName TEXT, UserID TEXT, Dept TEXT, EmpNo INTEGER, PCType TEXT ); Create database tutorialspoint; Create table article; Create view for_students; DROP Drops commands, views, tables, and databases from RDBMS. For example− Drop object_type object_name; Drop database tutorialspoint; Drop table article; Drop view for_students; ALTER Modifies database schema. ALTER TABLE User ADD COLUMN Internet BOOLEAN; Alter object_type object_name parameters; For example− Alter table article add subject varchar; This command adds an attribute in the relation article with the name subjectof string type. Data Manipulation Language SQL is equipped with data manipulation language (DML). DML modifies the database instance by inserting, updating and deleting its data. DML is responsible for all froms data modification in a database. SQL contains the following set of commands in its DML section −
- 42. SELECT/FROM/WHERE INSERT INTO/VALUES UPDATE/SET/WHERE DELETE FROM/WHERE These basic constructs allow database programmers and users to enter data and information into the database and retrieve efficiently using a number of filter options. SELECT/FROM/WHERE SELECT − This is one of the fundamental query command of SQL. It is similar to the projection operation of relational algebra. It selects the attributes based on the condition described by WHERE clause. FROM − This clause takes a relation name as an argument from which attributes are to be selected/projected. In case more than one relation names are given, this clause corresponds to Cartesian product. WHERE − This clause defines predicate or conditions, which must match in order to qualify the attributes to be projected. For example − Select author_name From book_author Where age > 50; This command will yield the names of authors from the relation book_authorwhose age is greater than 50. INSERT INTO/VALUES This command is used for inserting values into the rows of a table (relation). Syntax− INSERT INTO User (FirstName, LastName, UserID, Dept, EmpNo, PCType) 6 VALUES ("Jim", "Jones", "Jjones","Finance", 9, "DellDimR450"); INSERT INTO table (column1 [, column2, column3 ... ]) VALUES (value1 [, value2, value3 ... ]) Or INSERT INTO table VALUES (value1, [value2, ... ]) For example −
- 43. INSERT INTO tutorialspoint (Author, Subject) VALUES ("anonymous", "computers"); UPDATE/SET/WHERE This command is used for updating or modifying the values of columns in a table (relation). Syntax − UPDATE PayRoll SET Salary=Salary * 1.1; UPDATE User SET Dept="Marketing" WHERE EmpNo=9; UPDATE table_name SET column_name = value [, column_name = value ...] [WHERE condition] For example − UPDATE tutorialspoint SET Author="webmaster" WHERE Author="anonymous"; DELETE/FROM/WHERE This command is used for removing one or more rows from a table (relation). Syntax − DELETE * FROM User 8 WHERE EmpNo=99; DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE condition]; For example − DELETE FROM tutorialspoints WHERE Author="unknown"; DCL - Data Control Language Sr.No. Command & Description 1 GRANT Gives a privilege to user. 2 REVOKE Takes back privileges granted from user.
- 44. SQL Constraints Constraints are the rules enforced on data columns on a table. These are used to limit the type of data that can go into a table. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data in the database. Constraints can either be column level or table level. Column level constraints are applied only to one column whereas, table level constraints are applied to the entire table. 1.NOT NULL Constraint By default, a column can hold NULL values. If you do not want a column to have a NULL value, then you need to define such a constraint on this column specifying that NULL is now not allowed for that column. A NULL is not the same as no data, rather, it represents unknown data. Example For example, the following SQL query creates a new table called CUSTOMERS and adds five columns, three of which, are ID NAME and AGE, In this we specify not to accept NULLs − CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS( ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL, AGE INT NOT NULL, ADDRESS CHAR (25) , SALARY DECIMAL (18, 2), PRIMARY KEY (ID) );
- 45. 2. DEFAULT Constraint The DEFAULT constraint provides a default value to a column when the INSERT INTO statement does not provide a specific value. Example For example, the following SQL creates a new table called CUSTOMERS and adds five columns. Here, the SALARY column is set to 5000.00 by default, so in case the INSERT INTO statement does not provide a value for this column, then by default this column would be set to 5000.00. CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS( ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL, AGE INT NOT NULL, ADDRESS CHAR (25) , SALARY DECIMAL (18, 2) DEFAULT 5000.00, PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); If the CUSTOMERS table has already been created, then to add a DEFAULT constraint to the SALARY column, you would write a query like the one which is shown in the code block . 3. UNIQUE Constraint The UNIQUE Constraint prevents two records from having identical values in a column. In the CUSTOMERS table, for example, you might want to prevent two or more people from having an identical age. Example For example, the following SQL query creates a new table called CUSTOMERS and adds five columns. Here, the AGE column is set to UNIQUE, so that you cannot have two records with the same age. CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS( ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL, AGE INT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
- 46. ADDRESS CHAR (25) , SALARY DECIMAL (18, 2), PRIMARY Key(ID), ; 3. SQL - Primary Key constraints A primary key is a field in a table which uniquely identifies each row/record in a database table. Primary keys must contain unique values. A primary key column cannot have NULL values. A table can have only one primary key, which may consist of single or multiple fields. When multiple fields are used as a primary key, they are called a composite key. If a table has a primary key defined on any field(s), then you cannot have two records having the same value of that field(s). Note − You would use these concepts while creating database tables. Create Primary Key Here is the syntax to define the ID attribute as a primary key in a CUSTOMERS table. CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS( ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL, AGE INT NOT NULL, ADDRESS CHAR (25) , SALARY DECIMAL (18, 2), PRIMARY KEY (ID), }; Foreign Keyconsraints A foreign key is a key used to link two tables together. This is sometimes also called as a referencing key.
