Design of input
- 1. SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Whitten Bentley Dittman C H A P T E R 16 INPUT DESIGN AND PROTOTYPING Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 2. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Chapter Sixteen Input Design & Prototyping • Define the appropriate format and media for a computer input. • Explain the difference between data capture, data entry, and data input. • Identify and describe several automatic data collection technologies. • Apply human factors to the design of computer inputs. • Design internal controls for computer inputs. • Select proper screen-based controls for input attributes that are to appear on a GUI input screen. • Design a web-based input interface. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 3. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Chapter Map Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 4. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Data Capture and Data Entry Data capture – the identification and acquisition of new data (at its source). – Source documents – forms used to record business transactions in terms of data that describe those transactions. Data entry – the process of translating the source data or document (above) into a computer readable format. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 5. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Data Processing Data processing is all processing that occurs on the data after it is input from a machine readable form. – In batch processing, the entered data is collected into files called batches and processed as a complete batch. – In on-line processing, the captured data is processed immediately – In remote batch processing, data is entered and edited on-line, but collected into batches for subsequent processing. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 6. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Implementation Methods • Keyboard • Mouse • Touch Screen • Point-of-sale terminals • Sound and speech • Automatic data capture – Optical mark recognition (OMR) • Bar codes – Optical character recognition (OCR) – Magnetic Ink – Electromagnetic transmission – Smart cards – Biometric Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 7. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Taxonomy for Computer Inputs Process Method Data Capture Data Entry Data Processing Keyboard Data is usually captured on a business form that becomes the source document for input. Data can be collected real-time. Data is entered via keyboard. This is the most common input method but also the most prone to errors. OLD: Data can be collected into batch files (disk) for processing as a batch. NEW: Data is processed as soon as it has been keyed. Mouse Same as above. Used in conjunction with keyboard to simplify data entry. Mouse serves as a pointing device for a screen. Same as above, but the use of a mouse is most commonly associated with online and real-time processing. Touch Screen Same as above. Data is entered o a touch screen display or handheld device. Data entry users either touch commands and data choices or enter data using handwriting recognition. On PCs, touch screen choices are processed same as above. On handheld computers, data is sorted on the handheld for later processing as a remote batch. Point of Sale Data is captured as close to the point of sale as humanly possible. No source documents. Data is often entered directly by the customer or by an employee directly interacting with the customer. Data is almost always processed immediately as a transaction or inquiry. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 8. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Taxonomy for Computer Inputs (continued) Process Method Data Capture Data Entry Data Processing Sound Data is captured as close to the source as possible, even when the customer is remotely located. Data is entered using touch-tones (typically from a telephone). Usually requires fairly rigid command menu structure and limited input options. Data is almost always processed immediately as a transaction or inquiry. Speech Same as sound. Data (and commands) is spoken. This technology is not as mature and is much less reliable and common than other techniques. Data is almost always processed immediately as a transaction or inquiry. Optical Mark Data is recorded on optical scan sheets as marks or precisely formed letter, numbers, and punctuation. Eliminates the need for data entry. Data is almost always processed as a batch. Magnetic Ink Data is usually prerecorded on forms that are subsequently completed by the customer. The customer records additional information on the form. A magnetic ink reader reads the magnetized data. The customer-added data must be entered using another input method. Data is almost always processed as a batch. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 9. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Taxonomy for Computer Inputs (concluded) Process Method Data Capture Data Entry Data Processing Electromagnetic Data is recorded directly on the object to be described by data. Data is transmitted by radio frequency. Data is almost always processed immediately. Smart Card Data is recorded directly on a device to be carried by the customer, employee, or other individual that is described by that data. Data is read by smart card readers. Data is almost always processed immediately. Biometric Unique human characteristics become data Data is read by biometric sensors. Primary applications are security and medical monitoring Data is processed immediately. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 10. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Automatic Identification: Bar Codes Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 11. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Design Guidelines • Capture only variable data. – Not data that can be looked up. • Do not capture data that can calculated or stored in computer programs as constants. – Extended Price, Federal Withholding, etc. • Use codes for appropriate attributes. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 12. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Source Document / Form Design Guidelines • Include instructions for completing the form. • Minimize the amount of handwriting. • Data to be entered (keyed) should be sequenced top-to- bottom and left-to-right. • When possible use designs based on known metaphors. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 13. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Good Flow in a Form Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
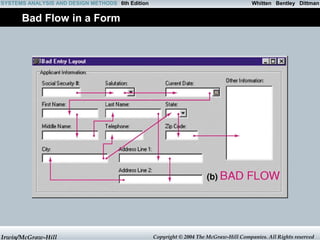
