Discard inport exchange table & tablespace
- 1. Managing data and data archiving using MySQL 5.6 new features of Portable Table-space and EXCHANGE PARTITION Marco “the Grinch” Tusa MySQL Conference Santa Clara 2013
- 2. About Pythian • Recognized Leader: – Global industry-leader in remote database administration services and consulting for Oracle, Oracle Applications, MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server – Work with over 250 multinational companies such as Forbes.com, Fox Sports, Nordion and Western Union to help manage their complex IT deployments • Expertise: – Pythian’s data experts are the elite in their field. We have the highest concentration of Oracle ACEs on staff—9 including 2 ACE Directors—and 2 Microsoft MVPs. – Pythian holds 7 Specializations under Oracle Platinum Partner program, including Oracle Exadata, Oracle GoldenGate & Oracle RAC • Global Reach & Scalability: – Around the clock global remote support for DBA and consulting, systems administration, special projects or emergency response
- 3. About Me Marco “The Grinch” – Former MySQL AB – 2 kids 1 wife – History of religions Ski; Snowboard; scuba diving; Mountain trekking
- 4. Scope This presentation is to illustrate an operative way to manage the partition or tables as file, and how to restore them safely and quickly. Simulate a case where historical data can be needed for future reuse, using simple file restore bypassing the need of reloading the data. Getting a better understanding of what you can really do with DISCARD/IMPORT an EXCHANGE PARTITION.
- 5. My Apology … This Will be A long “slide” ride
- 6. Scenario We have: • MySQL master with information loaded from OLTP system • MySQL Historical Server with serving reporting information We need: • Move Tablespace for a table and import back to a different table • Move a table from a schema to another. • Move out data by day from partition to a table not partitioned. • Import a table to Historical table partitioned.
- 7. Different solutions Portable tablespace is not the only solution Possible solutions 1. Using data export like mysqldump or Load INTO file 2. Single table backup (xtrabackup) 3. ELTP process
- 8. My Motto Use the right tool for the job… keep that in mind after the last slide
- 9. data dictionary • Metadata that keeps track of InnoDB-related objects such as tables, indexes, and table columns. • Check INFORMATION_SCHEMA – INNODB_SYS_TABLES – INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES • Check reference manual at chapter 19.30
- 10. data dictionary| INNODB_LOCKS | | INNODB_TRX | | INNODB_SYS_DATAFILES | | INNODB_LOCK_WAITS | | INNODB_SYS_TABLESTATS | | INNODB_CMP | | INNODB_FT_BEING_DELETED | | INNODB_CMP_RESET | | INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX | | INNODB_CMPMEM_RESET | | INNODB_FT_DELETED | | INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE_LRU | | INNODB_FT_INSERTED | | INNODB_CMPMEM | | INNODB_SYS_INDEXES | | INNODB_SYS_TABLES | | INNODB_SYS_FIELDS | | INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX_RESET | | INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE | ./. ./. | INNODB_FT_DEFAULT_STOPWORD | | INNODB_FT_INDEX_TABLE | | INNODB_FT_INDEX_CACHE | | INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES | | INNODB_METRICS | | INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN_COLS | | INNODB_FT_CONFIG | | INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS | | INNODB_SYS_COLUMNS | | INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN | +---------------------------------------+
- 11. data dictionary (digging) (root@localhost) [information_schema]>select * from INNODB_SYS_TABLES limit 3; +----------+----------------------------+------+--------+-------+-------------+------------+---------------+ | TABLE_ID | NAME | FLAG | N_COLS | SPACE | FILE_FORMAT | ROW_FORMAT | ZIP_PAGE_SIZE | +----------+----------------------------+------+--------+-------+-------------+------------+---------------+ | 14 | SYS_DATAFILES | 0 | 5 | 0 | Antelope | Redundant | 0 | | 11 | SYS_FOREIGN | 0 | 7 | 0 | Antelope | Redundant | 0 | | 12 | SYS_FOREIGN_COLS | 0 | 7 | 0 | Antelope | Redundant | 0 | | 24 | test/tbtest1#P#p001 | 1 | 12 | 10 | Antelope | Compact | 0 | +----------+----------------------------+------+--------+-------+-------------+------------+---------------+ TABLE_ID = Table identifier NAME = Table Name FLAG = If is it is a System Table [0] or User table [1] N_COLS = Self explanatory, Number of columns SPACE = This is the ID of the TABLESPACE