- 47. A Foreign Key is a column or a combination of columns whose values match a Primary Key in a different table. The relationship between 2 tables matches the Primary Key in one of the tables with a Foreign Key in the second table. If a table has a primary key defined on any field(s), then you cannot have two records having the same value of that field(s). Example Consider the structure of the following two tables. CUSTOMERS table CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS( ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL, AGE INT NOT NULL, ADDRESS CHAR (25) , SALARY DECIMAL (18, 2), PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); ORDERS table CREATE TABLE ORDERS ( ID INT NOT NULL, DATE DATETIME, CUSTOMER_ID INT references CUSTOMERS(ID), AMOUNT double, PRIMARY KEY (ID) );
- 48. CHECK Constraint The CHECK Constraint enables a condition to check the value being entered into a record. If the condition evaluates to false, the record violates the constraint and isn't entered the table. Example For example, the following program creates a new table called CUSTOMERS and adds five columns. Here, we add a CHECK with AGE column, so that you cannot have any CUSTOMER who is below 18 years. CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS( ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL, AGE INT NOT NULL CHECK (AGE >= 18), ADDRESS CHAR (25) , SALARY DECIMAL (18, 2), PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); Functional Dependency Functional dependency (FD) is a set of constraints between two attributes in a relation. Functional dependency says that if two tuples have same values for attributes A1, A2,..., An, then those two tuples must have to have same values for attributes B1, B2, ..., Bn. Functional dependency is represented by an arrow sign (→) that is, X→Y, where X functionally determines Y. The left-hand side attributes determine the values of attributes on the right-hand side.
- 49. Normalization If a database design is not perfect, it may contain anomalies, which are like a bad dream for any database administrator. Managing a database with anomalies is next to impossible. Update anomalies − If data items are scattered and are not linked to each other properly, then it could lead to strange situations. For example, when we try to update one data item having its copies scattered over several places, a few instances get updated properly while a few others are left with old values. Such instances leave the database in an inconsistent state. Deletion anomalies − We tried to delete a record, but parts of it was left undeleted because of unawareness, the data is also saved somewhere else. Insert anomalies − We tried to insert data in a record that does not exist at all. Normalization of Database Database Normalization is a technique of organizing the data in the database. Normalization is a systematic approach of decomposing tables to eliminate data redundancy(repetition) and undesirable characteristics like Insertion, Update and Deletion Anamolies. It is a multi-step process that puts data into tabular form, removing duplicated data from the relation tables. 1.First Normal form The 1st Normal form expects you to design your table in such a way that it can easily be extended and it is easier for you to retrieve data from it whenever required. If tables in a database are not even in the 1st Normal Form, it is considered as bad database design. Rules for First Normal Form The first normal form expects you to follow a few simple rules while designing your database, and they are:
- 50. Rule 1: Single Valued Attributes Each column of your table should be single valued which means they should not contain multiple values. We will explain this with help of an example later, let's see the other rules for now. Rule 2: Attribute Domain should not change This is more of a "Common Sense" rule. In each column the values stored must be of the same kind or type. For example: If you have a column dob to save date of births of a set of people, then you cannot or you must not save 'names' of some of them in that column along with 'date of birth' of others in that column. It should hold only 'date of birth' for all the records/rows. Rule 3: Unique name for Attributes/Columns This rule expects that each column in a table should have a unique name. This is to avoid confusion at the time of retrieving data or performing any other operation on the stored data. If one or more columns have same name, then the DBMS system will be left confused. Rule 4: Order doesn't matters This rule says that the order in which you store the data in your table doesn't matter. We re-arrange the relation (table) as below, to convert it to First Normal Form
