From data to AI with the Machine Learning Canvas by Louis Dorard Slides
- 2. From Data to AI with the MACHINE LEARNING CANVAS @louisdorard #bigdataspain
- 3. “A breakthrough in machine learning would be worth ten Microsofts” –Bill Gates
- 4. “In the next 20 years, machine learning will have more impact than mobile has.” –Vinod Khosla
- 5. 4
- 6. Skiing down the Gartner hype cycle with Waldo & the Machine Learning Canvas
- 10. What is ML?
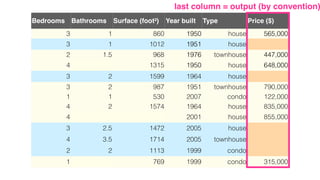
- 13. Bedrooms Bathrooms Surface (foot²) Year built Type Price ($) 3 1 860 1950 house 565,000 3 1 1012 1951 house 2 1.5 968 1976 townhouse 447,000 4 1315 1950 house 648,000 3 2 1599 1964 house 3 2 987 1951 townhouse 790,000 1 1 530 2007 condo 122,000 4 2 1574 1964 house 835,000 4 2001 house 855,000 3 2.5 1472 2005 house 4 3.5 1714 2005 townhouse 2 2 1113 1999 condo 1 769 1999 condo 315,000
- 14. Bedrooms Bathrooms Surface (foot²) Year built Type Price ($) 3 1 860 1950 house 565,000 3 1 1012 1951 house 2 1.5 968 1976 townhouse 447,000 4 1315 1950 house 648,000 3 2 1599 1964 house 3 2 987 1951 townhouse 790,000 1 1 530 2007 condo 122,000 4 2 1574 1964 house 835,000 4 2001 house 855,000 3 2.5 1472 2005 house 4 3.5 1714 2005 townhouse 2 2 1113 1999 condo 1 769 1999 condo 315,000 last column = output (by convention)
- 17. 16 Some use cases • Real-estate • Spam filtering • City bikes • Reduce churn • Anticipate demand property price email spam indicator location, context #bikes customer churn indicator product, store, date #sales Zillow Gmail BikePredict ChurnSpotter Blue Yonder RULES
- 18. @louisdorard
- 19. 1. Descriptive analysis 2. Predictive analysis 3. Prescriptive analysis 4. Automated decisions 18 (Big?) Data analysis “big data”, reporting & old-school BI… now we’re talking!
- 22. 1. Show churn rate against time 2. Predict which customers will churn next 3. Suggest what to do about each customer (e.g. propose to switch plan, send promotional offer, etc.) 21 Churn analysis
- 23. • Who: SaaS company selling monthly subscription • Question asked:“Is this customer going to leave within 1 month?” • Input: customer • Output: no-churn or churn • Data collection: history up until 1 month ago 22 Churn prediction
- 24. Assume we know who’s going to churn. What do we do? • Contact them (in which order?) • Switch to different plan • Give special offer • No action? 23 Churn prediction prevention
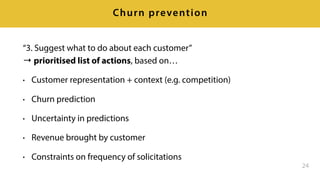
- 25. “3. Suggest what to do about each customer” → prioritised list of actions, based on… • Customer representation + context (e.g. competition) • Churn prediction • Uncertainty in predictions • Revenue brought by customer • Constraints on frequency of solicitations 24 Churn prevention
- 26. • Taking action for each TP (and FP) has a cost • For each TP we“gain”: (success rate of action) * (revenue /cust. /month) • Imagine… • perfect predictions • revenue /cust. /month = 10€ • success rate of action = 20% • cost of action = 2€ • What is the ROI? 25 Churn prevention ROI
- 29. 28 The Machine Learning Canvas The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- 30. • Not an adaptation of the Business Model Canvas • Describe the Learning part of a predictive system / an intelligent application: • What data are we learning from? • How are we using predictions powered by that learning? • How are we making sure that the whole thing“works”through time? 29 The Machine Learning Canvas
- 31. –Ingolf Mollat, Principal Consultant at Blue Yonder “The Machine Learning Canvas is providing our clients real business value by supplying the first critical entry point for their implementation of predictive applications.”
