This study investigates the impact of welding processes and microstructure on the abrasive wear resistance of hardfacing alloys. Two commercial hardfacing electrodes were analyzed, with findings indicating that the microstructure and composition, particularly the distribution and chemical makeup of carbides, significantly influence wear resistance. Results demonstrate that higher carbide content and finer microstructure correlate with improved abrasion resistance, emphasizing the importance of careful selection of welding parameters and materials.
![The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES)
|| Volume || 3 || Issue || 12 || December - 2014 || Pages || 35-44||
ISSN (e): 2319 – 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 – 1805
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 35
The Effects of Welding Processes and Microstructure on 3 Body
Abrasive Wear Resistances for Hardfacing Deposits
Dr. K. M. Kenchi Reddy 1
And Dr. C. T. Jayadeva 2
1,
Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sri Krishna Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India.
2,
Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Adichunchanagiri Institute of Technology, Chikmagalur,
India.
--------------------------------------------------ABSTRACT --------------------------------------------------------
Wear is the predominant factor that controls the life of any machine part. Metal parts often fail their intended
use not because they fracture and wear which causes them to lose dimension and functionally. Different
categories of wear exit, but most typical modes are abrasion,impact,Hardfacing is one of the most useful and
economic ways to improve the performance of components submitted to severe wear conditions. A study was
made to compare the microstructure and abrasion resistance of hardfacing alloys reinforced with primary
chromium carbides. The hardfacing alloys were deposited onto M.S. plate by shielded metal arc welding
(SMAW) process. Two different commercial hardfacing electrodes were employed to investigate the effect of the
microstructure. The abrasion tests were carried out in a dry sand-rubber wheel abrasion machine according to
the procedure A of ASTM G65 standard. Microstructure characterization and surface analysis were made using
optical and scanning electron microscope. The result shows that the wear resistance is determined by the size,
shape, distribution and chemical composition of the carbides, as well as by the matrix microstructure. The best
abrasion resistance was obtained in microstructure composed of chromium carbide alloy. Hardfacing is a
deposition of different metal over the parent metal to achieve required properties.
KEYWORDS: Abrasion resistance, Hardfacing alloys, Microstructure characterization, Wear mechanism,
welding.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Date of Submission: 03 December 2014 Date of Publication: 15 December 2014
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I. INTRODUCTION
Hardfacing is also known as Hardsurfacing is the application e specialized alloys by means of welding
process to resist abrasion, corrosion, high temperature, or impact. Such an alloy may be deposited on the
surface, an edge, or merely the point of a part subject to wear. Hardfacing deposits can functionalize surfaces
and reclaim components by extending their service life. Hardfacing is a key technology to fulfill these
requirements and to apply different hardfacing alloys on the base metals. Hardfacing increases the service life of
a part and there by extend the life time of machinery equipment efficiently.Core components such as crushers
are exposed to heavy wear and require efficient surface protection measures to avoid costly downtimes and to
reduce costs for expensive spare parts. Hardfacing is a commonly employed method to improve surface
properties of agriculture tools, components for mining operation, soil preparation equipments and earth moving
equipments [1], [2]. This process has been also adopted across many industries such as Cement, Mining, Steel,
Petro-chemical, Power, Sugar cane and Food. An alloy is homogeneously deposits onto the surface of a soft
material by welding with the purpose of increasing loss in ductility and toughness of the substrate. A wide
variety of hardfacing alloys are commercially available for protection against wear. Deposits with a
microstructure composed by disperse carbides in austenite matrix are extensively used for abrasion applications
and are typically classified according to the expected hardness. Nevertheless, the abrasion resistance of a
hardfacing alloys depends on many other factors such as the type, shape and distribution of hard phases, as well
as the toughness and strain hardening behavior of the matrix[3].
