Foundation of computing history final
- 1. K. P de Silva R.V Premabandu1
- 2. Introduction Considers various pioneers and their contribution to the Computing history. Their Concepts and Theories. How they became the basis of Computing. 2
- 3. Content George Boole Boolean Algebra Charles Babbage Difference Engine Analytic Engine Formalism Alan Turing Turing Machines Enigma Codes Turing Test in AI Claude Shannon Boolean Algebra and Switching Circuits Information Theory Cryptography Von Neumann Von Neumann Architecture. Konrad Zuse 3
- 4. George Boole Nineteenth century mathematician, His calculus of logic is known as Boolean Algebra. Introduced two quantities “0” and “1”. He then employed symbols such as x, y, z, etc., to represent collections or Classes. Introduced three operators (+ , - , x). These symbols obeyed a rich collection of algebraic laws such as Additive Identity, Associativity, Commutativity and etc. (1815–1864) 4
- 5. Boolean Algebra Foundation of all modern computers. Consists of propositions that are either true or false. Variables (e.g., A, B, etc.) are used to stand for propositions. Propositions must be either true or false. E.g. 2 + 2 = 4 is true. 2 ∗ 5 = 11 is false. Propositions may be combined using logical connectives to form new propositions. 5
- 6. Logical Connectives The standard logical connectives are… AND - ∧ OR - ∨ NOT - ¬ These connectives may be expressed using the other logical connectives Implication (⇒) Equivalence (⇔) E.g. A ⇒ B is equivalent to ¬A∨B E.g. A ⇔ B is equivalent to (A ⇒ B) ∧ (B ⇒ A) 6
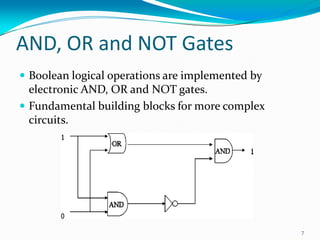
- 7. AND, OR and NOT Gates Boolean logical operations are implemented by electronic AND, OR and NOT gates. Fundamental building blocks for more complex circuits. 7
- 8. Charles Babbage Charles Babbage is considered to be one of the fathers of computing. He was interested in a method that calculation could be done mechanically. Introduced a design concept for Difference Engine and Analytic Engine. (1791) 8
- 9. Difference Engine Built in 1853. Compute polynomials of degree 4 on 15-digit numbers. Compute and print mathematical tables mechanically. The only operation that the Difference Engine can perform is the addition. Finite differences was the concept of calculating the answers. A key weakness is that it requires the intervention of humans to perform the calculation. 9
- 10. Difference Engine Difference Engine is on display in the Science Museum in London. 10
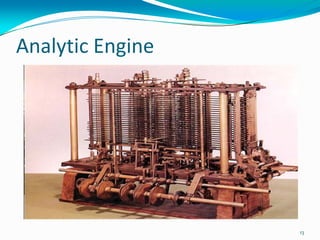
- 11. Analytic Engine Babbage proposed a revolutionary idea for analytic engine to resolve weaknesses of difference engine. Built in 1978. Included a processor, memory. Way to input information and output results. Capable of executing all possible tasks that may be expressed in algebraic notation. Used punched cards to store programs to perform the analysis and computation in the Analytic Engine. 11
- 12. Analytic Engine Punched cards in the design was extremely powerful. Two types Operation Cards Variable Cards Operation cards are used to define the operations. Variable cards define the variables. Ada Lovelace suggested to a method write a program in Analytic Engine. Over 100 years before Von Neumann’s architecture. 12
- 14. Formalism Formalism was proposed by David Hilbert. This formal system is the basis of modern predicate logic. A formal system consists of a formal language. Included axioms, definitions, universal and existential quantification, and formalization of proof. Determines the truth or falsity of any mathematical statement based on a Algorithm with set of rules. 14
- 15. Formalism E.g.1 x = y; this returns true if x is the same as y, and false otherwise. E.g.2 More complex expression such as f (x, y, z) = w is true if f (x, y, z) is identical with w, and false otherwise. E.g.3 P(x) returns true if x is prime. where P() is termed a concept. “P(5) = true” 15