- 14. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Bad Flow in a Form Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 15. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Metaphoric Screen Design • Other useful metaphors include a check, a register, and a calendar. • Pictures of objects can also be metaphors. For example, many Web sites use a picture of each credit card accepted instead of the names. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 16. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Internal Controls for Inputs • The number of inputs should be (to minimize risk of lost transactions). – For batch processing • Use batch control slips (batch no., no. of documents, control totals) • Use one-for-one checks against post-processing detail reports – For on-line systems • Log each transaction as it occurs to a separate audit file • Validate all data – Existence checks – Data-type checks – Domain checks – Combination checks – Self-checking digits – Format checks Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 17. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Repository-Based Prototyping and Development Define properties and constraints for a reusable field Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 18. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Repository-Based Prototyping and Development Define data validation code for a field Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 19. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Common GUI Controls (Windows and Web) 1. Text boxes 2. Radio buttons 3. Check boxes 4. List boxes 5. Drop down lists 6. Combination boxes 7. Spin boxes 8. Buttons Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 20. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Common GUI Controls Uses • Text boxes – When the input data values are unlimited in scope • Radio buttons – When data has limited predefined set of mutually exclusive values • Check boxes – When value set consists of a simple yes or no value • List boxes – When data has a large number of possible values • Drop down lists – When data has large number of possible values and screen space is too limited for a list box • Combination boxes – When need to provide the user with option of selecting a value from a list or typing a value that may or may not appear in the list • Spin boxes – When need to navigate through a small set of choices or directly typing a data value Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 21. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Advanced Controls (mostly Windows interfaces) 1. Drop down calendars 2. Slider edit controls 3. Masked edit controls 4. Ellipsis controls 5. Alternate numerical spinners 6. Check list boxes 7. Check tree boxes Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 22. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Advanced Controls (mostly Windows interfaces) Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 23. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Automated Tools for Input Design and Prototyping • Old Tools – Record Layout Charts – Display Layout Charts • Newer Prototyping Tools – Microsoft Access – CASE Tools – Visual Basic – Excel – Visio Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 24. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Design Process 1. Identify system inputs and review logical requirements. 2. Select appropriate GUI controls. 3. Design, validate and test inputs using some combination of: a) Layout tools (e.g., hand sketches, spacing charts, or CASE tools. b) Prototyping tools (e.g., spreadsheet, PC DBMS, 4GL) 4. As necessary, design source documents. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 25. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman A Logical Data Structure for Input Requirements ORDER = ORDER NUMBER + ORDER DATE + CUSTOMER NUMBER + CUSTOMER NAME + CUSTOMER SHIPPING ADDRESS = ADDRESS > + ( CUSTOMER BILLING ADDRESS = ADDRESS > ) + 1 { PRODUCT NUMBER + QUANTITY ORDERED } n + ( DEFAULT CREDIT CARD NUMBER ) ADDRESS = ( POST OFFICE BOX NUMBER ) + STREET ADDRESS + CITY + STATE + POSTAL ZONE Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 26. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman • It may be useful to walk through this technique for specifying “logical” output requirements. • The red and blue symbols are relational operators, that is, they specify the relationship between attributes to be included in the output in terms of • Sequence + • Selection [ data attributes] • Iteration min { data attributes } max • Optionality ( data attributes) • Many CASE tools support this logical notation. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 27. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Prototype for Video Title Maintenance Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
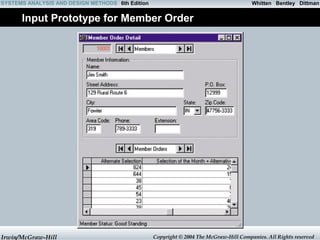
- 28. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Prototype for Member Order Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 29. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Prototype for Member Shopping Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
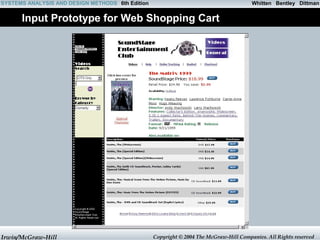
- 30. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Prototype for Web Shopping Cart Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
- 31. Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman Input Prototype for Web Interface Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved
Editor's Notes
- #3: No additional notes.
- #4: No additional notes
- #5: No additional notes.
- #6: No additional notes.
- #7: No additional notes.
- #11: No additional notes.
- #12: No additional notes.
- #13: No additional notes.
- #14: No additional notes.
- #15: No additional notes.
- #17: No additional notes.
- #18: No additional notes.
- #19: No additional notes.
- #20: No additional notes:
- #22: No additional notes:
- #23: No additional notes:
- #25: No additional notes.
- #28: No additional notes.
- #29: No additional notes.
- #30: No additional notes.
- #31: No additional notes.
- #32: No additional notes.
























![Whitten SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN METHODS 6th Edition Bentley Dittman
• It may be useful to walk through this technique for
specifying “logical” output requirements.
• The red and blue symbols are relational operators, that
is, they specify the relationship between attributes to be
included in the output in terms of
• Sequence +
• Selection [ data attributes]
• Iteration min { data attributes } max
• Optionality ( data attributes)
• Many CASE tools support this logical notation.
Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designofinput-140919120321-phpapp01/85/Design-of-input-26-320.jpg)