- 51. 2.Second normal Form (2NF) For a table to be in the Second Normal Form, it must satisfy two conditions: 1. The table should be in the First Normal Form. 2. There should be no Partial Dependency. What is Partial Dependency? Do not worry about it. First let's understand what is Dependency in a table? What is Dependency? Let's take an example of a Student table with columns student_id, name, reg_no(registration number), branch and address(student's home address). student_id name reg_no branch address In this table, student_id is the primary key and will be unique for every row, hence we can use student_id to fetch any row of data from this table Even for a case, where student names are same, if we know the student_id we can easily fetch the correct record. student_id name reg_no branch Address
- 52. 10 Akon 07-WY CSE Kerala 11 Akon 08-WY IT Gujarat Hence we can say a Primary Key for a table is the column or a group of columns(composite key) which can uniquely identify each record in the table. I can ask from branch name of student with student_id 10, and I can get it. Similarly, if I ask for name of student with student_id 10 or 11, I will get it. So all I need is student_id and every other column depends on it, or can be fetched using it. This is Dependency and we also call it Functional Dependency. What is Partial Dependency? Now that we know what dependency is, we are in a better state to understand what partial dependency is. For a simple table like Student, a single column like student_id can uniquely identfy all the records in a table. But this is not true all the time. So now let's extend our example to see if more than 1 column together can act as a primary key. Let's create another table for Subject, which will have subject_id and subject_name fields and subject_id will be the primary key. subject_id subject_name 1 Java 2 C++ 3 Php Now we have a Student table with student information and another table Subject for storing subject information. Let's create another table Score, to store the marks obtained by students in the respective subjects. We will also be saving name of the teacher who teaches that subject along with marks.
- 53. score_id student_id subject_id marks Teacher 1 10 1 70 Java Teacher 2 10 2 75 C++ Teacher 3 11 1 80 Java Teacher In the score table we are saving the student_id to know which student's marks are these and subject_id to know for which subject the marks are for. Together, student_id + subject_id forms a Candidate Key(learn about Database Keys) for this table, which can be the Primary key. Confused, How this combination can be a primary key? See, if I ask you to get me marks of student with student_id 10, can you get it from this table? No, because you don't know for which subject. And if I give you subject_id, you would not know for which student. Hence we need student_id + subject_id to uniquely identify any row. But where is Partial Dependency? Now if you look at the Score table, we have a column names teacher which is only dependent on the subject, for Java it's Java Teacher and for C++ it's C++ Teacher & so on. Now as we just discussed that the primary key for this table is a composition of two columns which is student_id & subject_id but the teacher's name only depends on subject, hence the subject_id, and has nothing to do with student_id. This is Partial Dependency, where an attribute in a table depends on only a part of the primary key and not on the whole key. How to remove Partial Dependency? There can be many different solutions for this, but out objective is to remove teacher's name from Score table. The simplest solution is to remove columns teacher from Score table and add it to the Subject table. Hence, the Subject table will become: subject_id subject_name Teacher
- 54. 1 Java Java Teacher 2 C++ C++ Teacher 3 Php Php Teacher And our Score table is now in the second normal form, with no partial dependency. score_id student_id subject_id Marks 1 10 1 70 2 10 2 75 3 11 1 80 Quick Recap 1. For a table to be in the Second Normal form, it should be in the First Normal form and it should not have Partial Dependency. 2. Partial Dependency exists, when for a composite primary key, any attribute in the table depends only on a part of the primary key and not on the complete primary key. 3. To remove Partial dependency, we can divide the table, remove the attribute which is causing partial dependency, and move it to some other table where it fits in well. 3.Third Normal Form(3NF) In our last tutorial, we learned about the second normal form and even normalized our Score table into the 2nd Normal Form. So let's use the same example, where we have 3 tables, Student, Subject and Score.
