Design Guidelines and Principles - Lecture 7 - Information Visualisation (4019538FNR)
- 1. 2 December 2005 Information Visualisation Design Guidelines and Principles Prof. Beat Signer Department of Computer Science Vrije Universiteit Brussel beatsigner.com
- 2. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 2 March 25, 2021 Guidelines ▪ No Unjustified 3D ▪ Power of the Plane ▪ Disparity of Depth ▪ Occlusion Hides Information ▪ Perspective Distortion Dangers ▪ Tilted Text is Not Legible ▪ No Unjustified 2D ▪ Eyes Beat Memory ▪ Resolution Over Immersion ▪ Overview First, Zoom and Filter, Details on Demand ▪ Responsiveness is Required
- 3. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 3 March 25, 2021 Guidelines … ▪ Get it Right in Black and White ▪ Function First, Form Next
- 4. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 4 March 25, 2021 No Unjustified 3D ▪ 3D visualisation easily justified for tasks involving shape understanding of inherently three-dimensional structures ▪ frequently for inherently spatial data ▪ in this case benefits of 3D visualisation outweigh the costs ▪ Depth cues (e.g. occlusion, perspective distortion or shadows and lighting) come with some costs ▪ e.g. legibility of text might be affected ▪ justify whether benefits of depth information outweigh the costs ▪ Power of the Plane ▪ perceived importance of items ordered on a plane probably domi- nated by reading conventions (e.g. left to right and top to bottom)
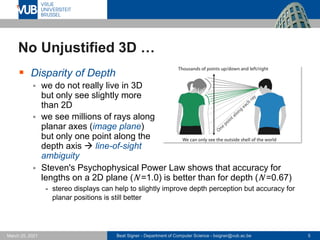
- 5. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 5 March 25, 2021 No Unjustified 3D … ▪ Disparity of Depth ▪ we do not really live in 3D but only see slightly more than 2D ▪ we see millions of rays along planar axes (image plane) but only one point along the depth axis → line-of-sight ambiguity ▪ Steven's Psychophysical Power Law shows that accuracy for lengths on a 2D plane (N =1.0) is better than for depth (N =0.67) - stereo displays can help to slightly improve depth perception but accuracy for planar positions is still better
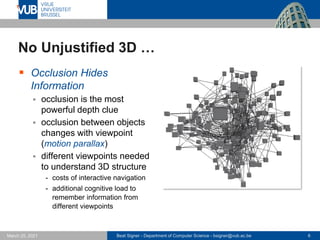
- 6. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 6 March 25, 2021 No Unjustified 3D … ▪ Occlusion Hides Information ▪ occlusion is the most powerful depth clue ▪ occlusion between objects changes with viewpoint (motion parallax) ▪ different viewpoints needed to understand 3D structure - costs of interactive navigation - additional cognitive load to remember information from different viewpoints
- 7. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 7 March 25, 2021 No Unjustified 3D … ▪ Perspective Distortion Dangers ▪ perspective distortion (fore- shortening) affects objects - objects appear smaller and change their position on the image plane ▪ bad thing for the visual encoding of abstract data - power of the plane is lost - e.g. more difficult to judge bar heights in 3D bar chart
- 8. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 8 March 25, 2021 No Unjustified 3D … ▪ Depth cues of shadows and surface shading ▪ adds visual clutter when visualising abstract data ▪ shading interferes with colour channels ▪ shadows might be mistaken for true marks ▪ Tilted Text is Not Legible ▪ fonts have been designed for optimal readability on 2D displays ▪ tilted text becomes blocky and jaggy (less readable) ▪ high-resolution displays and careful rendering might improve the legibility in the future
- 9. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 9 March 25, 2021 3D Visualisation for Shape Perception ▪ Benefits for understanding 3D geometric structures ▪ supports mental model via interactive navigation controls ▪ e.g. object structure easier to understand from 3D visuali- sation than 2D blueprints - but 2D blueprints better to determine the size of elements ▪ 3D outperforms 2D for shape understanding tasks - medical imagining datasets of human body - fluids flows - molecular cell interactions - …
- 10. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 10 March 25, 2021 Cluster-Calendar Time-Series Vis
- 11. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 11 March 25, 2021 Cluster-Calendar Time-Series Vis …
- 12. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 12 March 25, 2021 Layer-oriented Time Series Vis
- 13. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 13 March 25, 2021 Empirical Evidence of 3D vs. 2D ▪ Not always easy to prove the effect of using 3D infovis ▪ e.g. original claim of 3D benefits in 3D Data Mountain ▪ later shown that 2D Data Mountain has similar performance
- 14. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 14 March 25, 2021 No Unjustified 2D ▪ Laying out data in 2D space should also be justified compared to simply showing data with a 1D list ▪ information density (e.g. number of labels) is higher in lists ▪ ordered lists are excellent for lookup tasks ▪ Benefits of explicitly showing relationships outweigh the costs of required space when a task requires the understanding of the topological structure of a network ▪ Some tasks might be handled well by 1D lists even if the original data has a network structure
- 15. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 15 March 25, 2021 Eyes Beat Memory ▪ Cognitive load to switch between different views that are visible simultaneously is much lower than comparing to a memorised previous view ▪ Memory and Attention ▪ limited capacity of short-term memory (working memory) - cognitive load and failure to absorb all presented information if limit is reached ▪ limited human attention - e.g. conscious search for items gets more difficult for increasing number of items ▪ Animation versus Side-by-Side Views ▪ some animation-based idioms impose significant cognitive load ▪ animation powerful for transitions between dataset configurations - helps to maintain context
