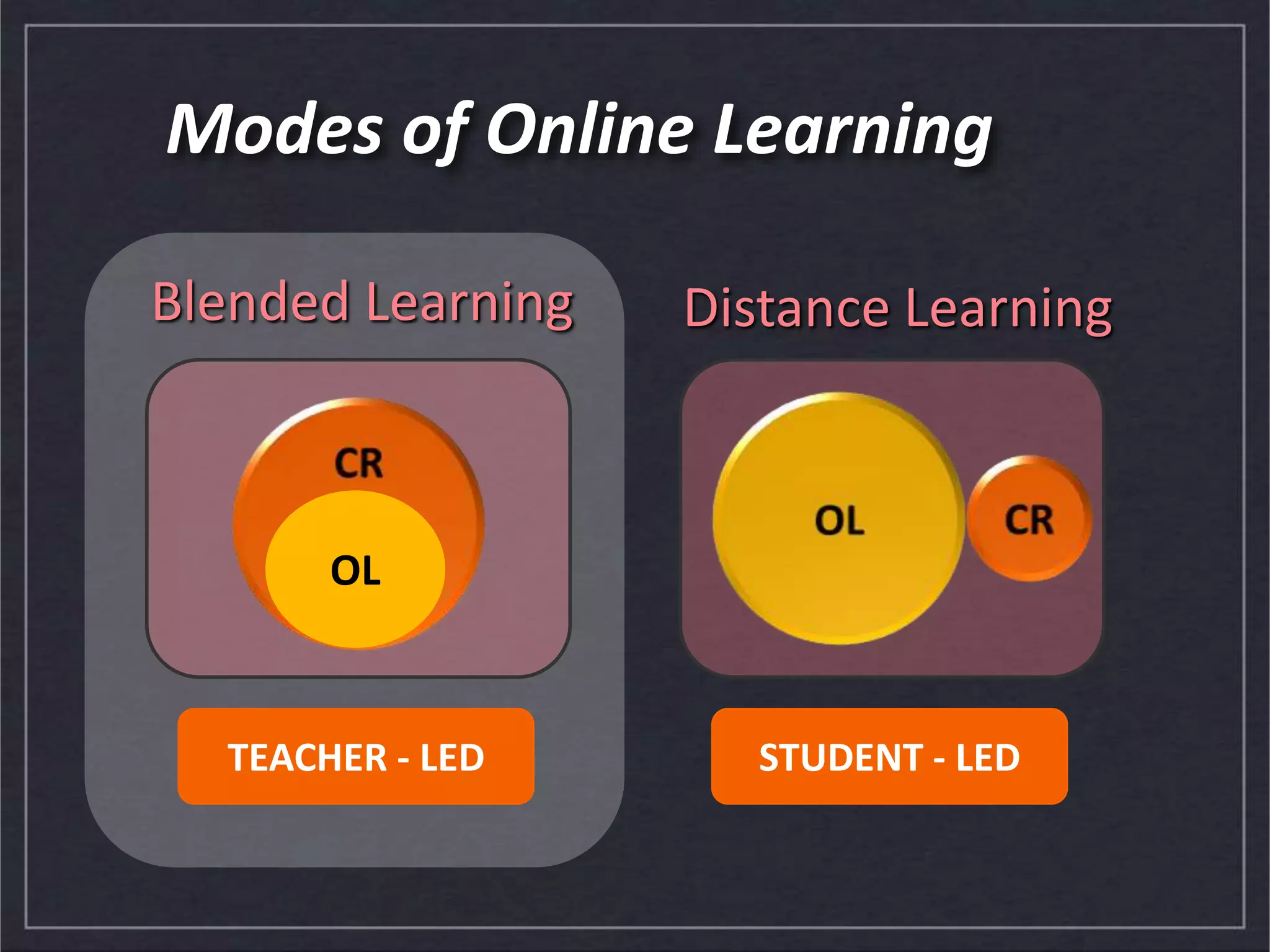
This document discusses e-learning and blended learning. It defines e-learning as learning facilitated through technology, typically available online through web formats and hyperlinks. Blended learning combines online and in-person learning, allowing students to access materials, collaborate online, and complete assignments. Moodle is introduced as a course management system that allows teachers to create online courses, manage student information, and track grades. The document provides guidance on starting small when designing online courses, testing activities before implementing them fully, and considering different course designs like introductory, skills-based, theory, and capstone courses. It suggests which Moodle tools are best suited to different course types.