Embedded system and real time operating system
- 2. Introduction An Embedded system is one that has computer – hardware with application software and RTOS embedded in it as one of its most important component . The hardware of a general- purpose computer is typically pre-defined like CPU, monitor, keyboard, mouse, CD-ROM…
- 3. Overview Of Embedded Systems Architecture: Every Embedded system consists of: Custom built hardware around a central processing unit (CPU). A software residing on the memory chip of hardware and an Operating system. The operating system runs above the hardware and the application software runs above the hardware.
- 4. Layout architecture of Embedded system
- 5. Building Blocks Of Embedded Systems: The various building blocks of an embedded system are: Central Processing Unit (CPU). Memory (ROM and RAM) Input Devices Output Devices Communication interfaces Application specific circuitry Contd....
- 6. Simplified hardware architecture of an Embedded system
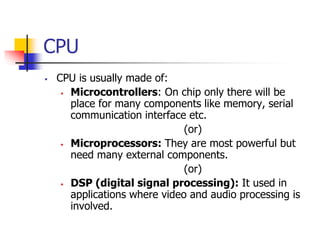
- 7. CPU CPU is usually made of: Microcontrollers: On chip only there will be place for many components like memory, serial communication interface etc. (or) Microprocessors: They are most powerful but need many external components. (or) DSP (digital signal processing): It used in applications where video and audio processing is involved.
- 8. Memory, Input and Output devices Memory: It is of 2 types-RAM and ROM.ROM is used for storing contents as it wont get erased if power is off, where as it gets erased in case of RAM Input devices: They wont have key board or mouse for taking input but sensors and transducers are used as input. Output devices: They have a limited capacity. usually LCD may be used to display some important parameter.
- 9. Communication Interfaces And Application Specific Circuitry Communication Interfaces: One embedded system communicates with another embedded system to transfer data by communication interfaces such as Universal Serial Bus (USB) Application specific circuitry: Sensors, transducers, special processing and control circuitry are required for an embedded system.
- 10. Special Features Of Embedded Systems: They do a specific task, i.e., they cannot be programmed to do many different things They are highly reliable They have to operate in extreme environment conditions like high temperature and humidity Embedded systems that address the consumer market (for example, electronic toys) are very cost- sensitive: Even a reduction of $0.1 is lot of cost saving.
- 11. Categories Of Embedded Systems Based on functionality and performance requirements, embedded systems can be categorized as: Stand-alone embedded systems Real-time systems Networked information appliances Mobile devices Stand alone Embedded Systems As the name implies, stand-alone systems work in stand-alone mode. They take inputs, process them and produce the desired output.
- 12. Categories Of Embedded Systems Real Time Systems Embedded systems in which some specific work has to be done in a specific time period are called real-time systems Hard RTS The system that has strict deadlines are called hard RTS. And any delay in time may lead to catastrophe .
- 13. Soft RTS: The systems that have strict deadlines, but not adhering to them once in a while may not lead to catastrophe. Networked Information Appliances Embedded systems that are provided with network interfaces and accessed by networks such as Local Area Network or the Internet are called networked information appliances
- 14. Mobile Devices:- The limitations of mobile devices- memory constraints, small size, lack of good user interfaces such as full-fledged keyboard and display etc like that of embedded systems.
- 15. Applications Consumer appliances DVD player, electronic toys, microwave oven, remote controls for TV and air-conditioner, V CD player, video game consoles, video recorders etc. Office automation: The office automation products using embedded systems are copying machine, fax machine, key telephone, modem, printer, scanner etc. Industrial automation: Pharmaceutical, cement, sugar, oil exploration, nuclear energy, electricity generation and transmission. The embedded systems for industrial use are designed to carry out specific tasks such as monitoring the temperature, pressure, humidity, voltage, current ,robotics and many more.
- 16. Examples for embedded systems
- 17. Applications Medical electronics: Diagnostic aids such as ECG, EEG, blood pressure measuring devices, X-ray scanners; equipment used in blood analysis, radiation, endoscopy etc.
- 18. Computer networking: Computer networking products such as bridges, routers, Integrated Services Digital Networks (ISDN) are examples of embedded systems. Telecommunications : terminal adapters, web cameras are embedded systems. IP phone, IP gateway, IP gatekeeper etc. are the latest embedded systems that provide very low-cost voice communication over the
- 19. Applications Insemination: The measuring equipment we use in laboratories to measure parameters such as weight, temperature, pressure, humidity, voltage, current etc. are all embedded systems. Testing and measurement are the fundamental requirements in all scientific and engineering activities.
- 20. Applications Security: Security of persons and information has always been a major issue . Security devices at homes, offices, airports etc. for authentication and verification are embedded systems. Finance: Financial dealing through cash and cheques are now slowly paving way for transactions using smart cards and ATM(Automatic Teller Machine, also expanded as Any Time Money) machines.
- 21. Conclusion Embedded systems represent a large and growing class of computing systems, which some believe will soon become even more significant than desktop computing systems The world would be nothing without embedded systems as all its requirements are basically themselves!!!
- 22. THANK YOU!