Chromium-rich electrodes are widely used due to low cost and availability; however, more expensive
tungsten or vanadium-rich alloys offer better performance due to a good combination of hardness and
toughness. Complex carbides electrodes are also used; especially when abrasive wear is accompanied by other
wear mechanisms [4].Several welding techniques such as oxyacetylene gas welding (OAW), gas metal arc
welding (GMAW), shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and submerged arc welding (SAW) can be used for
hardfacing. The most importance differences among these techniques lie in the welding efficiency, the weld](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f031201035044-150218035427-conversion-gate02/85/The-Effects-of-Welding-Processes-and-Microstructure-on-3-Body-Abrasive-Wear-Resistances-for-Hardfacing-Deposits-1-320.jpg)
![The Effects of Welding Processes and Microstructure…
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 36
plate dilution and the manufacturing cost of welding consumables [5]. SMAW, for example, is commonly used
due to the low cost of electrodes and easier application. The present investigation aims to study two commercial
electrodes in terms of their chemical composition, microstructure, hardness and abrasive wear resistance.
II. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
Base Metal : The selection of base metal is very essential in deciding what alloy to use for hardfacing deposit.
Since welding procedure differs according to the base metal. Mild steel was selected as the base metal for the
study which composes the main elements of carbon, silicon, manganese, sulphur, and phosphorous. The
chemical composition is given in Table 1.
Hardfacing Alloys : In the study, two different commercial hardfacing alloys were used for overlaying. These
are basically iron – based alloys having varying amount of chromium, carbon, silicon and other alloying
elements as they are more suitable for shielded metal arc welding process. Chemical compositions of two
electrodes are presented in table 2.
Table 1: Chemical Composition of Base Metal (In Weight Percentage)
C Si Mn S P Fe
0.18 0.32 1.47 0.013 0.029 Bal
Table 2: Chemical Composition of Hardfacing Alloy (In Weight Percentages)
Electrode C Si Mn S P Cr Mo Ni V Fe
Hardfacing-1 0.33 0.28 1.15 0.014 0.025 2.22 - - - Bal
Hardfacing-2 0.1 0.38 1.51 0.024 0.03 2.15 0.745 1.09 0.103 Bal
Welding Conditions
The standard size of test specimens of 16 nos. with the dimensions of 250×100×12 mm was selected
for the experiment.
The following precautions are taken before hardfacing:
The electrodes are perfectly dried in the furnace and baked at 250°C one hour before the use
Area of the weld is properly cleaned
Preheated the hardfacing area to a minimum of 200°C
2.4 Machine specifications
Name: TORNADO MIG 630 Arc welding machine
Current: 100-630 A
Input Voltage: 415 V ± 10% / 50-60 Hz / 3 Phase
Machine Capacity: 50 KVA
2.5 Stages of Experiment
The experiment was carried out in three stages to investigate the effect of welding parameters
such as current, travel speed and voltage on hardfacing electrodes and the corresponding hardness was
determined by using Vickers hardness testing machine.
1) In first stage, voltage (V) and travel speed (S) were kept constant and current (A) was increased.
2) In second stage, voltage (V) and current (A) were kept constant and travel speed (S) was increased.
3) In third stage, current (A) and travel speed (S) were kept constant and voltage (V) was increased
III. RESULTS OF THE EXPERIMENT
Hardness test
The specimens were cut to a size of 100x30x12mm for hardness testing and were polished using
standard metallographic procedure. Hardness testing of different welding deposits was carried out in Vickers
hardness testing machine using SHIMADZU HMV-2000 Micro Hardness Tester, The load applied is 500 Gms,
dwell time is 13 Sec with a square base diamond pyramid of opposite face angle 136° ±0.5°. The test method
adopted is as per IS: 1501-2002. Micro hardness surveys were made on these specimens using Vickers hardness
tester along the direction of thickness from the top surface towards the base metal after every 0.5 mm. These
surface values are plotted in the form of a graph shown in figure 1. The results of the hardness survey of heat
affected zone (HAZ) samples for every 0.5mm depth indicate that the hardness values are more on the weld
surface and decrease towards the base metal and remain constant on the base metal. Based on welding
parameters such as current, travel speed and voltage the micro hardness surveys were made on the each](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f031201035044-150218035427-conversion-gate02/85/The-Effects-of-Welding-Processes-and-Microstructure-on-3-Body-Abrasive-Wear-Resistances-for-Hardfacing-Deposits-2-320.jpg)
![The Effects of Welding Processes and Microstructure…
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 37
specimens using Vickers hardness tester along the direction of thickness from the top surface towards the base
metal after every 0.5 mm are illustrated in the cumulative graph for all the 16 specimens are shown in figure 1
for comparison.
