Document Object Model
- 1. Document Object Model (DOM) By D.Chomaskandar Chipkidz
- 2. Outline Introduction of DOM W3C Overview of DOM DOM Examples How the DOM Really works? Advantages and Disadvantages DOM or SAX Summary
- 4. Before going to the DOM HTML –How to Display the Data in the Webpage. XML – How to Describe the Data . DHTML - How to Add Movement or Animation to an HTML Document. JAVASCRIPT - How to make Web Content Dynamic.
- 5. World Wide Web Consortium-W3C
- 6. World Wide Web Consortium-W3C To Promote Open Standard For world wide web. W3C is a vendor Organization. Main Vendors are Netscape and Microsoft. Some W3C Standards are HTTP,HTML,XML,CSS. DOM is also Recommend by W3C.
- 7. W3C
- 8. Five Basic Levels Of W3C : Recommendation :- It is the Final outcome from W3C.All the Web functions are working properly. No Error HTML,CSS,DOM
- 9. In this layer the work is mostly complete .But some minor changes is occur. Partial Output Proposed Recommendation :-
- 10. Working Document.all Document.all Candidate Recommendation :- Not Working MOZILLA MICROSOFT IE
- 11. Working With Current Task. W3C MEMBERS Working Drafts
- 12. DOM NEUTRAL - INTERFACE HTML XML JAVA SCRIPT ANY LANGUAGE What is the DOM?
- 13. Status Of The DOM
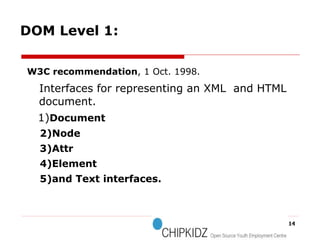
- 14. W3C recommendation , 1 Oct. 1998. Interfaces for representing an XML and HTML document. 1) Document 2)Node 3)Attr 4)Element 5)and Text interfaces. DOM Level 1:
- 15. W3C recommendation , 13 Nov. 2000. It contains six different specifications: 1)DOM2 Core 2)Views 3)Events 4)Style 5)Traversal and Range 6)and the DOM2 HTML. DOM Level 2:
- 16. W3C candidate recommendation , 7 Nov. 2003 It contains five different specifications: 1)DOM3 Core 2)Load and Save 3) Validation 4)Events 5)and XPath DOM Level 3:
- 17. Overview of DOM
- 19. Referencing Objects -Each Object is Identified by Object Name.
- 20. How To Use Referencing Objects Object Names General form is TO Access The History To Access The B ody object1.object2.object3.. window.history document.body
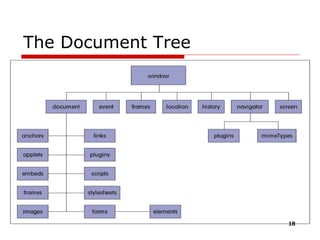
- 21. The DOM structure model It is a Hierarchy of Node objects node object Element Attribute etc
- 22. The DOM Interface The DOM has many interfaces to handle various node objects. Every interface has its “Attributes” and “Methods”. Compare with Object Oriented Programming (OOP). Method Method Property Attribute Object Class Interface OOP DOM
- 23. Document Tree Structure document document.body document. documentElement
- 24. child, sibling, parent
- 25. child , sibling , parent
- 26. child , sibling , parent
- 27. child , sibling , parent
- 28. <Company> <Tenth planet Tech> <Chipkidz> <Hr>Mr. Sakthi</Hr> <Members> <chomas>DOM </chomas> <perumal>SAAS </perumal> </members> </chipkidz> </Tenth planet Tech> ... DOM structure model ID=“BOLD”
- 29. DOM NODE Methods
- 30. document .firstChild .childNodes[0] .firstChild .parentNode .childNodes[1];
- 31. document .getElementById() .getElementByTag() returns a specific element returns an array of elements
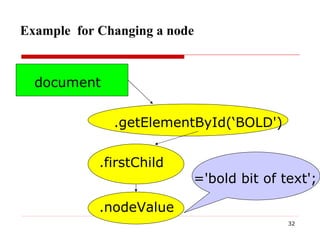
- 32. Example for Changing a node document .getElementById(‘BOLD') .firstChild .nodeValue ='bold bit of text';
- 33. Working with Object Collections -The Web Document Display in the window
- 34. Working with Object Properties
- 35. Example Source Code For Document Method document.body.style.backgroundColor
- 36. Examples For Document method <html> <head> <title>Change the Background</title> </head> <body> <script language = "JavaScript"> function background() { var color = document.bg.color.value; document.body.style.backgroundColor =color ; } </script> <form name="bg"> Type the Color Name:<input type="text" name="color" size="20"><br> Click the Submit Button to change this Background color as your Color.<br> <input type="button" value="Submit" onClick='background()'> </form> </body> </html>
- 37. How To Implement In The Blogspot
- 43. NAVIGATOR
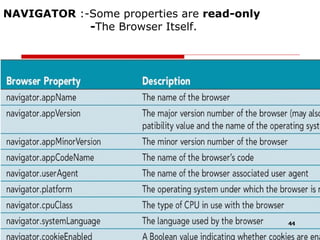
- 44. NAVIGATOR :-Some properties are read-only - The Browser Itself.