- 12. data dictionary (digging 2) (root@localhost) [information_schema]>select * from INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES where space=0 or space=10 limit 3; +-------+---------------------+------+-------------+----------------------+-----------+---------------+ | SPACE | NAME | FLAG | FILE_FORMAT | ROW_FORMAT | PAGE_SIZE | ZIP_PAGE_SIZE | +-------+---------------------+------+-------------+----------------------+-----------+---------------+ | 10 | test/tbtest1#P#p001 | 0 | Antelope | Compact or Redundant | 16384 | 0 | +-------+---------------------+------+-------------+----------------------+-----------+---------------+ SPACE = TABLESPACE id, this is the one! NAME = Table Name FLAG = If is it is a System Table [0] or User table [1]
- 13. data dictionary (digging 3) +----------------+---------+----------+-------+-----------+---------------------+ | PARTITION_NAME | Data MB | Index MB | SPACE | PAGE_SIZE | Tablespace | +----------------+---------+----------+-------+-----------+---------------------+ | p001 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 10 | 16384 | test/tbtest1#P#p001 | | p002 | 156.71 | 43.20 | 11 | 16384 | test/tbtest1#P#p002 | +----------------+---------+----------+-------+-----------+---------------------+ SELECT PARTITION_NAME,TRUNCATE((DATA_LENGTH/1024)/1024,2) as 'Data MB',TRUNCATE ((INDEX_LENGTH/1024)/1024,2) as 'Index MB', SPACE,PAGE_SIZE, CONCAT (TABLE_SCHEMA,'/',TABLE_NAME,'#P#',PARTITION_NAME) as Tablespace from Partitions join INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES on NAME=CONCAT (TABLE_SCHEMA,'/',TABLE_NAME,'#P#',PARTITION_NAME) where TABLE_NAME='tbtest1' limit 2;
- 14. DISCARD & IMPORT • File per TABLE active (innodb_file_per_table = 1) • Table must be FLUSH and locked for READS • Online DDL can be done while TABLESPACE is discard as for Chapter 5.5.1. “Overview of Online DDL” (not on the discarded table) • Partitions CANNOT be removed directly.
- 15. DISCARD & IMPORT REMEMBER Importing Tablespaces Cost time… and more.
- 16. Exchange Partition what for? Available from MySQL 5.6 over Convert a (sub)Partition to a stand alone Table. Convert a Table without partition to a Partition.
- 17. Exchange Partition limitations • Table MUST have same structure. • If partition has sub partition cannot be move • Table exchange with a partition MUST respect partition data condition. • Table and Partition MUST have same Storage Engine.
- 18. Work Environment System | Dell Inc.; PowerEdge T710; Platform | Linux Release | CentOS release 6.3 (Final) Kernel | 2.6.32-279.1.1.el6.x86_64 Processors | physical = 2, cores = 8, virtual = 16, hyperthreading = yes Speeds | 16x2394.080 Models | 16xIntel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5620 @ 2.40GH /dev/sda1 Part 1 64 518192640 /dev/sda2 Part 64 243069 1998784166400 RAID10
- 19. Hands on First work is to DETACH a Table and IMPORT it to a different table in a different Server. 1/
- 20. Hands on Steps Assuming we already have the table in place: 1. Take the table creation to replicate the structure SHOW CREATE TABLE test.tbtest_child1G 2. Lock the table to copy it FLUSH TABLE test.tbtest_child1 WITH READ LOCK; 3. Copy to the other server the files DON'T forget the .cnf to a backup directory. 4. UNLOCK TABLES; 5. Create a fake table using the create statement stored before 6. Detach the table ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 DISCARD TABLESPACE; 7. MOVE !!! the *.ibd file in a safe place 8. Copy over the previous files from the backup directory 9. CHECK PERMISSION!! 10. Import back the table space ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 IMPORT TABLESPACE; 11. Analyze / check table; 2/
- 21. DISCARD & IMPORT (commands) • FLUSH TABLES test.tbtest_child1 WITH READ LOCK; (root@mysqlt1) [test]>FLUSH TABLES test.tbtest1 WITH READ LOCK; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) • ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 DISCARD TABLESPACE; (root@mysqlt1) [test]>ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 DISCARD TABLESPACE; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) • ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 IMPORT TABLESPACE; (root@mysqlt1) [test]>ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 IMPORT TABLESPACE; Query OK, 0 rows affected (2.04 sec)
- 22. Implementing the steps Create the table on the target and discard the tablespace CREATE TABLE `tbtest_child1` ( `a` int(11) NOT NULL, `bb` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL, `partitionid` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `stroperation` varchar(254) DEFAULT NULL, `time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, PRIMARY KEY (`a`,`bb`), UNIQUE KEY `bb` (`bb`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 (root@mysqlt3) [test]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_child1 DISCARD TABLESPACE; 1/
