Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing in Cloud Databases
- 1. Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing in Cloud Databases Junpei Kawamoto (Kyushu University, Japan) Patricia L. Gillett (École Polytechnique de Montréal)
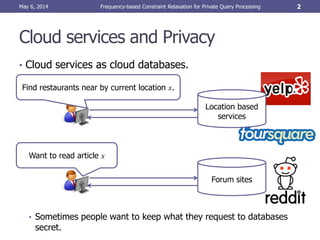
- 2. Cloud services and Privacy • Cloud services as cloud databases. • Sometimes people want to keep what they request to databases secret. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 2 Find restaurants near by current location x. Location based services Want to read article x Forum sites
- 3. Private query processing • Methodologies to obtain data w/o exposing queries. • Several protocols such as cPIR† & bbPIR†† are introduced. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 3 Cloud Database Current location x query res. Encode x Compute query results w/o decoding queries †Kushilevitz, E. and Ostrovsky, R.: Replication Is Not Needed: Single Database, Computationally- Private Information Retrieval, Proc. of the 38th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 364-373, 1997. E.g. Location Based Services ††Wang, S., Agrawal, D., and Abbadi, A.: Generalizing PIR for Practical Private Retrieval of Public Data, Proc. of the 24th Annual IFIP WG 11.3 Working Conference on Data and Applications Security and Privacy, pp. 1-16, 2010.
- 4. Three ideas of private queries • We introduce three ideas for our discussion; • Search intention: what users hope to obtain from cloud services, • Query: request users send to servers to obtain data, • Handled set: data set which servers must check to compute the results. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 4 Location x Want information associated with location x (search intention) query res. Cloud DB Must check these items to compute the result(Handled set) Handled set for x
- 5. Existing private querying protocols • Most existing protocols impose two constraints: 1. Queries are encoded in such a way that servers can handle query processes but cannot actually decode queries; 2. Servers are made to check all data in the databases when computing any query result. • (2) means servers cannot distinguish any data in the DB. • Servers spend O(n) computational cost executing each query, where the database has n entries. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 5 Cloud DB check all data any time query
- 6. • There are cases in which we do not need to retrieve the entire database to sufficiently obscure search intentions. • It may be enough to hide where I am in downtown. • What area is enough to ensure our privacy? • E.g. • Servers may guess the search intention is x with high probability. • We should consider frequency of search intentions. Constraint Relaxation May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 6 shop x shop a shop b shop c Popular place Unpopular places Specified by a handled set a handled set
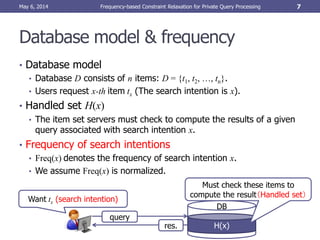
- 7. Database model & frequency • Database model • Database D consists of n items: D = {t1, t2, …, tn}. • Users request x-th item tx (The search intention is x). • Handled set H(x) • The item set servers must check to compute the results of a given query associated with search intention x. • Frequency of search intentions • Freq(x) denotes the frequency of search intention x. • We assume Freq(x) is normalized. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 7 Want tx (search intention) query res. DB H(x) Must check these items to compute the result(Handled set)
- 8. Definition: Query Risk • A measure of exposure risk for private queries. • The query risk of search intention x and handled set H(x) is • Conditional probability that the search intention is x given that we know the handled set H used. • The more frequent x is, the higher the risk becomes. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 8 )( )(Freq )(Freq ))(|(Risk xHy y x xHx frequenc y E.g. • Risk(3|{1,2,3,4,5}) = 3/9 • Risk(1|{1,2,3,4,5}) = 1/9 • Risk(1|{1,2}) = 1/3
- 9. Definition: Privateness • The maximum risk of complete protocols: • We assume query risks should be less than or equals to the maximum risk of complete protocols: • Complete protocols are widely accepted that is the max. risk is, too. • Our approach will also be considered private if it satisfies this condition. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 9 ))(|(Riskmax))(|(Risk completerelaxed yHyxHx Dy ))(|(Riskmax complete xHx Dx i.e. w/o relaxation Our handled set Handled set for existing protocols
- 10. Definition: Query processing cost • Query processing costs on servers. • We evaluate them by the size of handled sets. • The cost of search intention x is . May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 10 |)(|)(Cost xHx query res. DB H(x) H(x) query res. DB vs.
- 11. The problem • Find handled set H such that, for search intention x: 1. , 2. , 3. minimize Cost(x), 4. if multiple solutions have equal cost, chose the one maximizes • We solve this problem by Dynamic Programming. • O(n) algorithm but details are in our paper. • We also extend these problem and algorithm to • range queries in 1D data, • exact match queries in 2D data. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 11 x Î H(x) )|(Riskmax))(|(Risk DyxHx Dy )( )(FreqxHy y
- 12. The protocol • Our protocol employs some existing protocol (PIR, etc.). • We assume the frequencies are public information. • User: whose search intension is x, 1. Compute optimized handled set H(x) using query frequencies. 2. Compute a private query for x assuming a DB has only items in H(x). 3. Send the query and H(x) to the cloud server. • The cloud server receiving the query, 1. Consider a sub-database consists of items in H(x). 2. Process the received query and return the result to the user. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 12 query res. H(x) : sub-DB Cost: O(|H(x)|)
- 13. • Dataset • Query logs from †. • Sampled 100,000 songs and 1,800,145 queries. Evaluation May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 13 †http://www.dtic.upf.edu/~ocelma/MusicRecommendationDataset/lastfm-1K.html Frequency of search intention x. x-axis: search intentions x y-axis: # of times users requested item tx
- 14. Evaluation • Comparison of query risks. • In most cases, risks are bigger than those of the complete protocols. • Do not exceed the maximum risks of the complete protocol. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 14 relaxed (avg.) is computed by Dx xHxx ))(|(Risk)(Freq min. max. avg. comp. 5.6×10−7 3.9×10−3 1.0×10−5 relaxed 3.4×10−3 3.9×10−3 3.5×10−3 Query risk of search intention x.
- 15. Evaluation • Comparison of query costs. • Our relaxation methodologies reduce costs in most cases. • The average cost is 6.5% that of complete protocols. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 15 relaxed (avg.) is computed by Freq(x)´Cost(x) xÎD å min. max. avg. comp. 100000 100000 100000 relaxed 2 100000 6417 Query cost of search intention x.
- 16. Conclusion • We introduced a frequency-based constraint relaxation methodology for private queries. • We relaxed constraint (2) of the complete protocols so that only a subset of the database is retrieved for each query. • We evaluated our proposal using a real dataset from . • Our protocol can reduce computational costs in servers in most cases, • The risk of a query being exposed is not bigger than the maximum risk in complete protocols. May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 16 Servers must check all data in the databases when computing any query result.
- 17. Acknowledgement • This work is partly supported by • The Nakajima Foundation, • Artificial Intelligence Research Promotion Foundation, • Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (26730065), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS). May 6, 2014 Frequency-based Constraint Relaxation for Private Query Processing 17 Thank you for your attention!