Functional Programming with Immutable Data Structures
- 1. Functional Programming with Immutable Data Structures Why Imperative Languages are Fundamentally Broken in a Multi-Threaded Environment Ivar Thorson Italian Institute of Technology November 2, 2010
- 2. Ivar Thorson
- 7. Rigid Body Dynamics Simulations
- 8. The Next 37 minutes:
- 9. Important abstractions of functional programming
- 10. particularly for a 4-year old language
- 12. Rich Hickey
- 13. What I have learned from his work
- 14. Clojure: Blending theoretical abstractions + practical know-how
- 15. Target Audience: C, C++, Java, Matlab Programmers
- 16. Tempting to start with a feature tour!
- 17. But you won’t understand why Clojure is cool without context
- 20. Actually, I’m going to try to knock the cup out of your hand.
- 22. Three Outdated Concepts 1. Variables
- 23. Three Outdated Concepts 1. Variables 2. Syntax
- 24. Three Outdated Concepts 1. Variables 2. Syntax 3. Object Orientation
- 25. Goal is to convince you that
- 26. Goal is to convince you that 1. shared mutable data is now a philosophically bankrupt idea.
- 27. Goal is to convince you that 1. shared mutable data is now a philosophically bankrupt idea. 2. code and data should be structured as trees
- 28. Goal is to convince you that 1. shared mutable data is now a philosophically bankrupt idea. 2. code and data should be structured as trees 3. OOP isn’t the best way to achieve OOP’s goals
- 29. Speaking bluntly
- 30. Speaking bluntly 1. everything you know is wrong (15 min)
- 31. Speaking bluntly 1. everything you know is wrong (15 min) 2. lisp parentheses are better than syntax (10 min)
- 32. Speaking bluntly 1. everything you know is wrong (15 min) 2. lisp parentheses are better than syntax (10 min) 3. OOP inheritance sucks (5 min)
- 33. disclaimer: some hyperbole in previous statements
- 34. Oh noes, too many parentheses!
- 35. Good reasons for parentheses
- 36. Good reasons for parentheses 1. Lisp is homoiconic
- 37. Good reasons for parentheses 1. Lisp is homoiconic 2. Parentheses uniquely define tree-shaped computations
- 38. Good reasons for parentheses 1. Lisp is homoiconic 2. Parentheses uniquely define tree-shaped computations 3. Parentheses enable structural editing
- 39. For now, please be patient
- 40. Introduction: Motivation for multi-threaded programming
- 42. 1. Last 40 years: Moore’s Law
- 43. 1. Last 40 years: Moore’s Law 2. “Transistor count will double every 2 years”
- 44. # of transistors ≈ CPU performance
- 46. Constraining physical relationship between power density, swiching time, oxide thickness
- 48. The future of hardware is increasingly parallel
- 49. The future of software will be ruled by Amdahl’s law
- 51. Some things are sequential: Two women cannot have a baby in 4.5 months.
- 53. 1. Dividing up work is already a hard design task
- 54. 1. Dividing up work is already a hard design task 2. Resource contention makes this problem harder
- 56. Common multi-threaded bugs: Invalid state
- 57. Common multi-threaded bugs: Invalid state Race conditions
- 58. Common multi-threaded bugs: Invalid state Race conditions Deadlocks
- 59. Common multi-threaded bugs: Invalid state Race conditions Deadlocks Livelocks
- 60. Common multi-threaded bugs: Invalid state Race conditions Deadlocks Livelocks Resource starvation
- 61. What if most bugs were merely due to the imperative programming model?
- 62. Part 1: The Functional Programming Style
- 64. Pure functions always return the same result when they get the same input.
- 66. Pure functions don’t... ...look outside their box
- 67. Pure functions don’t... ...look outside their box ...modify anything, anywhere
- 68. Pure functions don’t... ...look outside their box ...modify anything, anywhere ...print messages to the user
- 69. Pure functions don’t... ...look outside their box ...modify anything, anywhere ...print messages to the user ...write to disk
- 70. Pure functions have no side effects
- 71. Nothing would change if you ran the function again – anywhere!
- 72. f (x) = x2 + 1
- 73. Pure functions just return a value, and do nothing more.
- 74. Pure functions compose to other pure functions
- 76. f (a, b, c) = (a + b)/(c ∗ 2)
- 77. Languages that emphasize the use of pure functions are called functional languages
- 78. Imperative languages describe computation in terms of changes to state.
- 79. C, C++, Java, and most engineering languages are imperative.
- 80. Imperative languages describe memory operations instead of purely functional operations.
- 82. Imperative style: directly causing side effects on memory.
- 83. The assignment operator changes memory...often a side effect!
- 84. Could you write a C program...
- 85. Could you write a C program... without any non-local variables?