Figure1. Hardness survey of heat affected zone (HAZ) for 16 samples
Alloy (hardfacing 1) is the main martensitic with some kinds of austenite. Fine primary chromium
carbides are well distributed throughout the micro section. The hardness on the Weldment and HAZ towards the
base metal has been surveyed for every 0.5 mm depth and the values are plotted in figure 1. The chemistry of
the Fe/Cr carbides is reported for hypereutectic FeCrC alloys in literature to M7C3 structure [6-9]. The hardness
values of the ledeburitic matrix which are determined to about 500 HV 0.5 are close to previous investigations
from Fischer [10] and Buytoz [11]. Beside small and evenly distributed primary chromium carbide at a volume
content of approximately 5% can be detected which are supposed to be of major importance for increasing the
resistance against abrasion due to their high hardness. While observing the alloy of hardfacing 2 the constituents
of primary chromium carbides are not well distributed throughout the micro structure. After the dry sand
abrasion test comparisons were made between electrode 1 and electrode 2, the electrode 1 is more wear
resistance than electrode 2.
A closed net or skeleton of brittle Fe/Cr carbides is clearly surrounds the primary dendrites. Higher
welding amperage, higher arc travel and higher voltage leads to decreasing hardness. Overall the chromium
carbides are irregularly distributed. There is a higher density of original carbides close to the fusion line,
whereas at the surface only rests of carbides are visible. BAIRD spectroscope is used to analyze the
microstructure of the specimens. Cross sections of the weld were polished and etched with kalling’s and Nital
2%. Different types of carbides present in the microstructures were first identified on the basis of their
morphologies and confirmed by micro hardness measurements. The wear resistance is in fact proportional
to the volume fraction in hypereutectoid Steels [12]. Furthermore, the original orientation of the colony and the
mean inter lamellar spacing have effects on wear resistance [13]. Several authors investigated that the
relationship between wear resistance and hardness is affected by microstructure [13, 14].
Wear resistance increased in the structural sequence from spheroidite to pearlite and from tempered
martensite to bainite [12, 15]. Microstructure shows pearlite with subsequent formation of interdendritic
carbides. However, the carbide content in the weld deposit made with welding parameters at current 200A,
travel speed 21.4cm/min and voltage 25V is higher than that with weld deposit made with welding parameters at
current 300A, travel speed 23.1 cm/min and voltage 25V for the same electrode. Furthermore coarser
microstructure are observed in weld deposit made with higher heat input at higher amperage current and travel
speed for the same electrode keeping more or less similar microstructural constituents. These microstructural
characteristics are also reflected in the hardness values. Higher amount of carbide and finer structure, in general
resulted in higher hardness, whereas lower hardness values were recorded in weld deposits with less amount of
carbides and coarser structure. Several Authors [16, 17] have suggested that abrasive wear resistance increases
in direct relationship with the volume of the hard constituent. It is interesting to note that weld deposits made
with high heat input with higher amperage of current for the same alloy system possess higher wear resistance.
Apparently one would expect lower wear resistance in the weld deposit made with high heat input, due to lower
hardness value. Alloy mainly martensitic with some islands of austenite. Chromium Carbides are well
distributed throughout the micro section (specimen 5, 8, 12). (Ledeburitic matrix).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f031201035044-150218035427-conversion-gate02/85/The-Effects-of-Welding-Processes-and-Microstructure-on-3-Body-Abrasive-Wear-Resistances-for-Hardfacing-Deposits-3-320.jpg)

![The Effects of Welding Processes and Microstructure…
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 39
Figure 5. Stages of abrasion; a) initial, b) middle and c) end of tests
In three-body abrasion, the sand particles behaved in one of the following ways. From free fall, the
sand particles gained energy from the rubber wheel (figure 5.a) and then struck the sample surface, which would
result in the formation of pits. Secondly, the abrasive particles were embedded in the rubber wheel, transforming
the three-body abrasion into multi-pass Two-body abrasion (figure 5.b). Thirdly, the particles roll at the
interface causing plastic deformation to the hardfaced alloy (figure 5.c). These stages are illustrated in figure
5.a-5.c respectively.
