DATATYPES IN JAVA primitive and nonprimitive.pptx
- 1. DATA TYPES IN JAVA By A. AMEER RASHED KHAN, M.Sc., M.Phil., Assistant Processor, Department of Computer Science with Data Science The New College
- 2. In Java, data types define how variables' values are kept in memory. Each variable has a data type that determines the type of value it will store. Types of Data Type Primitive Data Type: such as boolean, char, int, short, byte, long, float, and double Non-Primitive Data Type or Reference Data type: such as String, Array, etc. WHAT IS DATA TYPE?
- 5. PRIMITIVE DATA TYPES Primitive data types are the building blocks of data manipulation in the Java programming language. There are 8 types of primitive data types:
- 6. 1. BOOLEAN TYPE A boolean data type can only store true or false values. They can be used to determine whether two values are equal (basically in conditional statements to return true or false). It is most commonly used as a flag variable to identify true or false conditions. False is the default boolean value. Furthermore, the size of the boolean type is determined by the java virtual machine. Therefore, it fluctuates on different platforms.
- 7. 2. BYTE TYPE It is an 8-bit signed two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between -128 to 127 (inclusive). Its default value is 0. The byte data type is used to save memory in large arrays where the memory savings is most required. It saves space because a byte is 4 times smaller than an integer. It can also be used in place of "int" data type.
- 8. 3. SHORT TYPE The short data type is a 16-bit signed two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between -32,768 to 32,767 (inclusive). Its default value is 0. The short data type can also be used to save memory just like byte data type. A short data type is 2 times smaller than an integer.
- 9. 4. INT TYPE The int data type is a 32-bit signed two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between - 2,147,483,648 (-2^31) to 2,147,483,647 (2^31 -1) (inclusive). Its default value is 0. The int data type is generally used as a default data type for integral values unless if there is no problem about memory.
- 10. 5. LONG TYPE The longest data type among all integer data types is the long (64-bit two’s complement integer). The long data type can store values from -9223372036854775808 (-2^63) to 9223372036854775807 (2^63 -1). This is used when int datatype is insufficient to store the value. Keep in mind that the value should finish with a "L or l".Y
- 11. 6. FLOAT TYPE It is a form of floating-point data that stores values with decimal precision. It isn't used for precise data like currencies or analysis. A Float value is a single-precision 32-bit or 4 bytes IEEE 754 floating-point and have a 7-digit decimal precision. Keep in mind that the value should finish with a "F or f."
- 12. 7. DOUBLE TYPE The double data type resembles the float data type. The difference between the two is that in the case of decimal precision, it double twice the float. It, like float, is used for decimal values and should not be utilized for precise quantities. A double value is a double-precision 64-bit or 8 bytes IEEE 754 floating-point and upto 16- digit decimal precision.
- 13. 8. CHAR TYPE The char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode character and is used to store a single character. It stores both lower case and upper case characters which must be enclosed in single quotes. Its value range is from 'u0000' (or 0) to 'uffff' (or 65,535 inclusive). what is u0000 ? It is because java uses Unicode system not ASCII code system. The u0000 is the lowest range of Unicode system.
- 14. 8. CHAR TYPE The char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode character and is used to store a single character. It stores both lower case and upper case characters which must be enclosed in single quotes. Its value range is from 'u0000' (or 0) to 'uffff' (or 65,535 inclusive). what is u0000 ? It is because java uses Unicode system not ASCII code system. The u0000 is the lowest range of Unicode system.
- 16. NON-PRIMITIVE OR REFERENCE DATA TYPE Non-primitive data types are called reference types because they refer to objects. They are unable to immediately store the value of a variable in memory. They save the variable's memory address. Non-primitive data types, as opposed to primitive data types, are user-defined. They are generated by programmers and can be set to null. All non-primitive data types are of similar size.
- 17. 1. STRINGS Strings are defined as an array of characters. In Java, the distinction between a character array and a string is that a string is intended to retain a sequence of characters in a single variable, but a character array is a collection of individual char type entities. In contrast to C/C++, Java strings do not end with a null character. String literals are enclosed in double-quotes.
- 18. 2. ARRAY An array is a collection of variables with similar types that share a name. Arrays in Java act differently than arrays in C/C++. All arrays in Java are allocated dynamically. Because arrays are objects in Java, we can use member length to determine their length. This is different from C/C++ where we find length using size. A Java array variable can be declared similarly to other variables by adding [] after the data type.
- 19. 2. ARRAY cont. The variables in the array are ordered and each has an index beginning from 0. A static field, a local variable, or a method parameter can all be utilized with a Java array. The length of an array must be provided by an int number and not long or short. The immediate superclass of an array type is Object.
- 20. 3. CLASS A class is a data type that is defined by the user and from which objects are formed. Class are similar to object constructors in that they allow you to create objects. A group of objects is referred to as a class. Logic quantities are said to be classes. Classes do not take up any memory space. A class is sometimes known as an object's template. Fields, methods, and constructors are examples of class members. Both static and instance initializers exist in a class.
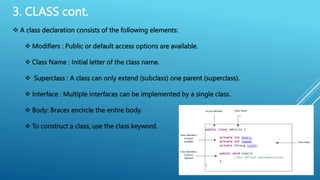
- 21. 3. CLASS cont. A class declaration consists of the following elements: Modifiers : Public or default access options are available. Class Name : Initial letter of the class name. Superclass : A class can only extend (subclass) one parent (superclass). Interface : Multiple interfaces can be implemented by a single class. Body: Braces encircle the entire body. To construct a class, use the class keyword.
- 22. 4. INTERFACES An interface can have variables and methods, much like a class, but by default, the methods declared in an interface are abstract (only method signature, no body). Interfaces define what a class must perform rather than how it must do it. It is the blueprint of the class. a lot of the time in the world (). As a result, it provides a set of methods that the class must implement. If a class implements an interface but does not include method bodies for all of the interface's functions, the class must be designated abstract.
- 23. 5. ENUM An enum is a type of "class" that represents a collection of constants (unchangeable variables, like final variables). Use the enum keyword (rather than class or interface) to build an enum, then separate the constants with a comma. It should be noted that they should be written in capital letters.
- 24. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PRIMITIVE AND NON-PRIMITIVE DATA TYPES The main difference between primitive and non-primitive data types are: In Java, primitive types are predefined (predefined). Non-primitive types are specified by the programmer rather than by Java (except for String). Non-primitive types can invoke methods that execute specific actions, whereas primitive types cannot. Non-primitive types can be null, whereas primitive types always have a value. Non-primitive types begin with an uppercase letter, whereas primitive types begin with a lowercase letter. A primitive type's size is determined by the data type, whereas non-primitive types all have the same size.
- 25. THANK YOU

















![2. ARRAY
An array is a collection of variables with similar types that share a name. Arrays in Java act
differently than arrays in C/C++.
All arrays in Java are allocated dynamically.
Because arrays are objects in Java, we can use member length to determine their length. This
is different from C/C++ where we find length using size.
A Java array variable can be declared similarly to other variables by adding [] after the data
type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinjava-240704172245-5ae732fa/85/DATATYPES-IN-JAVA-primitive-and-nonprimitive-pptx-18-320.jpg)