- 55. Student Table student_id name reg_no branch Address 10 Akon 07-WY CSE Kerala 11 Akon 08-WY IT Gujarat 12 Bkon 09-WY IT Rajasthan Subject Table subject_id subject_name Teacher 1 Java Java Teacher 2 C++ C++ Teacher 3 Php Php Teacher Score Table score_id student_id subject_id Marks 1 10 1 70 2 10 2 75 3 11 1 80 In the Score table, we need to store some more information, which is the exam name and total marks, so let's add 2 more columns to the Score table.
- 56. score_id student_id subject_id marks exam_name total_marks Requirements for Third Normal Form For a table to be in the third normal form, 1. It should be in the Second Normal form. 2. And it should not have Transitive Dependency. What is Transitive Dependency? With exam_name and total_marks added to our Score table, it saves more data now. Primary key for our Score table is a composite key, which means it's made up of two attributes or columns → student_id + subject_id. Our new column exam_name depends on both student and subject. For example, a mechanical engineering student will have Workshop exam but a computer science student won't. And for some subjects you have Prctical exams and for some you don't. So we can say that exam_name is dependent on both student_id and subject_id. And what about our second new column total_marks? Does it depend on our Score table's primary key? Well, the column total_marks depends on exam_name as with exam type the total score changes. For example, practicals are of less marks while theory exams are of more marks. But, exam_name is just another column in the score table. It is not a primary key or even a part of the primary key, and total_marks depends on it. This is Transitive Dependency. When a non-prime attribute depends on other non- prime attributes rather than depending upon the prime attributes or primary key. How to remove Transitive Dependency? Again the solution is very simple. Take out the columns exam_name and total_marks from Score table and put them in an Exam table and use the exam_id wherever required.
- 57. Score Table: In 3rd Normal Form score_id student_id subject_id marks exam_id The new Exam table exam_id exam_name total_marks 1 Workshop 200 2 Mains 70 3 Practicals 30 Advantage of removing Transitive Dependency The advantage of removing transitive dependency is, Amount of data duplication is reduced. Data integrity achieved. Boyce Codd normal form (BCNF) It is an advance version of 3NF that’s why it is also referred as 3.5NF. BCNF is stricter than 3NF. A table complies with BCNF if it is in 3NF and for every functional dependency X->Y, X should be the super key of the table. Example: Suppose there is a company wherein employees work in more than one department. They store the data like this:
- 58. emp_id emp_nationality emp_dept dept_type dept_no_of_emp 1001 Austrian Production and planning D001 200 1001 Austrian stores D001 250 1002 American design and technical support D134 100 1002 American Purchasing department D134 600 Functional dependencies in the table above: emp_id -> emp_nationality emp_dept -> {dept_type, dept_no_of_emp} Candidate key: {emp_id, emp_dept} The table is not in BCNF as neither emp_id nor emp_dept alone are keys. To make the table comply with BCNF we can break the table in three tables like this: emp_nationality table: emp_id emp_nationality 1001 Austrian
- 59. 1002 American emp_dept table: emp_dept dept_type dept_no_of_emp Production and planning D001 200 stores D001 250 design and technical support D134 100 Purchasing department D134 600 emp_dept_mapping table: emp_id emp_dept 1001 Production and planning
- 60. 1001 Stores 1002 design and technical support 1002 Purchasing department Functional dependencies: emp_id -> emp_nationality emp_dept -> {dept_type, dept_no_of_emp} Candidate keys: For first table: emp_id For second table: emp_dept For third table: {emp_id, emp_dept} This is now in BCNF as in both the functional dependencies left side part is a key. Transaction Processing A transaction can be defined as a group of tasks. A single task is the minimum processing unit which cannot be divided further. Let’s take an example of a simple transaction. Suppose a bank employee transfers Rs 500 from A's account to B's account. This very simple and small transaction involves several low-level tasks. A’s Account Open_Account(A) Old_Balance = A.balance New_Balance = Old_Balance - 500 A.balance = New_Balance Close_Account(A)
- 61. B’s Account Open_Account(B) Old_Balance = B.balance New_Balance = Old_Balance + 500 B.balance = New_Balance Close_Account(B) ACID Properties A transaction is a very small unit of a program and it may contain several lowlevel tasks. A transaction in a database system must maintain Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability − commonly known as ACID properties − in order to ensure accuracy, completeness, and data integrity. Atomicity − This property states that a transaction must be treated as an atomic unit, that is, either all of its operations are executed or none. There must be no state in a database where a transaction is left partially completed. States should be defined either before the execution of the transaction or after the execution/abortion/failure of the transaction. Consistency − The database must remain in a consistent state after any transaction. No transaction should have any adverse effect on the data residing in the database. If the database was in a consistent state before the execution of a transaction, it must remain consistent after the execution of the transaction as well. Durability − The