- 16. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 16 March 25, 2021 Eyes Beat Memory … ▪ Change Blindness ▪ we fail to notice even major changes if our attention is directed elsewhere ▪ makes it difficult to track complex changes across multiframe animations
- 17. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 17 March 25, 2021 Video: Change Blindness
- 18. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 18 March 25, 2021 Resolution Over Immersion ▪ Trade-off between the number of available pixels (resolution) and the level of immersion (feeling of presence in virtual reality) ▪ available number of pixels is most critical constraint in vis design - extremely rare that immersion is worth the cost in resolution ▪ Another issue of immersive environments (e.g. via head- mounted displays) is its special-purpose setting ▪ not integrated with a user's typical computer-based workflow ▪ no support for task switching between vis and other applications ▪ Immersive environments might be helpful for shape understanding tasks as described earlier
- 19. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 19 March 25, 2021 Overview First, Zoom and Filter, Details on Demand ▪ Ben Shneiderman's Visual Information-Seeking Mantra ▪ overview and need to see details ▪ role of data reduction and navigation ▪ Overview has the goal to summarise ▪ shows all items of a dataset simultaneously ▪ helps to find regions that should be further investigated ▪ often shown at the beginning of an exploration process ▪ Overview construction ▪ geometric zooming might not be sufficient - number of marks might become larger than the number of available pixels ▪ number of marks might be reduced via aggregation - similar to semantic zooming
- 20. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 20 March 25, 2021 Overview First, Zoom and Filter, Details on Demand … ▪ Detail view might pop up in response to a select action but detail view might also be permanently visible side-by- side with an overview
- 21. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 21 March 25, 2021 Responsiveness is Required ▪ Visual Feedback ▪ user should get feedback that an action has been completed - e.g. highlighting of a selected item ▪ when navigating, the feedback is normally represented by the new frame that is drawn based on a new viewpoint ▪ visual feedback should typically take place within one second (immediate response) ▪ if an action takes significantly longer than what the user might expect, some progress indicator should be shown
- 22. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 22 March 25, 2021 Responsiveness is Required … ▪ Latency and Interaction Design ▪ different implementations of the operation to see more details for an item - clicking on the item (slowest) - hovering over the item for some short period of dwell time - hovering over the item without dwell time (fastest) ▪ different mechanisms for visual feedback (details) - fixed detail pane at the side of the screen (eyes have to be moved) - popup window at the current cursor location (potential occlusion) - visual highlight directly in the view (e.g. highlighting neighbours in graph) ▪ Interactivity Costs ▪ interaction requires human time and attention - trade-off between finding automatable aspects and relying on the human in the loop to detect patterns
- 23. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 23 March 25, 2021 Get it Right in Black and White ▪ Design guideline for effective use of colour by Maureen Stone ▪ ensure that the most crucial aspects of the visual representation are even legible in black and white - suggests using the luminance channel for the most important attribute
- 24. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 24 March 25, 2021 Function First, Form Next ▪ Focus should be on the function first ▪ form can be refined for an effective but originally "ugly" design ▪ beautiful but ineffective design cannot be refined ▪ However, visual beauty does matter! ▪ given two equally effective systems, users prefer the more beautiful design
- 25. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 25 March 25, 2021 Exercise 6 ▪ Analysis and Validation
- 26. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 26 March 25, 2021 Further Reading ▪ This lecture is mainly based on the book Visualization Analysis & Design ▪ chapter 6 - Rules of Thumb
- 27. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 27 March 25, 2021 References ▪ Visualization Analysis & Design, Tamara Munzner, Taylor & Francis Inc, (Har/Psc edition), May, November 2014, ISBN-13: 978-1466508910 ▪ Video: Change Blindness ▪ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IGQmdoK_ZfY ▪ Ben Shneiderman, The Eyes Have It: A Task by Data Type Taxonomy for Information Visualizations, In Proceedings of VL 1996, IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages ▪ https://doi.org/10.1109/VL.1996.545307
- 28. Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - [email protected] 28 March 25, 2021 References … ▪ A. Cockburn and B. McKenzie, 3D or not 3D?: Evaluating the Effect of the Third Dimension in a Document Management System, Proceedings of CHI 2001 ▪ https://doi.org/10.1145/365024.365309
- 29. 2 December 2005 Next Lecture Visualisation Techniques