Effective Android UI - English
- 1. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Effective Android UI Pedro Vicente Gómez Sánchez Android Expert [email protected] @pedro_g_s github.com/pedrovgs
- 2. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs
- 3. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Irene Herranz Managing Director Alberto Gragera Technical Director Jorge Barroso Android Expert Davide Mendolia Full Stack Engineer
- 4. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs This talk is the continuation of Software Design Patterns on Android http://www.slideshare.net/PedroVicenteGmezSnch/software-design-patterns-on-android
- 5. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Is the UI code less important? Are we using Android SDK properly? How can I improve the UI code?
- 6. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs ● Introduction. ● Resources and qualifiers. ● Custom Views. ● Model View Presenter. ● Model View ViewModel. ● MVP vs MVVM. ● Some advices.
- 7. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs https://github.com/pedrovgs/EffectiveAndroidUI
- 8. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs ● MVP and MVVM samples. ● How to work with Fragments. ● Communication between Fragments and Activities. ● How to use Dagger as Dependency Injector. ● How to use resources to support different screen densities, device orientation and different Android versions. ● How to use styles and themes. ● How to use Navigator or ActionCommand to implement activities navigation. ● How to use custom qualifiers with resources. ● How to use different layouts: RelativeLayout, LinearLayout, FrameLayout, etc. ● Usage of merge, include and view stub. ● How to implement a ListView using Renderers. ● Simple Interactors implementation described in “Software Design Patterns on Android” talk. ● How to use Dagger with different scopes, Application scope and Activity scope. Introduction https://github.com/pedrovgs/EffectiveAndroidUI
- 9. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Introduction: S4 - Android 4.4.2
- 10. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Introduction: DraggablePanel https://github.com/pedrovgs/DraggablePanel
- 11. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Introduction: MDPI device
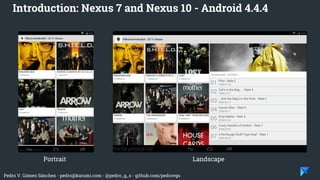
- 12. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Introduction: Nexus 7 and Nexus 10 - Android 4.4.4 Portrait Landscape
- 13. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs How can we change the UI depending on the device?
- 14. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Android resources are one of the Android SDK powerful tools to work with the UI layer. Some common resources are: ● Color: Colors available for your application. In colors.xml you can declare your color palette. ● Drawable: Shapes and statics assets ready to be used in Image components as src or background. ● Layout: XML files to describe the application UI and to be inflated by the system. ● Menu: Android menus can be described in xml files and used directly from our activities. ● Integer: Integer values ready to be used in xml files or java code. ● XML: XML configuration files that can be used to indicate different configuration parameters. Not really common. Resources and qualifiers
- 15. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs For complex projects where we have to support tons of different devices with different screen densities and sizes and different Android API versions we need to use our resources and qualifiers properly to get the max development performance. Qualifiers are really important to work with different Android configurations. We can prepare different resources for different Android configurations and these resources are going to be provided automatically. Configuration based on qualifiers: ● Screen density: ldpi, mdpi, hdpi, xhdpi, etc. ● Language: es, en, fr, en-rUS, etc. ● Min width: sw600dp, sw720dip. ● Available width or height: w720dp, h1024dp. ● Screen orientation: landscape, portrait. ● Android API level: v7, v8, v9, etc. Resources and qualifiers
- 16. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs How have we used resources and qualifiers in Effective Android UI project? ● Layouts: ○ layout-v10: Android 2.X is using one layout with just one fragment. ○ layout-v11: Android 3.X y 4.X (except tablets in landscape). ○ layout-sw600dp-land: Layout with two fragments in landscape. ● Values: ○ values-mdpi: Mdpi and ldpi devices are using one column for the GridView and different ImageView height. ○ values-hdpi: Hdpi, xhdpi and xxhdpi devices with screen width lower than 820 dip are using two columns for the GridView and another ImageView height. ○ values-w820: Devices with more than 820 dip width are going to use 3 columns for the GridView configuration. Resources and qualifiers
- 17. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Resources and qualifiers http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/resources/providing-resources.html How it’s working if we haven’ t declared every possible configuration?
- 18. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Custom Views
- 19. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Main motivations to use custom views are: ● Create a non implemented Android SDK widget. ● Group presentation logic for different views. Really useful with MVVM. ● Add semantic to UI layer components. ● Avoid code duplicity. Custom Views
- 20. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs There are 5 approaches to implement your custom views: ● Extend an already written widget like TextView, ImageView. ● Extend View and override onDraw method using the Canvas API. ● Extend one Layout/ViewGroup and inflate your own layout file. ● Extend one Layout/ViewGroup and wait for views added by other developers using this custom view. ● Inflate different layouts provided by the custom view client Custom Views
- 21. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Custom Views http://github.com/pedrovgs/Nox
- 22. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Are you ready to talk about MVP and MVVM?
