Distributed OS - An Introduction
- 1. Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms By Andrew S. Tanenbaum and Maarten van Steen
- 2. Outline 1. Introduction 2. Communication 3. Processes 4. Naming 5. Synchronization 6. Consistency and Replication 7. Fault Tolerance 8. Security 9. Distributed Object-based Systems 10. Distributed File Systems 11. Distributed Document-based systems 12. Distributed Coordination-based Systems
- 4. Definition of a Distributed System (1) A distributed system is: A collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single coherent system
- 5. Definition of a Distributed System (2) A distributed system organized as middleware Note that the middleware layer extends over multiple machines 1.1
- 6. Transparency in a Distributed System Different forms of transparency in a distributed system Transparency Description Access Hide differences in data representation and how a resource is accessed Location Hide where a resource is located Migration Hide that a resource may move to another location Relocation Hide that a resource may be moved to another location while in use Replication Hide that a resource may be shared by several competitive users Concurrency Hide that a resource may be shared by several competitive users Failure Hide the failure and recovery of a resource Persistence Hide whether a (software) resource is in memory or on disk
- 7. Scalability Problems Examples of scalability limitations Concept Example Centralized services A single server for all users Centralized data A single on-line telephone book Centralized algorithms Doing routing based on complete information
- 8. Scaling Techniques 1. Hiding communication latencies 2. Distribution 3. Replication
- 9. Scaling Techniques (1) 1.4 The difference between letting: a) a server or b) a client check forms as they are being filled
- 10. Scaling Techniques (2) 1.5 An example of dividing the DNS name space into zones
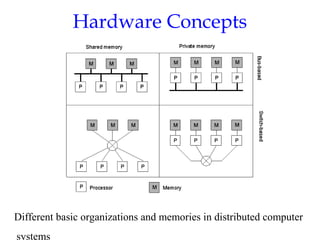
- 11. Hardware Concepts 1.6 Different basic organizations and memories in distributed computer systems
- 12. Multiprocessors (1) A bus-based multiprocessor 1.7
- 13. Multiprocessors (2) a) A crossbar switch b) An omega switching network 1.8
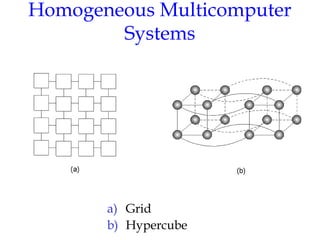
- 14. Homogeneous Multicomputer Systems a) Grid b) Hypercube 1-9
- 15. Software Concepts An overview of • DOS (Distributed Operating Systems) • NOS (Network Operating Systems) • Middleware System Description Main Goal DOS Tightly-coupled OS for multi-processors and homogeneous multicomputers Hide and manage hardware resources NOS Loosely-coupled OS for heterogeneous multicomputers (LAN and WAN) Offer local services to remote clients Middleware Additional layer atop of NOS implementing general-purpose services Provide distribution transparency
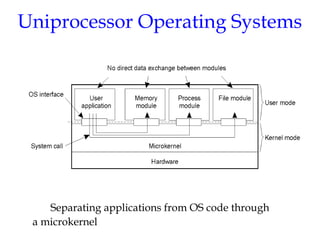
- 16. Uniprocessor Operating Systems Separating applications from OS code through a microkernel 1.11
- 17. Multiprocessor Operating Systems (1) A monitor to protect an integer against concurrent access monitor Counter { private: int count = 0; public: int value() { return count;} void incr () { count = count + 1;} void decr() { count = count – 1;} }
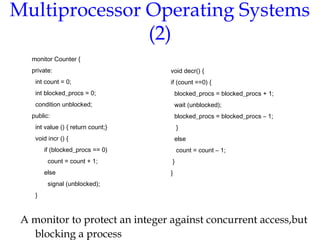
- 18. Multiprocessor Operating Systems (2) A monitor to protect an integer against concurrent access,but blocking a process monitor Counter { private: int count = 0; int blocked_procs = 0; condition unblocked; public: int value () { return count;} void incr () { if (blocked_procs == 0) count = count + 1; else signal (unblocked); } void decr() { if (count ==0) { blocked_procs = blocked_procs + 1; wait (unblocked); blocked_procs = blocked_procs – 1; } else count = count – 1; } }
- 19. Multicomputer Operating Systems (1) General structure of a multicomputer operating system 1.14
- 20. Multicomputer Operating Systems (2) Alternatives for blocking and buffering in message passing 1.15
- 21. Multicomputer Operating Systems (3) Relation between blocking, buffering, and reliable communications Synchronization point Send buffer Reliable comm. guaranteed? Block sender until buffer not full Yes Not necessary Block sender until message sent No Not necessary Block sender until message received No Necessary Block sender until message delivered No Necessary
- 22. Distributed Shared Memory Systems (1) a) Pages of address space distributed among four machines b) Situation after CPU 1 references page 10 c) Situation if page 10 is read only and replication is used
- 23. Distributed Shared Memory Systems (2) False sharing of a page between two independent processes 1.18
- 24. Network Operating System (1) General structure of a network operating system 1-19
- 25. Network Operating System (2) Two clients and a server in a network operating system 1-20
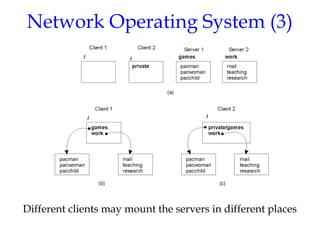
- 26. Network Operating System (3) Different clients may mount the servers in different places 1.21
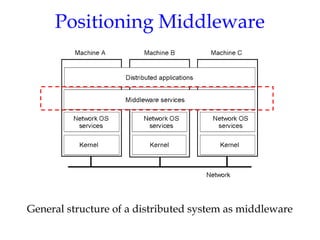
- 27. Positioning Middleware General structure of a distributed system as middleware 1-22
- 28. Middleware and Openness In an open middleware-based distributed system, the protocols used by each middleware layer should be the same, as well as the interfaces they offer to applications 1.23
- 29. Comparison between Systems A comparison between multiprocessor OS, multicomputer OS, network OS, and middleware based distributed systems Item Distributed OS Network OS Middleware- based OSMultiproc. Multicomp. Degree of transparency Very High High Low High Same OS on all nodes Yes Yes No No Number of copies of OS 1 N N N Basis for communication Shared memory Messages Files Model specific Resource management Global, central Global, distributed Per node Per node Scalability No Moderately Yes Varies Openness Closed Closed Open Open
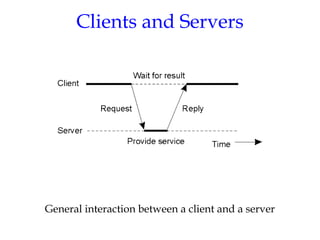
- 30. Clients and Servers General interaction between a client and a server 1.25
- 31. An Example Client and Server (1) The header.h file used by the client and server
- 32. An Example Client and Server (2) A sample server
- 33. An Example Client and Server (3) A client using the server to copy a file 1-27 b
- 34. Processing Level The general organization of an Internet search engine into three different layers 1-28
- 35. Multitiered Architectures (1) Alternative client-server organizations (a) – (e) 1-29
- 36. Multitiered Architectures (2) An example of a server acting as a client 1-30
- 37. Modern Architectures An example of horizontal distribution of a Web service 1-31
- 38. Thanks for Your Attention!