Wear is generally a complex process, which is influenced by the many system variables, such as
materials properties, environment and mode of loading. In this study, two Fe-Cr-C hardfaced alloys of different
composition and microstructure were investigated under three-body abrasion.Various researchers have been
demonstrated that the application of hardfaced alloy on cast iron/mild steel significantly increases the surface
hardness and results in increased resistance to abrasive wear [18-19], it has been shown in this work that the
hardness of two hardfaced alloys were very different, their wear loss were dissimilar under the same test
conditions. This indicates that the importance of microstructural parameters, such as the amount and size of the
carbides, weld parameters, toughness and type of phases in determining the wear resistance [20-22].
The development of Fe-Cr-C hardfacing has been based around the understanding that good wear
resistance is obtained with materials that have a high volume fraction of hard phases that are supported in a
tough matrix. Both hardfacing 1 (type 1 electrode) and hardfacing 2 (type 2 electrode) are composed of similar
phases; however, hardfacing 1 has a significantly larger amount of carbide phases than hardfacing 2.
Figure 6. Wear loss of weld sample Figure 7. Wear loss of weld samples
15 min 30 min
The wear resistance increases with increase in chromium, carbon and silicon present in the hardfaced
alloy 1. The experimental results are in agreement with those reported [23-24] on hardfacing alloys tested under
low stress against a rubber wheel. Meanwhile, decrease in the wear resistance with decreasing chromium,
carbon and silicon were observed in type 2 electrode and is in consistent with other published works.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f031201035044-150218035427-conversion-gate02/85/The-Effects-of-Welding-Processes-and-Microstructure-on-3-Body-Abrasive-Wear-Resistances-for-Hardfacing-Deposits-5-320.jpg)
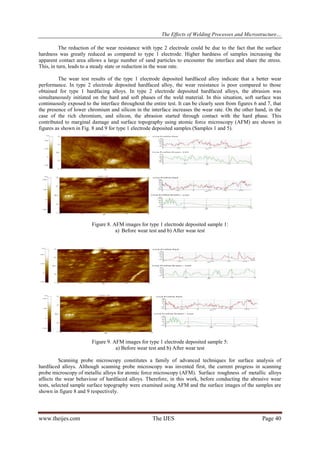


![The Effects of Welding Processes and Microstructure…
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 43
effectively stop the abrasive form cutting or ploughing into the surface layer during the wear process, thereby
noticeably lowering the wear loss. However, the grooves were not deeper than samples 1 and 3. This hardfacing
deposit presented higher abrasion resistance, because the large quantity of carbides rich in titanium, uniformly
distributed in the matrix, blocked the abrasive particles. Further, the resistance of silica, manganese and
chromium elements to the abrasive could be attributed to its higher hardness. Further observations of Figure 12
also provide evidence of cutting and cracking of the carbides. This is due to the hardness of the carbide groups
in the sample 5 being lower than that of abrasive SiO2. It is reasonable to believe that the wear resistance of the
materials will increase if the hardness of the hardfacing alloy is improved.
Analysis of Fractography of worn out specimens : The Fractography analysis has been done for low, medium
and high worn out specimens based on welding parameters such as current (200 and 300 A) and travel speed
(21.4 cm/min) after dry sand abrasion testing. Figures 10-12 shows the scanned electron fractography of
chromium hard faced with welding technology using varying welding current. All samples shows directional
solidification after welding chromium as hardfacing on low carbon steel specimens. Figure 10(a & b) reports
chromium hard faced mild steel using 200 ampere current but it shows more wear loss compared to other two
specimens and both sample shows a fair amount of scraches since the size of test sand is bigger and harder than
that of surface coatings. Similarly the figures 11 (a & b) shows the chromium hard faced mild steel using 200
ampere current and at normal running speed, indicated that more wear resistance compared to figure 10 (a & b).
Figure 12 (a & b) shows randomly distrbuted pits approximately 10 to 20 micrometer which is close to matrix.
Surface coating using 300 ampere and normal welding speed is decrease gradually as welding current increases.