- 23. Implementing the steps ON TARGET Check the directory, you will only have: -rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 8700 Apr 17 16:56 tbtest_child1.frm ON SOURCE Check the directory and be sure to have these files : -rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 655 Apr 17 14:51 tbtest_child1.cfg -rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 8700 Apr 15 16:44 tbtest_child1.frm -rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 192937984 Apr 16 17:27 tbtest_child1.ibd Copy file from SOURCE to TARGET root@mysqlt1 test]# scp tbtest_child1.* mysql@mysqlt3:/home/mysql/ mysql_instances/instances/mt56master/data/test 2/
- 24. Implementing the steps On Target Import the table space: (root@mysqlt3) [test]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_child1 IMPORT TABLESPACE; Query OK, 0 rows affected (2.34 sec) Check the table as well (root@mysqlt3) [test]>check table tbtest_child1; | Table | Op | Msg_type | Msg_text | | test.tbtest_child1 | check | status | OK | Done: (root@mysqlt3) [test]>select count(*) from tbtest_child1; | count(*) | | 358682 | 3/
- 25. Checking the ids On Source (mysqlt1): >select * from INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES where NAME like '%tbtest_child1%'; | SPACE | NAME | FLAG | FILE_FORMAT | ROW_FORMAT | PAGE_SIZE | ZIP_PAGE_SIZE | | 8 | test/tbtest_child1 | 0 | Antelope | Compact or Redundant | 16384 | 0 | Import same data file to 3 different table On Target (mysqlt3): | SPACE | NAME | FLAG | FILE_FORMAT | ROW_FORMAT | PAGE_SIZE | ZIP_PAGE_SIZE | | 6 | test/tbtest_child1 | 0 | Antelope | Compact or Redundant | 16384 | 0 | | 9 | test2/tbtest_child1 | 0 | Antelope | Compact or Redundant | 16384 | 0 | | 10 | test2/tbtest_child2 | 0 | Antelope | Compact or Redundant | 16384 | 0 |
- 26. Fully portable? • Move to different Schema • Move to different table (same structure different name) • Move to different Server
- 27. Possible usage Implement a daily refresh of a QA environment from Production Slave script to: • Lock relevant tables for READ • Copy tables directly on target or temporary area • Unlock tables • Create tables on Target • Detach dummy tablespace OR the one previously used • Import table space
- 28. What about Locks? What I will do: • Choose a table with few GB • Copy from source mysqlt1 to mysqlt3 • Import table while I have inserts/reads running on different Schema/ tables 1/
- 29. What about Locks? On Source let choose a table more consistent: marco@mysqlt1) [test]>show table status like 'tbtest3'G Name: tbtest3 Engine: InnoDB Data_length: 14676918272 - 13.6GB On Target (mysqlt3): • Running Inserts or Select on a different schema • ALTER IMPORT require “System Lock” • Kill the process will put your dataset in danger 2/
- 30. Check the error log! The import has different phases and when it start is better: InnoDB: Discarding tablespace of table "test"."tbtest3": Data structure corruption InnoDB: Importing tablespace for table 'test/tbtest3' that was exported from host 'mysqlt1' InnoDB: Phase I - Update all pages InnoDB: Sync to disk InnoDB: Sync to disk - done! InnoDB: Phase III - Flush changes to disk InnoDB: Phase IV - Flush complete InnoDB: "test"."tbtest3" autoinc value set to 41727984 Interrupting the process will corrupt the InnoDB dictionary NO ACTION RUNNING WHILE IMPORTING
- 31. How much it costs? Cost change in relation to the machine power • On my own PC : [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_10MB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (3.11 sec) [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_100MB IMPORT TABLESPACE;(10.17 sec) [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_1GB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (8 min 53.98 sec) • On the server: [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_10MB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (1.01 sec) [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_100MB IMPORT TABLESPACE;(3.20 sec) [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_1GB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (1 min 14.31 sec) [test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_15GB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (2 min 30.04 sec) Check Table on 15GB: 55 min 46.35 sec!