- 45. Example Source Code For Navigator Method navigator.appName navigator.appVersion navigator.appCodeName navigator.platform navigator.cookieEnabled
- 46. Example For NAVIGATOR <html><body><script type="text/javascript"> document.write("<p>Browser: "); document.write(navigator.appName + "</p>"); document.write("<p>Browserversion: "); d ocument.write(navigator.appVersion + "</p>"); document.write("<p>Code: "); document.write(navigator.appCodeName + "</p>"); document.write("<p>Platform: "); document.write(navigator.platform + "</p>"); document.write("<p>Cookies enabled: "); document.write(navigator.cookieEnabled + "</p>"); document.write("<p>Browser's user agent header: "); document.write(navigator.userAgent + "</p>"); </script></body></html>
- 48. MOZILLA
- 52. GOOGLE CHORME GOOGLE CHORMEZ GOOGLE CHORME
- 56. How the DOM Really works?
- 57. The Relation Graph Web Client side program (e.g.: JavaScript) Web Server side program (e.g.: ASP) Console program (e.g.: C++, Java) Output DOM XML document XML+HTML document
- 58. Attributes childNodes nodeName nodeValue firstChild lastChild previousSibling nextSiblin Methods insertBefore replaceChild removeChild appendChild An Example — Most Frequently Used Interface, Node
- 59. DOM in Programming Languages Java C++ C# VB.Net, etc.
- 60. DOM Advantages & Disadvantages
- 61. DOM Advantages & Disadvantages ADVANTAGES Robust API for the DOM tree Relatively simple to modify the data structure and extract data Disadvantages Stores the entire document in memory As Dom was written for any language, method naming conventions don’t follow standard java programming conventions
- 62. SAX
- 63. SAX - Simple API for XML Industry-standard API for parsing XML data. Unidirectional. Event-driven.
- 64. The History of SAX Not a W3C recommendation. Created by members of the xml-dev mailing list, led by David Megginson. SAX implementations for Java and C++ have been around for a while. SAX2 is the current API revision .
- 65. DOM OR SAX
- 66. DOM or SAX DOM Suitable for small documents Easily modify document Memory intensive;Load the complete XML document SAX - Suitable for large documents; saves significant amounts of memory Only traverse document once, start to end Event driven Limited standard functions.
- 67. Some DOM Supporting Browsers Konqueror Camino Opera Safari
- 68. SUMMARY
- 69. Summary DOM is a tree representation of an XML document in memory Dom provides a robust API to easily Modify and extract data from an XML document JAXP provides a vendor –neutral interface to the underlying DOM or SAX Parser
- 70. References www.w3.org/DOM http://developer.mozilla.org/en/Gecko_DOM_Reference www.corewebprogramming.com http://www.w3schools.com
- 71. QUESTIONS ?
- 72. [email_address] For more Information http://web2sharing.wordpress.com For any Queries
- 73. THANK YOU

























![document .firstChild .childNodes[0] .firstChild .parentNode .childNodes[1];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/documentobjectmodel-12521271465799-phpapp02/85/Document-Object-Model-30-320.jpg)


































![[email_address] For more Information http://web2sharing.wordpress.com For any Queries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/documentobjectmodel-12521271465799-phpapp02/85/Document-Object-Model-72-320.jpg)