database should be durable enough to hold all its latest updates even if the system fails or restarts. If a transaction updates a chunk of data in a database and commits, then the database will hold the modified data. If a transaction commits but the system fails before the data could be written on to the disk, then that data will be updated once the system springs back into action. Isolation − In a database system where more than one transaction are being executed simultaneously and in parallel, the property of isolation states that all the transactions will be carried out and executed as if it is the only transaction in the system. No transaction will affect the existence of any other transaction. Serializability When multiple transactions are being executed by the operating system in a multiprogramming environment, there are possibilities that
- 62. instructions of one transactions are interleaved with some other transaction. Schedule − A chronological execution sequence of a transaction is called a schedule. A schedule can have many transactions in it, each comprising of a number of instructions/tasks. Serial Schedule − It is a schedule in which transactions are aligned in such a way that one transaction is executed first. When the first transaction completes its cycle, then the next transaction is executed. Transactions are ordered one after the other. This type of schedule is called a serial schedule, as transactions are executed in a serial manner. In a multi-transaction environment, serial schedules are considered as a benchmark. The execution sequence of an instruction in a transaction cannot be changed, but two transactions can have their instructions executed in a random fashion. This execution does no harm if two transactions are mutually independent and working on different segments of data; but in case these two transactions are working on the same data, then the results may vary. This ever-varying result may bring the database to an inconsistent state. To resolve this problem, we allow parallel execution of a transaction schedule, if its transactions are either serializable or have some equivalence relation among them. States of Transactions A transaction in a database can be in one of the following states −
- 63. Active − In this state, the transaction is being executed. This is the initial state of every transaction. Partially Committed − When a transaction executes its final operation, it is said to be in a partially committed state. Failed − A transaction is said to be in a failed state if any of the checks made by the database recovery system fails. A failed transaction can no longer proceed further. Aborted − If any of the checks fails and the transaction has reached a failed state, then the recovery manager rolls back all its write operations on the database to bring the database back to its original state where it was prior to the execution of the transaction. Transactions in this state are called aborted. The database recovery module can select one of the two operations after a transaction aborts − o Re-start the transaction o Kill the transaction Committed − If a transaction executes all its operations successfully, it is said to be committed. All its effects are now permanently established on the database system. Concurrency Control In a multiprogramming environment where multiple transactions can be executed simultaneously, it is highly important to control the concurrency of transactions. We have concurrency control protocols to ensure atomicity, isolation, and serializability of concurrent transactions. Concurrency control protocols can be broadly divided into two categories − Lock based protocols Time stamp based protocols Lock-based Protocols Database systems equipped with lock-based protocols use a mechanism by which any transaction cannot read or write data until it acquires an appropriate lock on it. Locks are of two kinds −
- 64. Binary Locks − A lock on a data item can be in two states; it is either locked or unlocked. Shared/exclusive − This type of locking mechanism differentiates the locks based on their uses. If a lock is acquired on a data item to perform a write operation, it is an exclusive lock. Allowing more than one transaction to write on the same data item would lead the database into an inconsistent state. Read locks are shared because no data value is being changed. There are four types of lock protocols available − Simplistic Lock Protocol Simplistic lock-based protocols allow transactions to obtain a lock on every object before a 'write' operation is performed. Transactions may unlock the data item after completing the ‘write’ operation. Pre-claiming Lock Protocol Pre-claiming protocols evaluate their operations and create a list of data items on which they need locks. Before initiating an execution, the transaction requests the system for all the locks it needs beforehand. If all the locks are granted, the transaction executes and releases all the locks when all its operations are over. If all the locks are not granted, the transaction rolls back and waits until all the locks are granted. Two-Phase Locking 2PL This locking protocol divides the execution phase of a transaction into three parts. In the first part, when the transaction starts executing, it seeks permission for the locks it requires. The second part is where the transaction acquires all the locks. As soon as the transaction releases its first lock, the third phase starts. In this phase, the transaction cannot demand any new locks; it only releases the acquired locks.