- 32. Work with Partitions Use Exchange Partition: • The table use for the exchange cannot use partitions • Data must match the partition condition • No foreign Key or part of Reference • Any AUTO_INCREMENT get reset in the Exchange • Privileges: ALTER; INSERT; CREATE; DROP;
- 33. Exchange Partition How to convert a partition to a Table move the table to another server. Then load data and move it back. 1/
- 34. Exchange Partition We will use the Partition p020 space ID 89 +----------------+---------+----------+-------+-----------+---------------------+ | PARTITION_NAME | Data MB | Index MB | SPACE | PAGE_SIZE | Tablespace | +----------------+---------+----------+-------+-----------+---------------------+ | p001 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 70 | 16384 | test/tbtest2#P#p001 | <snip> | p020 | 138.73 | 40.18 | 89 | 16384 | test/tbtest2#P#p020 | <snip> | p060 | 176.73 | 51.26 | 129 | 16384 | test/tbtest2#P#p060 |+----------------+---------+----------+-------+-----------+---------------------+ 2/
- 35. Exchange Partition Steps are: • Create external table to exchange (if not existing) • ALTER TABLE <name> EXCHANGE PARTITION <Pname> WITH TABLE <T2name>; • Detach/import if it is require • Exchange back • Load data delta back. 3/
- 36. Exchange Partition Check the rows in the table and in the partition: (root@mysqlt1) [test]>select count(*) from tbtest2; | count(*) | | 20863248 | 1 row in set (41.16 sec) (root@mysqlt1) [test]>select count(*) from tbtest2 PARTITION(p020); | count(*) | | 320819 | 1 row in set (1.61 sec) 4/
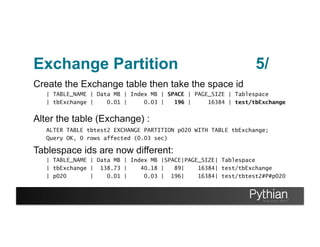
- 37. Exchange Partition Create the Exchange table then take the space id | TABLE_NAME | Data MB | Index MB | SPACE | PAGE_SIZE | Tablespace | tbExchange | 0.01 | 0.03 | 196 | 16384 | test/tbExchange Alter the table (Exchange) : ALTER TABLE tbtest2 EXCHANGE PARTITION p020 WITH TABLE tbExchange; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) Tablespace ids are now different: | TABLE_NAME | Data MB | Index MB |SPACE|PAGE_SIZE| Tablespace | tbExchange | 138.73 | 40.18 | 89| 16384| test/tbExchange | p020 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 196| 16384| test/tbtest2#P#p020 5/
- 38. Moving Partition back Data in the tbExchange table can be read, insert and modify. But must keep Partition definition consistency: >update tbExchange set partitionid="2013-04-21" where autoInc=41683899; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 >select autoInc,partitionid from tbExchange order by autoInc DESC limit 4; | autoInc | partitionid | | 41683901 | 2013-04-20 | | 41683899 | 2013-04-21 |-------- I change this | 41683897 | 2013-04-20 | | 41683895 | 2013-04-20 | 1/
- 39. Moving Partition back I got an error trying to import it back: >ALTER TABLE tbtest2 EXCHANGE PARTITION p020 WITH TABLE tbExchange; ERROR 1737 (HY000): Found a row that does not match the partition We must correct the value or move it to the correct partition BEFORE Exchanging. >update tbExchange set partitionid="2013-04-20" where autoInc=41683899; >ALTER TABLE tbtest2 EXCHANGE PARTITION p020 WITH TABLE tbExchange; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.54 sec) ------- Note the time Exchange an empty table takes 0.03 sec, time increase with dimension. 2/
- 40. Moving Partition back While our tbExchange was a single table, data was inserted in the tbtest2 partition p020: | count(*) | | 2424 | We need to move them back: >insert into tbtest2 select * from tbExchange; Query OK, 2424 rows affected (0.42 sec) Records: 2424 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 >select count(*) from tbtest2 PARTITION(p020); | count(*) | | 323244 | 3/
- 41. Two point to review • Exchange cost – Time – Locks • Auto_Increment values – Main table insert – Exchange table insert
- 42. Exchange cost • Empty Table – While inserting on different table (0.11 sec) – While inserting on the same table (0.36 sec) • Filled table 208M 324860 Rows – While inserting on different table (0.60 sec) – While inserting on the same table (1.11 sec) • Filled table 4.4GB 8447488 Rows – While inserting on different table (42.40 sec) – While inserting on the same table (58.32 sec) If table larger then Bufferpool go out for dinner!