- 23. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Model View Presenter
- 24. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Model View Presenter is a software design pattern that comes from MVC and is used to build user interfaces. In this pattern, the “presenter” has the responsibility to implement all the presentation logic and data transformation in order to send information to the view. Works as an abstraction between the UI layer and the business logic layer. The “view” in MVP is going to be abstracted using an interface implemented by Android components. Model View Presenter
- 25. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs The main problem that MVP solves is related to testing, to avoid coupling and to avoid code duplicity. The usage of MVP improves the testability of your code because we can test all our UI code without executing framework code, just with unit tests. To do this, all the presentation logic is moved to the presenter. The view implementation is going to be really lightweight. Model View Presenter
- 26. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs One of the key points related to MVP is to leave your presenters free of Android dependencies. By removing all your Android code from your presenters you’ll be able to test it easily. Model View Presenter
- 27. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Using MVP, Activity Fragments and Custom Views are going to implement a presenter “view” interface and are going to be configured as presenter views. Views are going to contain code to implement your view details - described in the View interface - and to connect user actions with presenters. Model View Presenter
- 28. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs
- 29. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Even if we are using MVP, we need to connect our component lifecycle to our presenter in order to notify whether the view is ready to work or not. Some methods like “onSavedInstanceState” will update our presenter state if needed. Model View Presenter
- 30. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Model View Presenter To implement user events - like a button clicked - our view implementation will delegate to the presenter to take some decisions.
- 31. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs If you want to extract navigation implementation out of Activities or Fragments you can use a “Navigator”. Using one Navigator you can avoid some cycles in the collaboration diagram between view implementations and presenter when a user action has to open another activity or modify the navigation stack. To do this, you need to be able to inject Activity context using a dependency injector. Model View Presenter
- 32. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Model View ViewModel
- 33. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Model View ViewModel is a software design pattern derived from Presentation Model (by Martin Fowler). It’s commonly used to build user interfaces and used by Microsoft to implement Windows applications. The power of this pattern is in the usage of a binding engine, but we can use it without one. The binding engine is going to avoid all the boilerplate code we have to write to connect our view model with the view to keep it updated. Model View ViewModel
- 34. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs ViewModel implementations will contain all the logic state of the view. “Visibility”, “is focused?”, “is clickable?”, “has been clicked?” and keeps references to all the data related to the view. If you want to implement a reactive UI you have to connect your ViewModels with your events mechanism to be able to change the view state changing the ViewModel information. Android UI components lifecycle will be connected with the ViewModel as we were already doing with MVP. Model View ViewModel
- 35. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs In MVVM ViewModel implementation will not contain a view instance, it is going to use an events mechanism - data binding engine - to communicate state changes to the view implementation. In this pattern, the “View” is not an interface, is just an implementation using the ViewModel. Activities, Fragments and Custom Views will keep an instance of the View Model and will register different listeners to know when the View Model has changed. Model View ViewModel
- 36. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs In the view implementation we are using - Activities, Fragments or Custom Views - we will execute Action Commands offered by the ViewModel. Model View ViewModel
- 37. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs
- 38. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs If the user clicks a widget, the view implementation will get an Action Command from the View Model to execute it. This implementation will be really interesting when Action Commands are going to represent UI actions that could be really repetitive like open Activities or show Toasts. Model View ViewModel
- 39. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs View Models represent big views like Activities and return little ViewModels for Custom Views or ListView rows. This implementation is really easy to adopt if you use Renderers. Model View ViewModel
- 40. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs To implement MVVM is really convenient to connect our ViewModels and view implementations using a binding engine. This is going to reduce all the boilerplate needed to connect these elements manually and is going to get a reactive view. Model View ViewModel RoboBinding AndroidBinding
- 41. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs ¿ MVP vs MVVM ?
- 42. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs
- 43. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs ● MVVM data binding engines are really powerful, but not every library supports obfuscation. ● MVP used to be easier to understand and implement. ● If you use little presenters your MVP implementation will look like MVVM, be careful with the presenter size! ● MVP could be easier to test, depending on the binding engine you are using. ● MVVM is going to be faster to implement, if you use binding, because you have to write less code. ● Both patterns are going to improve code quality and testability. MVP vs MVVM
- 44. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs The motivations of this patterns are the same. These patterns try to solve the same problems. Both patterns are going to abstract our model implementation and view implementation. This is useful to change any UI boundary layer implementation as you wish. MVP vs MVVM
- 45. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs To me, MVP is not better than MVVM and vice versa. Think about these patterns and use the one you understand better. MVP vs MVVM
- 46. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs ● Avoid expensive tasks executed over the UI thread. ● Avoid code duplicity. ● Measure your UI performance using performance tools. ● Use themes, styles, dimensions and colors properly. ● Think in the UI layer like an isolated domain. ● Write testable code and test it. ● Return all the information needed to paint your UI. ● Implement your ListView and Adapters recycling your views. ● Write code for your buddies, not for the machine. Some advices
- 47. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs Questions? [email protected] @pedro_g_s github.com/pedrovgs
- 48. Pedro V. Gómez Sánchez - [email protected] - @pedro_g_s - github.com/pedrovgs