- 86. Could you write a C program... without any non-local variables? where = is only used for initialization?
- 87. Next: Variables are fundamentally a bad abstraction in multithreaded environments.
- 88. Claim #1. Shared mutable data is now philosophically bankrupt
- 90. x = x + 1
- 91. x = x + 1 x = 3 (...last time I checked!)
- 92. x = x + 1 x = 3 (...last time I checked!) In my universe, 3 = 3 + 1 is never true
- 93. The Big Problem: the concept of variables encourage us to forget about time.
- 94. x[t] = x0 x[t + 1] = x[t] + 1
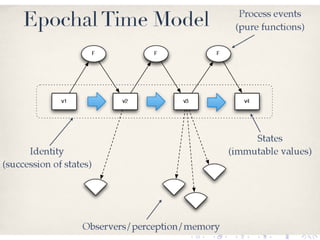
- 95. The value of x for a given t is immutable and unchanging!
- 96. The Most Important Slide
- 97. The Most Important Slide x is a name, an identity of a sequence of values
- 98. The Most Important Slide x is a name, an identity of a sequence of values x has different values at different times
- 99. The Most Important Slide x is a name, an identity of a sequence of values x has different values at different times The values of x are related by pure functions
- 100. The Most Important Slide x is a name, an identity of a sequence of values x has different values at different times The values of x are related by pure functions In this case, by the increment function
- 103. The idea of a variable confuses identity and the most current value!
- 105. Locking: a tactic for winning a battle.
- 106. What we need is a strategy to win the war.
- 107. “What if all data was immutable?” – Rich Hickey (not the first one to ask this question)
- 108. Keeping Old Immutable Data
- 109. Keeping Old Immutable Data x@(t=0) → 5
- 110. Keeping Old Immutable Data x@(t=0) → 5 x@(t=1) → 6
- 111. Keeping Old Immutable Data x@(t=0) → 5 x@(t=1) → 6 x@(t=13) → 7
- 112. Keeping Old Immutable Data x@(t=0) → 5 x@(t=1) → 6 x@(t=13) → 7 x@(t=15) → 8
- 113. Keeping Old Immutable Data x@(t=0) → 5 x@(t=1) → 6 x@(t=13) → 7 x@(t=15) → 8 ...
- 115. The old values of the data are kept and indexed by time
- 116. The old values of the data are kept and indexed by time Data is immutable once created – we cannot/will not change it!
- 117. The old values of the data are kept and indexed by time Data is immutable once created – we cannot/will not change it! Values only destroyed when unneeded
- 118. Doesn’t keeping old copies of data consume too much memory?
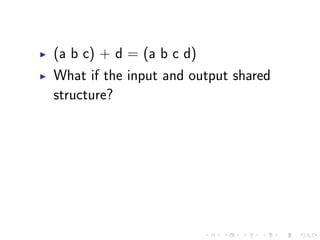
- 120. (a b c) + d = (a b c d)
- 121. (a b c) + d = (a b c d) What if the input and output shared structure?
- 122. (a b c) + d = (a b c d) What if the input and output shared structure? Sharing structure is dangerous for mutable data
- 123. (a b c) + d = (a b c d) What if the input and output shared structure? Sharing structure is dangerous for mutable data ...but sharing structure is safe if the data is immutable.
- 124. The Trick: Represent the list as a tree
- 125. input tree → pure function → output tree
- 127. both trees are immutable but distinct
- 128. Same approach works also for insertions, modifications, deletions, and all other list operations.
- 129. a million threads, a million trees, a million references to trees, zero locks
- 130. If you want a more current worldview, just get its reference
- 131. Advantages of immutable trees:
- 132. Advantages of immutable trees: No locking required
- 133. Advantages of immutable trees: No locking required No ’stopping the world’ to see (readers don’t block writers)
- 134. Advantages of immutable trees: No locking required No ’stopping the world’ to see (readers don’t block writers) Worldview never becomes corrupted
- 135. Advantages of immutable trees: No locking required No ’stopping the world’ to see (readers don’t block writers) Worldview never becomes corrupted Minimizes memory use while maintaining multiple copies
- 136. Advantages of immutable trees: No locking required No ’stopping the world’ to see (readers don’t block writers) Worldview never becomes corrupted Minimizes memory use while maintaining multiple copies Unused nodes are garbage-collected
- 137. We’ve gone a long way, but we’re only half way to real concurrency
- 139. Immutability lets us read concurrently, but not write concurrently to a single piece of data
- 142. How can we coordinate the actions of different threads working on the same data at the same time?