- 43. Locks • The Table is lock with METADATA lock as expected | Id | db | Command | Time | State | Info | 1322 | test | Query | 28 | verifying data with partition | ALTER TABLE tbtest2 EXCHANGE PARTITION p020 WITH TABLE tbExchange2 | | 1345 | test | Query | 27 | Waiting for table metadata lock | insert INTO tbtest2 | 1346 | test | Query | 27 | Waiting for table metadata lock | insert INTO tbtest2
- 44. Auto Increment • We start from an empty table and do Exchange Name: tbtest2 Engine: InnoDB Rows: 21395605 Auto_increment: 44418048 Name: tbExchange1 Engine: InnoDB Rows: 0 Auto_increment: 1 Name: tbtest2 Engine: InnoDB Rows: 19105637 Auto_increment: 44418048 Name: tbExchange1 Engine: InnoDB Rows: 1858477 Auto_increment: 44415912
- 45. Auto Increment… what happened? When partition get Exchanged Increment value is reset to the MAX(AUTO_INCREMENT) tbtest2 (source table) >select max(autoinc) from tbtest2; +--------------+ | max(autoinc) | +--------------+ | 44418023 | +--------------+ tbExchange1(external) >select max(autoinc) from tbExchange1; +--------------+ | max(autoinc) | +--------------+ | 44415913 | +--------------+
- 46. Auto Increment… what happened? If we add records on tbExchange? tbtest2 (source table) | partitionid | autoinc | | 2013-04-28 | 44415915 | | 2013-04-28 | 44415917 | | 2013-04-28 | 44415919 | | 2013-04-28 | 44415921 | NOT GOOD! | 2013-04-28 | 44415923 | | 2013-04-28 | 44415925 | | 2013-04-28 | 44415927 | | 2013-04-25 | 44415929 | | 2013-04-25 | 44415931 | tbExchange1(external) | partitionid | autoinc | | 2013-04-20 | 44415915 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415917 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415919 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415921 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415923 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415925 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415927 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415929 | | 2013-04-20 | 44415931 |
- 47. Auto Increment… what happened? I had no issue because: • The PK was compose by autoinc and partitionid • The number of inserts was lower the table Auto_increment value. `autoInc` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `partitionid` DATE NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`autoInc`,`partitionid`),
- 48. Conclusions Discard / Import : – It is a very invasive operation (system lock) – You must know what you are doing (not for beginners) – Useful to perform refresh (but needs scripting) Exchange: – Easy to use and not too invasive (metalock but fast) – Auto Increment could be an issue (plan your PK)
- 49. Q&A
- 50. Thank you To contact us [email protected] 1-877-PYTHIAN To follow us http://www.pythian.com/blog http://www.facebook.com/pages/The- Pythian-Group/163902527671 @pythian http://www.linkedin.com/company/pythian To contact Me [email protected] [email protected] To follow me http://www.tusacentral.net/ https://www.facebook.com/marco.tusa.94 @marcotusa http://it.linkedin.com/in/marcotusa/











![data dictionary (digging)
(root@localhost) [information_schema]>select * from INNODB_SYS_TABLES limit 3;
+----------+----------------------------+------+--------+-------+-------------+------------+---------------+
| TABLE_ID | NAME | FLAG | N_COLS | SPACE | FILE_FORMAT | ROW_FORMAT | ZIP_PAGE_SIZE |
+----------+----------------------------+------+--------+-------+-------------+------------+---------------+
| 14 | SYS_DATAFILES | 0 | 5 | 0 | Antelope | Redundant | 0 |
| 11 | SYS_FOREIGN | 0 | 7 | 0 | Antelope | Redundant | 0 |
| 12 | SYS_FOREIGN_COLS | 0 | 7 | 0 | Antelope | Redundant | 0 |
| 24 | test/tbtest1#P#p001 | 1 | 12 | 10 | Antelope | Compact | 0 |
+----------+----------------------------+------+--------+-------+-------------+------------+---------------+
TABLE_ID = Table identifier
NAME = Table Name
FLAG = If is it is a System Table [0] or User table [1]
N_COLS = Self explanatory, Number of columns
SPACE = This is the ID of the TABLESPACE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-11-320.jpg)
![data dictionary (digging 2)
(root@localhost) [information_schema]>select * from INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES where space=0 or space=10
limit 3;
+-------+---------------------+------+-------------+----------------------+-----------+---------------+
| SPACE | NAME | FLAG | FILE_FORMAT | ROW_FORMAT | PAGE_SIZE | ZIP_PAGE_SIZE |
+-------+---------------------+------+-------------+----------------------+-----------+---------------+
| 10 | test/tbtest1#P#p001 | 0 | Antelope | Compact or Redundant | 16384 | 0 |
+-------+---------------------+------+-------------+----------------------+-----------+---------------+
SPACE = TABLESPACE id, this is the one!