The chromium plated using 300 ampere and at moderate travel speed shows the high wear resistance
compared other two samples. The rate of wear of chromium welded using 200 ampere and moderate speed
almost is twice than the other samples prepared using 300 ampere as shown in the figures 10 and 12
respectively. This wear loss is predicted through the fractography of rubber wheel abrasion test as shown in the
figure 10 and 12 (a & b) respectively. It is clearly indicated that, the wear track will be small and narrow
indicates there will be less in wear and wear resistance is increased from the specimen 8 & 5 respectively. Also,
results indicate that, the wear resistance increases with increasing hardness. The wear loss will be 1.6075 grams
for the specimen 1 which is at 377 HV 0.5 is decreased by 0.6007 of the specimen 5 which is hardness 418 HV
0.5. It is clearly observed both from wear results and fractography, the wear resistance is increased by 62% by
varying welding current and travel speed and keeping welding parameters is constant.
V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
SEM photographs showing as weld dendritic structure of the Fe-Cr-C hardfacing alloy, eutectic
carbides, mapping elements Fe-Cr-C of austenite and eutectic carbide. Fractography analysis was conducted to
worn-out specimens of low medium and high abrasion resistance. Results showed that small and narrow wear
track clearly indicates there will be less in wear and the wear resistance increases with increasing hardness. It is
clear that a significant effect of primary carbides in the weld deposits leading to improved abrasive wear.
Microstructure plays an important role in the abrasive wear of the weld deposits, though a linear relationship
between wear resistance and hardness has been observed for similar microstructural characteristics,
microstructure having coarser carbide and less grain boundary area, possesses better wear resistance than
microstructure containing fine carbide and fine grain size resistance. ASTM G-65 is a reliable low stress
abrasion test to assess the performance of the hardfacing deposits used in actual service conditions.Results
reveal that weld metal chemistry, welding heat input and test duration have significant influence on abrasion
resistance. Hardness can be used as a predictor of wear resistance only for weld deposits having similar
microstructural characteristics.Wear resistance increases with increase in chromium, silicon and carbon content
of weld deposit as well as with increase in heat input.The hardness mainly depends on process parameters such
as welding current, speed of arc travel and voltage.
REFERENCES
[1] P. Crook, “ Friction and wear of hardfacing alloys”, ASM Handbook, Friction, Lubrication and Wear Technology, vol. 18, pp.
758-762, 1992.
[2] I.M. Hutching, “Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials”, Tribology, pp. 133-171, 1992.
[3] S. Chatterjee, T.K. Pal, “Wear behavior of hardfacing deposits on cast iron”, Wear 255, pp. 417-425, 2003.
[4] S.H. Choo, C.K. Kim, K. Euh, S. Lee, J.Y. Jung, S. Alm, “Correlation of microstructure with the wear resistance and fracture
toughness of hardfacing alloys reinforced with the complex carbides” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31A, pp. 3041-3052, 2000.
[5] R.S. Chandel, “Hardfacing consumables and their characteristics for mining and mineral processing industry”, Indian Weld, pp.
26–34, 2001.
[6] O.N. Dogan, J.A. Hawk, G. Laird II, “Solidification structure and abrasion resistance of high chromium white irons”,
Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28A, pp. 1315–1328, 1997.
[7] C.E.C. Rense, G.R. Edwards, H.R. Frost, “The effect of open-arc process variables on the microstructure and wear resistance of a
typical chromium-carbide-type hardfacing deposit”, J. Mater. Energy Syst. 5 (3), pp. 149–159, 1983.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f031201035044-150218035427-conversion-gate02/85/The-Effects-of-Welding-Processes-and-Microstructure-on-3-Body-Abrasive-Wear-Resistances-for-Hardfacing-Deposits-9-320.jpg)
![The Effects of Welding Processes and Microstructure…
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 44
[8] H. Berns, A. Fischer, “Wear resistant of Fe-Cr-C hard surfacing weld deposits with additions of B, Ti and Mn, in: K.C.
Ludema (Ed.)”, Wear of Materials, ASME, New York, pp. 298–302, 1983.
[9] L.Xu and N.Kennon, “A Study of the Abrasive Wear of Carbon Steels”, Wear, Vol 148, pp 101-112, 1991.
[10] H. Berns, A. Fischer, “Microstructure of Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Alloys with additions of Nb, Ti &, B”, Materials Characterization,
vol. 39, pp. 499-527, 1997.