- 65. Two-phase locking has two phases, one is growing, where all the locks are being acquired by th1e transaction; and the second phase is shrinking, where the locks held by the transaction are being released. To claim an exclusive (write) lock, a transaction must first acquire a shared (read) lock and then upgrade it to an exclusive lock. Strict Two-Phase Locking The first phase of Strict-2PL is same as 2PL. After acquiring all the locks in the first phase, the transaction continues to execute normally. But in contrast to 2PL, Strict-2PL does not release a lock after using it. Strict- 2PL holds all the locks until the commit point and releases all the locks at a time. Strict-2PL does not have cascading abort as 2PL does. Timestamp-based Protocols The most commonly used concurrency protocol is the timestamp based protocol. This protocol uses either system time or logical counter as a timestamp. Lock-based protocols manage the order between the conflicting pairs among transactions at the time of execution, whereas timestamp-based protocols start working as soon as a transaction is created.
- 66. Every transaction has a timestamp associated with it, and the ordering is determined by the age of the transaction. A transaction created at 0002 clock time would be older than all other transactions that come after it. For example, any transaction 'y' entering the system at 0004 is two seconds younger and the priority would be given to the older one. In addition, every data item is given the latest read and write- timestamp. This lets the system know when the last ‘read and write’ operation was performed on the data item. Timestamp Ordering Protocol The timestamp-ordering protocol ensures serializability among transactions in their conflicting read and write operations. This is the responsibility of the protocol system that the conflicting pair of tasks should be executed according to the timestamp values of the transactions. The timestamp of transaction Ti is denoted as TS(Ti). Read time-stamp of data-item X is denoted by R-timestamp(X). Write time-stamp of data-item X is denoted by W-timestamp(X). Timestamp ordering protocol works as follows − If a transaction Ti issues a read(X) operation − o If TS(Ti) < W-timestamp(X) Operation rejected. o If TS(Ti) >= W-timestamp(X) Operation executed. o All data-item timestamps updated. If a transaction Ti issues a write(X) operation − o If TS(Ti) < R-timestamp(X) Operation rejected. o If TS(Ti) < W-timestamp(X) Operation rejected and Ti rolled back. o Otherwise, operation executed.
- 67. Thomas' Write Rule This rule states if TS(Ti) < W-timestamp(X), then the operation is rejected and Ti is rolled back. Time-stamp ordering rules can be modified to make the schedule view serializable. Instead of making Ti rolled back, the 'write' operation itself . Deadlock In a multi-process system, deadlock is an unwanted situation that arises in a shared resource environment, where a process indefinitely waits for a resource that is held by another process. For example, assume a set of transactions {T0, T1, T2, ...,Tn}. T0 needs a resource X to complete its task. Resource X is held by T1, and T1 is waiting for a resource Y, which is held by T2. T2 is waiting for resource Z, which is held by T0. Thus, all the processes wait for each other to release resources. In this situation, none of the processes can finish their task. This situation is known as a deadlock. Deadlocks are not healthy for a system. In case a system is stuck in a deadlock, the transactions involved in the deadlock are either rolled back or restarted. Deadlock Prevention To prevent any deadlock situation in the system, the DBMS aggressively inspects all the operations, where transactions are about to execute. The DBMS inspects the operations and analyzes if they can create a deadlock situation. If it finds that a deadlock situation might occur, then that transaction is never allowed to be executed. There are deadlock prevention schemes that use timestamp ordering mechanism of transactions in order to predetermine a deadlock situation. Wait-Die Scheme In this scheme, if a transaction requests to lock a resource (data item), which is already held with a conflicting lock by another transaction, then one of the two possibilities may occur −
- 68. If TS(Ti) < TS(Tj) − that is Ti, which is requesting a conflicting lock, is older than Tj − then Ti is allowed to wait until the data-item is available. If TS(Ti) > TS(tj) − that is Ti is younger than Tj − then Ti dies. Ti is restarted later with a random delay but with the same timestamp. This scheme allows the older transaction to wait but kills the younger one. Wound-Wait Scheme In this scheme, if a transaction requests to lock a resource (data item), which is already held with conflicting lock by some another transaction, one of the two possibilities may occur − If TS(Ti) < TS(Tj), then Ti forces Tj to be rolled back − that is Tiwounds Tj. Tj is restarted later with a random delay but with the same timestamp. If TS(Ti) > TS(Tj), then Ti is forced to wait until the resource is available. This scheme, allows the younger transaction to wait; but when an older transaction requests an item held by a younger one, the older transaction forces the younger one to abort and release the item. In both the cases, the transaction that enters the system at a later stage is aborted. Deadlock Avoidance Aborting a transaction is not always a practical approach. Instead, deadlock avoidance mechanisms can be used to detect any deadlock situation in advance. Methods like "wait-for graph" are available but they are suitable for only those systems where transactions are lightweight having fewer instances of resource. In a bulky system, deadlock prevention techniques may work well. Wait-for Graph This is a simple method available to track if any deadlock situation may arise. For each transaction entering into the system, a node is created. When a transaction Ti requests for a lock on an item, say X, which is held by some other transaction Tj, a directed edge is created from Ti to Tj. If Tj releases item X, the edge between them is dropped and Ti locks the data item.