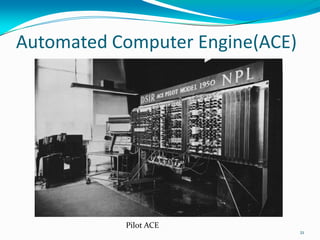
- 16. Alan Turing Was a British mathematician who was highly influential in the development of Computer Science. Engaged in the Design work in the development of first stored program computer.(ACE) Introduced the concept of Turing machine. Designed a electromechanical machine known has bombe to break in to Enigma Codes. (1912-1954)16
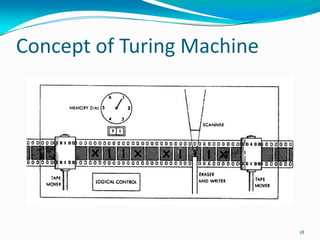
- 17. Turing Machine Turing machine is very simple machine. Equivalent to an actual physical Computer. The machine may read from and write to the tape. Has an associated set of rules that defines its behavior. Programmed to solve any problem for which there is an algorithm. It was used to determine the solvability of certain problem. 17
- 18. Concept of Turing Machine 18
- 19. Enigma Machine & Enigma Codes The Enigma machine 19
- 20. Bombe Machine Turing was able brake Enigma codes by his Bombe machine. Cardboard replica of bombe. 20
- 21. Automated Computer Engine(ACE) Pilot ACE 21
- 22. Turing Test Turing devised a famous experiment that would allow a computer to be judged as a conscious and thinking machine. The concept of this Turing test was the foundation of Artificial Intelligence. 22
- 23. Claude Shannon Shannon found that Boolean algebra could be employed to simplify the design of circuits and telephone routing switches. He laid the foundation of modern Information Theory. Shannon proposed the idea of converting any kind of data to binary digits. 23
- 24. Boolean Algebra & Switching Circuits Switching circuit “Xab” between two terminals a and b Xab = 0 if open Xab = 1 if closed 24
- 25. Information Theory Sending information rapidly and reliably from the source point to the destination point without any distraction. 25
- 26. Cryptography Secure way of communication between two parties. Messages are encrypted according to a Mathematical function. 26
- 27. John von Neumann Hungarian mathematician. Made fundamental contributions to a vast number of fields including computer science. His work on Quantum Mechanics was very influential. He introduced an Architecture during his work on ENIAC & EDVAC. 27
- 28. Von Neumann Architecture The early machines could perform only a particular task. This architecture uses a single store for both machine instructions and programs. Much simpler to reconfigure the computer for a different task. 28
- 30. Manchester Mark I was the first computer with Von Neumann architecture. Ferranti produced the world’s first commercial computer in 1951. Von Neumann Architecture 30
- 32. Konrad Zuse Was a German Engineer. Pioneered in building first functional tape stored, program-controlled computer.( Z3) He designed the first high-level programming language Plankalkül. 32
- 33. Summary Considered the contributions of important people in the history of computing including Boole, Babbage, Shannon, Turing and von Neumann. Boole was an English mathematician who developed Boolean Algebra which is the foundation of all modern computers. Charles Babbage did pioneering work on the Difference Engine and Analytic Engine. Turing is famous for his work on a theoretical mathematical machine termed the “Turing Machine”. 33
- 34. Summary He also made contributions to the cryptography and to Artificial Intelligence. Claude Shannon was the first person to see the applicability of Boolean Algebra to simplify the design of circuits and telephone routing switches. Von Neumann was a mathematician gave his name to the Von Neumann architecture that is used in almost all computers. Zuse was a German engineer who developed the Z3 machine in 1941. He also developed the Plankalkul high-level programming language in 1946. 34
- 35. References A Brief History of Computing by Gerard O’Regan. www.wikipedia.com 35
- 37. 37