NAME = Table Name
FLAG = If is it is a System Table [0] or User table [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-12-320.jpg)








![DISCARD & IMPORT (commands)
• FLUSH TABLES test.tbtest_child1 WITH READ LOCK;
(root@mysqlt1) [test]>FLUSH TABLES test.tbtest1 WITH READ LOCK;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
• ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 DISCARD
TABLESPACE;
(root@mysqlt1) [test]>ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 DISCARD TABLESPACE;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
• ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 IMPORT
TABLESPACE;
(root@mysqlt1) [test]>ALTER TABLE test.tbtest_child1 IMPORT TABLESPACE;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (2.04 sec)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-21-320.jpg)
![Implementing the steps
Create the table on the target and discard the tablespace
CREATE TABLE `tbtest_child1` (
`a` int(11) NOT NULL,
`bb` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
`partitionid` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`stroperation` varchar(254) DEFAULT NULL,
`time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`,`bb`),
UNIQUE KEY `bb` (`bb`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
(root@mysqlt3) [test]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_child1 DISCARD TABLESPACE;
1/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-22-320.jpg)
![Implementing the steps
ON TARGET Check the directory, you will only have:
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 8700 Apr 17 16:56 tbtest_child1.frm
ON SOURCE Check the directory and be sure to have these files :
-rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 655 Apr 17 14:51 tbtest_child1.cfg
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 8700 Apr 15 16:44 tbtest_child1.frm
-rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 192937984 Apr 16 17:27 tbtest_child1.ibd
Copy file from SOURCE to TARGET
root@mysqlt1 test]# scp tbtest_child1.* mysql@mysqlt3:/home/mysql/
mysql_instances/instances/mt56master/data/test
2/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-23-320.jpg)
![Implementing the steps
On Target Import the table space:
(root@mysqlt3) [test]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_child1 IMPORT TABLESPACE;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (2.34 sec)
Check the table as well
(root@mysqlt3) [test]>check table tbtest_child1;
| Table | Op | Msg_type | Msg_text |
| test.tbtest_child1 | check | status | OK |
Done:
(root@mysqlt3) [test]>select count(*) from tbtest_child1;
| count(*) |
| 358682 |
3/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-24-320.jpg)




![What about Locks?
On Source let choose a table more consistent:
marco@mysqlt1) [test]>show table status like 'tbtest3'G
Name: tbtest3
Engine: InnoDB
Data_length: 14676918272 - 13.6GB
On Target (mysqlt3):
• Running Inserts or Select on a different schema
• ALTER IMPORT require “System Lock”
• Kill the process will put your dataset in danger
2/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-29-320.jpg)

![How much it costs?
Cost change in relation to the machine power
• On my own PC :
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_10MB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (3.11 sec)
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_100MB IMPORT TABLESPACE;(10.17 sec)
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_1GB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (8 min 53.98 sec)
• On the server:
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_10MB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (1.01 sec)
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_100MB IMPORT TABLESPACE;(3.20 sec)
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_1GB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (1 min 14.31 sec)
[test_tablespace1]>ALTER TABLE tbtest_15GB IMPORT TABLESPACE; (2 min 30.04 sec)
Check Table on 15GB: 55 min 46.35 sec!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-31-320.jpg)




![Exchange Partition
Check the rows in the table and in the partition:
(root@mysqlt1) [test]>select count(*) from tbtest2;
| count(*) |
| 20863248 |
1 row in set (41.16 sec)
(root@mysqlt1) [test]>select count(*) from tbtest2 PARTITION(p020);
| count(*) |
| 320819 |
1 row in set (1.61 sec)
4/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discardinportexchange-130429194307-phpapp02/85/Discard-inport-exchange-table-tablespace-36-320.jpg)