- 69. The system maintains this wait-for graph for every transaction waiting for some data items held by others. The system keeps checking if there's any cycle in the graph. Here, we can use any of the two following approaches − First, do not allow any request for an item, which is already locked by another transaction. This is not always feasible and may cause starvation, where a transaction indefinitely waits for a data item and can never acquire it. The second option is to roll back one of the transactions. It is not always feasible to roll back the younger transaction, as it may be important than the older one. With the help of some relative algorithm, a transaction is chosen, which is to be aborted. This transaction is known as the victim and the process is known as victim selection. DBMS - Data Recovery Recovery DBMS is a highly complex system with hundreds of transactions being executed every second. The durability and robustness of a DBMS depends on its complex architecture and its underlying hardware and system software. If it fails or crashes amid transactions, it is expected that the system would follow some sort of algorithm or techniques to recover lost data.
- 70. Failure Classification To see where the problem has occurred, we generalize a failure into various categories, as follows − Transaction failure A transaction has to abort when it fails to execute or when it reaches a point from where it can’t go any further. This is called transaction failure where only a few transactions or processes are hurt. Reasons for a transaction failure could be − Logical errors − Where a transaction cannot complete because it has some code error or any internal error condition. System errors − Where the database system itself terminates an active transaction because the DBMS is not able to execute it, or it has to stop because of some system condition. For example, in case of deadlock or resource unavailability, the system aborts an active transaction. System Crash There are problems − external to the system − that may cause the system to stop abruptly and cause the system to crash. For example, interruptions in power supply may cause the failure of underlying hardware or software failure. Examples may include operating system errors. Disk Failure In early days of technology evolution, it was a common problem where hard-disk drives or storage drives used to fail frequently. Disk failures include formation of bad sectors, unreachability to the disk, disk head crash or any other failure, which destroys all or a part of disk storage. Storage Structure We have already described the storage system. In brief, the storage structure can be divided into two categories − Volatile storage − As the name suggests, a volatile storage cannot survive system crashes. Volatile storage devices are placed very close to the CPU; normally they are embedded onto the chipset itself. For example, main
- 71. memory and cache memory are examples of volatile storage. They are fast but can store only a small amount of information. Non-volatile storage − These memories are made to survive system crashes. They are huge in data storage capacity, but slower in accessibility. Examples may include hard-disks, magnetic tapes, flash memory, and non- volatile (battery backed up) RAM. Recovery and Atomicity When a system crashes, it may have several transactions being executed and various files opened for them to modify the data items. Transactions are made of various operations, which are atomic in nature. But according to ACID properties of DBMS, atomicity of transactions as a whole must be maintained, that is, either all the operations are executed or none. When a DBMS recovers from a crash, it should maintain the following − It should check the states of all the transactions, which were being executed. A transaction may be in the middle of some operation; the DBMS must ensure the atomicity of the transaction in this case. It should check whether the transaction can be completed now or it needs to be rolled back. No transactions would be allowed to leave the DBMS in an inconsistent state. There are two types of techniques, which can help a DBMS in recovering as well as maintaining the atomicity of a transaction − Maintaining the logs of each transaction, and writing them onto some stable storage before actually modifying the database. Maintaining shadow paging, where the changes are done on a volatile memory, and later, the actual database is updated. Log-based Recovery Log is a sequence of records, which maintains the records of actions performed by a transaction. It is important that the logs are written prior to the actual modification and stored on a stable storage media, which is failsafe. Log-based recovery works as follows −
- 72. The log file is kept on a stable storage media. When a transaction enters the system and starts execution, it writes a log about it. <Tn, Start> When the transaction modifies an item X, it write logs as follows − <Tn, X, V1, V2> It reads Tn has changed the value of X, from V1 to V2. When the transaction finishes, it logs − <Tn, commit> The database can be modified using two approaches − Deferred database modification − All logs are written on to the stable storage and the database is updated when a transaction commits. Immediate database modification − Each log follows an actual database modification. That is, the database is modified immediately after every operation. Recovery with Concurrent Transactions When more than one transaction are being executed in parallel, the logs are interleaved. At the time of recovery, it would become hard for the recovery system to backtrack all logs, and then start recovering. To ease this situation, most modern DBMS use the concept of 'checkpoints'. Checkpoint Keeping and maintaining logs in real time and in real environment may fill out all the memory space available in the system. As time passes, the log file may grow too big to be handled at all. Checkpoint is a mechanism where all the previous logs are removed from the system and stored permanently in a storage disk. Checkpoint declares a point before which the DBMS was in consistent state, and all the transactions were committed. Recovery When a system with concurrent transactions crashes and recovers, it behaves in the following manner −
- 73. The recovery system reads the logs backwards from the end to the last checkpoint. It maintains two lists, an undo-list and a redo-list. If the recovery system sees a log with <Tn, Start> and <Tn, Commit> or just <Tn, Commit>, it puts the transaction in the redo-list. If the recovery system sees a log with <Tn, Start> but no commit or abort log found, it puts the transaction in undo-list. All the transactions in the undo-list are then undone and their logs are removed. All the transactions in the redo-list and their previous logs are removed and then redone before saving their logs.