- 32. 31 Cross Industry Standard Process for Data Mining By Kenneth Jensen - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 ML Canvas
- 33. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. background specifics LEARNPREDICT EVALUATE GOAL (what, why, who) how how how well
- 36. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. background specifics LEARNPREDICT EVALUATE GOAL (what, why, who) Domain Integration Predictive Engine
- 37. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. background specifics #1 #2#3#4 #5 #6 #7#8 #9#10
- 38. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. On 1st day of every month: • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit customers Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight. Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s customers. • Monitor churn rate • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1
- 39. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. On 1st day of every month: • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit customers Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight. Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s customers. • Monitor churn rate • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1
- 40. • We predict customer would churn but they don’t… • Great! Prevention works! • Sh*t! Data inconsistent… • (Store which actions were taken?)
- 42. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. On 1st day of every month: • Randomly filter out 50% of customers (hold-out set) • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit customers Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight. Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used • Monitor churn rate • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1 Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s customers.
- 43. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. On 1st day of every month: • Randomly filter out 50% of customers (hold-out set) • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit customers Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight. Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s hold-out set (or the whole set, when initializing this system). We do this overnight (along with making predictions). • Monitor churn rate • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1
- 44. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. On 1st day of every month: • Randomly filter out 50% of customers (hold-out set) • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit customers Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight. Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s hold-out set (or the whole set, when initializing this system). We do this overnight (along with making predictions). • Accuracy of last month’s predictions on hold-out set • Compare churn rate & lost revenue between last month’s hold-out set and remaining set • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations • Monitor ROI (based on diff. in lost revenue & cost of solicitations) Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1
- 45. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. On 1st day of every month: • Randomly filter out 50% of customers (hold-out set) • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit customers Before soliciting customers: • Evaluate new model’s accuracy on pre-defined customer profiles • Simulate decisions taken on last month’s customers (using model learnt from customers 2 months ago). Compute ROI w. different # customers to solicit & hypotheses on retention success rate (is it >0?) Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight (along with building the model that powers these predictions and evaluating it). Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s hold-out set (or the whole set, when initializing this system). We do this overnight (along with offline evaluation and making predictions). • Accuracy of last month’s predictions on hold-out set • Compare churn rate & lost revenue between last month’s hold-out set and remaining set • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations • Monitor ROI (based on diff. in lost revenue & cost of solicitations) Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1
- 46. The Machine Learning Canvas (v0.4) Designed for: Designed by: Date: Iteration: . Decisions How are predictions used to make decisions that provide the proposed value to the enduser? ML task Input, output to predict, type of problem. Value Propositions What are we trying to do for the enduser(s) of the predictive system? What objectives are we serving? Data Sources Which raw data sources can we use (internal and external)? Collecting Data How do we get new data to learn from (inputs and outputs)? Making Predictions When do we make predictions on new inputs? How long do we have to featurize a new input and make a prediction? Offline Evaluation Methods and metrics to evaluate the system before deployment. Features Input representations extracted from raw data sources. Building Models When do we create/update models with new training data? How long do we have to featurize training inputs and create a model? Live Evaluation and Monitoring Methods and metrics to evaluate the system after deployment, and to quantify value creation. machinelearningcanvas.com by Louis Dorard, Ph.D. Licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License. Before