- 143. ”Treat changes in an identity’s value as a database transaction.” – Rich Hickey
- 144. Database Details:
- 145. Database Details: Software Transactional Memory (STM)
- 146. Database Details: Software Transactional Memory (STM) Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC)
- 147. The STM Guarantees:
- 148. The STM Guarantees: Atomicity (All or nothing)
- 149. The STM Guarantees: Atomicity (All or nothing) Consistency (Validation before commits)
- 150. The STM Guarantees: Atomicity (All or nothing) Consistency (Validation before commits) Isolation (Transactions can’t see each other)
- 152. Transactions are speculative and may be retried if there is a collision.
- 153. For even more concurrency:
- 154. For even more concurrency: Sometimes you don’t care about the order of function application
- 155. For even more concurrency: Sometimes you don’t care about the order of function application Commutative writers won’t need to retry
- 156. For even more concurrency: Sometimes you don’t care about the order of function application Commutative writers won’t need to retry Writers don’t interfere with other writers!
- 158. STMs exist for other languages...
- 159. STMs exist for other languages... ... but Clojure is first to have built-in STM with pervasive immutability
- 160. Part 1 Summary: In Clojure...
- 161. Part 1 Summary: In Clojure... ...Readers don’t block anybody
- 162. Part 1 Summary: In Clojure... ...Readers don’t block anybody ...Writers don’t block anybody
- 163. Part 1 Summary: In Clojure... ...Readers don’t block anybody ...Writers don’t block anybody ...Writers retry if conflicting
- 164. Part 1 Summary: In Clojure... ...Readers don’t block anybody ...Writers don’t block anybody ...Writers retry if conflicting ...Writers don’t retry if commutative
- 165. Variables couldn’t do this because:
- 166. Variables couldn’t do this because: Confuse identity and values
- 167. Variables couldn’t do this because: Confuse identity and values Are mutable and can be corrupted
- 168. Variables couldn’t do this because: Confuse identity and values Are mutable and can be corrupted Assume a single thread of control, no interruptions
- 169. Variables couldn’t do this because: Confuse identity and values Are mutable and can be corrupted Assume a single thread of control, no interruptions Maintain only the last written copy
- 170. ”Mutable stateful objects are the new spaghetti code” – Rich Hickey
- 171. ”We oppose the uncontrolled mutation of variables.” – Stuart Halloway
- 172. ”Mutable objects are a concurrency disaster.” – Rich Hickey
- 173. ”The future is a function of the past, but doesn’t change it.” – Rich Hickey
- 174. ”Many people can watch a baseball game, but only one can be at bat.” – Rich Hickey
- 175. Part 2: Revenge of the Lisp
- 176. Claim #2: Your language’s syntax is unneccesarily complex
- 177. Now we’ll explain why lisp has parentheses!
- 179. Pure functions represent computation as trees
- 180. Reason 1: The tree structure is made explicitly visible by the parentheses
- 182. Infix Notation 1 + 1
- 183. Prefix Notation (+ 1 1)
- 184. (fn arg1 arg2 arg3 ...)
- 185. 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
- 186. (+ 1 2 3 4)
- 187. With prefix notation, you can forget about the rules of precedence.
- 188. 6 + 12 / 2 * 3
- 189. (6 + 12) / (2 * 3)
- 190. (/ (+ 6 12) (* 2 3))
- 191. (/ (+ 6p 12) (* 2 3))
- 194. Lisp code’s tree of computation is exceptionally visible and regular.
- 196. Homoiconic = Homo + icon = ”same” + ”representation”
- 197. The property where code & a language primitive look the same.
- 198. An example: Writing C with XML
- 199. for (i=0; i<100; i++) { printf("%dn", i); dostuff(); }
- 200. <for> <init>i = 0</init> <test>i < 100</test> <count>i++</count> <body> <print format="%d" args="i"/> <dostuff/> </body> </for>
- 201. Imagine how simple it would be to use an XML generator to emit compilable source code.
- 202. We could modify our code programmatically.
- 203. In lisp, you can write programs that write programs.
- 204. (list 1 2 3) -> (1 2 3)
- 205. (list ’+ 1 2 3) -> (+ 1 2 3) (+ 1 2 3) -> 6
- 206. (defmacro and ([] true) ([x] x) ([x & rest] ‘(let [and# ~x] (if and# (and ~@rest) and#))))
- 207. Why lispers go nuts:
- 208. Why lispers go nuts: Macros in lisp are far more powerful than in other languages.
- 209. Why lispers go nuts: Macros in lisp are far more powerful than in other languages. You can build new constructs that are just as legitimate as existing constructs like if
- 210. Why lispers go nuts: Macros in lisp are far more powerful than in other languages. You can build new constructs that are just as legitimate as existing constructs like if You can abstract away boilerplate code
- 211. Aside
- 212. Aside If Java used parentheses properly, XML wouldn’t exist
- 213. Aside If Java used parentheses properly, XML wouldn’t exist Lisp parentheses describe structure
- 214. Aside If Java used parentheses properly, XML wouldn’t exist Lisp parentheses describe structure Most languages use ad-hoc syntax, data formats
- 215. Aside If Java used parentheses properly, XML wouldn’t exist Lisp parentheses describe structure Most languages use ad-hoc syntax, data formats Simplicity is elegance
- 216. Reason 3: Structural Editing
- 217. Good editors let you work with code in blocks and forget about the parentheses.