[11] M.H. Korkut, O. Yilmaz, S. Buytoz, “Effect of aging on the microstructure and toughness of the interface zone of a gas tungsten
arc (GTA) synthesized Fe–Cr–Si–Mo–C coated low carbon steel”, Surf. Coat. Technol, 157, pp. 5–13, 2002.
[12] J. Larsen-Badse, “The abrasion resistance of some hardened and tempered carbon steels”, Trans. Metall.S.O.C., A.I.M.E., pp.
1461- 1466, 1966.
[13] S. Bhattacharaya, “Wear and friction in steel, aluminium and magnesium alloy, pearlitic and spheroidized steels”, Wear, vol. 61,
pp. 133-141, 1980.
[14] P.J. Mutton, J.D. Watson, “Some effects of microstructure on abrasive resistance on abrasive resistance of metals”, Wear, vol.
48, pp. 385-398, 1978.
[15] K.H. ZumGahr, “Microstructure and wear of materials”, Tribology Series 10, 1986.
[16] M.A. Moore, “The abrasive wear resistance of surface coatings”, Agricultural of Eng. Res., vol. 20, pp. 167-179, 1974.
[17] H.R. Shetty, T.H. Kosel, N.F. Fiore, “A study of abrasive wear mechanism in cobalt bases alloys”, Wear, vol. 84(3), pp. 327-343,
1983.
[18] R.S. Chandel, “Hardfacing consumables and their characteristics for mining and mineral processing industry”, Indian Weld. J.,
pp. 26–34, 2001.
[19] D.J. Kotecki, J.S. Ogborn, “Abrasion resistance of iron-based hardfacing alloys”, Weld. J., vol. 74 (8), 269s–278s. 1995.
[20] D.K. Dwivedi, “Microstructure and abrasive wear behaviour of iron base hardfacing”, Mater. Sci. Technol, vol. 10 1326–1330,
2004.
[21] C.E.C. Rense, G.R. Edwards, H.R. Frost, “The effect of open-arc process variables on the microstructure and wear resistance of a
typical chromium-carbide-type hardfacing deposit”, J. Mater. Energy Syst. 5 (3), pp. 149–159, 1983.
[22] H. Berns, A. Fischer, “Wear resistant of Fe-Cr-C hard surfacing weld deposits with additions of B, Ti and Mn, in: K.C. Ludema
(Ed.)”, Wear of Materials, ASME, New York, pp. 298–302, 1983.
[23] Y.F. Zhou, Y.L. Yang, D. Li, J. Yang, Y.W. Jiang, X.J. Ren and Q.X. Yang, “Effect of Titanium content on microstructure and
wear resistance of Fe-Cr-C hardfacing Layers”, Welding Journal, vol. 91, pp. 230-236, 2012.
[24] H.X. Chen, Z.C. Chang, J.C. Lu, H.T. Lin, Wear 166, 197-201, 1993.
1. Dr.K.M.Kenchi Reddy is born in Karnataka, India on 4thAugust 1961. He earned his
Undergraduate degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1986 from University of Mysore,
Karnataka, India, Postgraduate degree in Production Engineering and System Technology
from Mysore University in the year 1994 and Ph.D in Hardfacing on Mild Steel from
VTU, Belgaum, India in the year 2013. Presently working as Professor in the Department
of Mechanical Engineering, Sri Krishna Institute of Technology, Bangalore. He has
published 12 papers in National/ International conferences/journals. He is a Life Member
of Indian Society for Technical Education
2. Dr. C. T Jayadeva is born in Karnataka, India on 18th July 1963. He earned his
Undergraduate degree in Industrial and Production Engineering in 1986 from University
of Mysore, Karnataka, Postgraduate degree in Industrial Engineering from university of
Calicut, Kerala in the year 1993 and Ph, D in Quality Management from VTU, Belgaum,
India in the year 2008. He worked as Principal at Yagachi Institute of Technolgy, Hassan,
Karnataka and presently working as Professor in the Department of Mechanical
Engineering, AIT, Chikmaglur, Karnataka, He has published 24 papers in
National/International conferences/journals. He is a Life Member of Indian Society for
Technical Education.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f031201035044-150218035427-conversion-gate02/85/The-Effects-of-Welding-Processes-and-Microstructure-on-3-Body-Abrasive-Wear-Resistances-for-Hardfacing-Deposits-10-320.jpg)