soliciting customers: • Evaluate new model’s accuracy on pre-defined customer profiles • Simulate decisions taken on last month’s customers (using model learnt from customers 2 months ago). Compute ROI w. different # customers to solicit & hypotheses on retention success rate (is it >0?) Predict answer to “Is this customer going to churn in the coming month?” • Input: customer • Output: ‘churn’ or ‘no- churn’ class (‘churn’ is the Positive class) • Binary Classification Context: • Company sells SaaS with monthly subscription • End-user of predictive system is CRM team We want to help them… • Identify important clients who may churn, so appropriate action can be taken • Reduce churn rate among high-revenue customers • Improve success rate of retention efforts by understanding why customers may churn • CRM tool • Payments database • Website analytics • Customer support • Emailing to customers Every month, we see which of last month’s customers churned or not, by looking through the payments database. Associated inputs are customer “snapshots” taken last month. Every month we (re-)featurize all current customers and make predictions for them. We do this overnight (along with building the model that powers these predictions and evaluating it). Basic customer info at time t (age, city, etc.) Events between (t - 1 month) and t: • Usage of product: # times logged in, functionalities used, etc. • Cust. support interactions • Other contextual, e.g. devices used Every month we create a new model from the previous month’s hold-out set (or the whole set, when initializing this system). We do this overnight (along with offline evaluation and making predictions). • Accuracy of last month’s predictions on hold-out set • Compare churn rate & lost revenue between last month’s hold-out set and remaining set • Monitor (#non-churn among solicited) / #solicitations • Monitor ROI (based on diff. in lost revenue & cost of solicitations) Customer retention Louis Dorard Sept. 2016 1 On 1st day of every month: • Randomly filter out 50% of customers (hold-out set) • Filter out ‘no-churn’ • Sort remaining by descending (churn prob.) x (monthly revenue) and show prediction path for each • Solicit as many customers as suggested by simulation
- 47. • Assist data scientists, software engineers, product and business managers, in aligning their activities • Make sure all efforts are directed at solving the right problem! • Choose right algorithm / infrastructure / ML solution prior to implementation • Guide project management • machinelearningcanvas.com 46 Why fill in ML canvas?
- 49. –Jeremy Howard “Great predictive modeling is an important part of the solution, but it no longer stands on its own; as products become more sophisticated, it disappears into the plumbing.”
- 50. Example: send promotional offers via email to SaaS customers, based on predicted churn • Compute feature values for given input (a.k.a.“featurize”; involves merging data sources, aggregating data…) • Collect training data (inputs and outputs) • Provide predictive model from given training set (i.e. learn) • Provide prediction against model for given input (context) • Provide optimal decision from given contextual data, predictions, uncertainties, constraints, objectives, costs • Apply given decision 49 Software components in real-world ML / AI
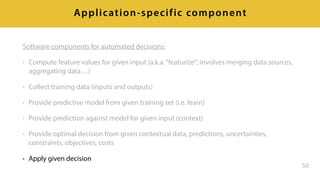
- 51. Software components for automated decisions: • Compute feature values for given input (a.k.a.“featurize”; involves merging data sources, aggregating data…) • Collect training data (inputs and outputs) • Provide predictive model from given training set (i.e. learn) • Provide prediction against model for given input (context) • Provide optimal decision from given contextual data, predictions, uncertainties, constraints, objectives, costs • Apply given decision 50 Application-specific component
- 52. Software components for automated decisions: • Compute feature values for given input (a.k.a.“featurize”; involves merging data sources, aggregating data…) • Collect training data (inputs and outputs) • Provide predictive model from given training set (i.e. learn) • Provide prediction against model for given input (context) • Provide optimal decision from given contextual data, predictions, uncertainties, constraints, objectives, costs • Apply given decision 51 Optimization / Operations Research component
- 53. Software components for automated decisions: • Compute feature values for given input (a.k.a.“featurize”; involves merging data sources, aggregating data…) • Collect training data (inputs and outputs) • Provide predictive model from given training set (i.e. learn) • Provide prediction against model for given input (context) • Provide optimal decision from given contextual data, predictions, uncertainties, constraints, objectives, costs • Apply given decision 52 Machine Learning components
- 54. Software components for automated decisions: • Compute feature values for given input (a.k.a.“featurize”; involves merging data sources, aggregating data…) • Collect training data (inputs and outputs) • Provide predictive model from given training set (i.e. learn) • Provide prediction against model for given input (context) • Provide optimal decision from given contextual data, predictions, uncertainties, constraints, objectives, costs • Apply given decision 53 Data Engineering components
- 55. 54
- 56. follow us: @papisdotio WE’RE HIRING!