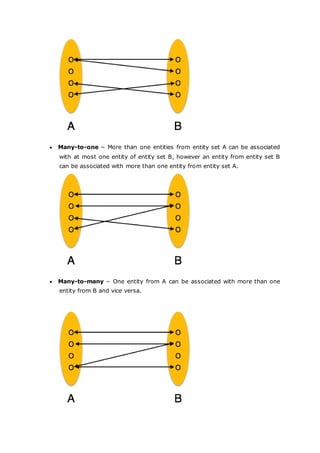




























![ SELECT/FROM/WHERE
INSERT INTO/VALUES
UPDATE/SET/WHERE
DELETE FROM/WHERE
These basic constructs allow database programmers and users to enter
data and information into the database and retrieve efficiently using a
number of filter options.
SELECT/FROM/WHERE
SELECT − This is one of the fundamental query command of SQL. It is
similar to the projection operation of relational algebra. It selects the
attributes based on the condition described by WHERE clause.
FROM − This clause takes a relation name as an argument from which
attributes are to be selected/projected. In case more than one relation
names are given, this clause corresponds to Cartesian product.
WHERE − This clause defines predicate or conditions, which must match in
order to qualify the attributes to be projected.
For example −
Select author_name
From book_author
Where age > 50;
This command will yield the names of authors from the
relation book_authorwhose age is greater than 50.
INSERT INTO/VALUES
This command is used for inserting values into the rows of a table
(relation).
Syntax−
INSERT INTO User (FirstName, LastName, UserID, Dept, EmpNo, PCType) 6 VALUES
("Jim", "Jones", "Jjones","Finance", 9, "DellDimR450");
INSERT INTO table (column1 [, column2, column3 ... ]) VALUES (value1 [, value2, value3 ...
])
Or
INSERT INTO table VALUES (value1, [value2, ... ])
For example −](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databasemanagementsystembygursharansingh-180608050732/85/Database-management-system-by-Gursharan-singh-42-320.jpg)
![INSERT INTO tutorialspoint (Author, Subject) VALUES ("anonymous", "computers");
UPDATE/SET/WHERE
This command is used for updating or modifying the values of columns in
a table (relation).
Syntax −
UPDATE PayRoll SET Salary=Salary * 1.1;
UPDATE User SET Dept="Marketing" WHERE EmpNo=9;
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = value [, column_name = value ...] [WHERE condition]
For example −
UPDATE tutorialspoint SET Author="webmaster" WHERE Author="anonymous";
DELETE/FROM/WHERE
This command is used for removing one or more rows from a table
(relation).
Syntax −
DELETE * FROM User 8 WHERE EmpNo=99;
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE condition];
For example −
DELETE FROM tutorialspoints
WHERE Author="unknown";
DCL - Data Control Language
Sr.No. Command & Description
1 GRANT
Gives a privilege to user.
2
REVOKE
Takes back privileges granted from user.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databasemanagementsystembygursharansingh-180608050732/85/Database-management-system-by-Gursharan-singh-43-320.jpg)





