- 219. Hard-to-show Examples When you type (, emacs adds the )
- 220. Hard-to-show Examples When you type (, emacs adds the ) Indentation is automatic
- 221. Hard-to-show Examples When you type (, emacs adds the ) Indentation is automatic You can easily navigate heirarchically
- 222. Hard-to-show Examples When you type (, emacs adds the ) Indentation is automatic You can easily navigate heirarchically Take next three expressions, apply them to a function
- 223. Summary of Lisp Parentheses
- 224. Summary of Lisp Parentheses Parentheses render explicit the tree-structure of your program
- 225. Summary of Lisp Parentheses Parentheses render explicit the tree-structure of your program Homoiconicity lets you write programs with programs
- 226. Summary of Lisp Parentheses Parentheses render explicit the tree-structure of your program Homoiconicity lets you write programs with programs Structural Editing is fun and easy
- 227. Syntax is bad because
- 228. Syntax is bad because It hides the program’s structure
- 229. Syntax is bad because It hides the program’s structure It destroys homoiconicity
- 230. Syntax is bad because It hides the program’s structure It destroys homoiconicity It is needlessly complex
- 231. ”Things should be made as simple as possible – but no simpler.” – Albert Einstein
- 232. Part 3: OOP isn’t the only path to Polymorphism and Code Reuse
- 233. OOP has good goals
- 234. OOP has good goals 1. to group objects together
- 235. OOP has good goals 1. to group objects together 2. to encapsulate
- 236. OOP has good goals 1. to group objects together 2. to encapsulate 3. to dispatch polymorphically
- 237. OOP has good goals 1. to group objects together 2. to encapsulate 3. to dispatch polymorphically 4. to reuse code
- 238. These are all good ideas and good goals.
- 239. However, OOP is not the only way to reach these goals.
- 240. Claim #3: ”Functions compose better than objects.”
- 241. The fundamental mechanism of OOP – the inheritance of data, interfaces, type, or methods from a parent – is often more difficult to use in practice than techniques that use functions to achieve the same effect.
- 242. Functions are simpler than objects.
- 243. Objects are semantic compounds of types, data, and methods.
- 244. Implementation inheritance is bad:
- 245. Implementation inheritance is bad: Forces “is-a” relationship instead of “has-a”, and “has-a” is almost always better
- 246. Implementation inheritance is bad: Forces “is-a” relationship instead of “has-a”, and “has-a” is almost always better Heirarchical nominalization is difficult
- 247. Implementation inheritance is bad: Forces “is-a” relationship instead of “has-a”, and “has-a” is almost always better Heirarchical nominalization is difficult Changes to a class affect all the subclasses
- 248. An example will help clarify.
- 249. Balls
- 250. Balls Ball class (presumably round)
- 251. Balls Ball class (presumably round) rollingBall subclass
- 252. Balls Ball class (presumably round) rollingBall subclass bouncingBall subclass
- 253. Problems
- 254. Problems What happens if we want to make a ball that both rolls and bounces?
- 255. Problems What happens if we want to make a ball that both rolls and bounces? Do/Can we inherit from both?
- 256. Problems What happens if we want to make a ball that both rolls and bounces? Do/Can we inherit from both? What if our ball cracks and loses its bounciness?
- 257. Problems What happens if we want to make a ball that both rolls and bounces? Do/Can we inherit from both? What if our ball cracks and loses its bounciness? Is a non-round rugby ball a subclass of ball too?
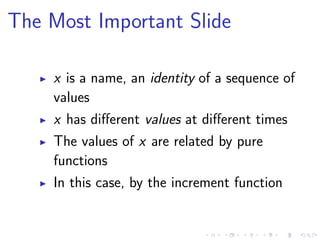
- 259. Interfaces are Simpler Define functional interfaces, but don’t inherit the implementation
- 260. Interfaces are Simpler Define functional interfaces, but don’t inherit the implementation If you want to use another object’s function to accomplish a task, just use it
- 261. Interfaces are Simpler Define functional interfaces, but don’t inherit the implementation If you want to use another object’s function to accomplish a task, just use it No need to encapsulate their function in an object
- 262. Interfaces are Simpler Define functional interfaces, but don’t inherit the implementation If you want to use another object’s function to accomplish a task, just use it No need to encapsulate their function in an object Multiple interfaces are simpler than multiple inheritance
- 263. FREE THE VERBS!! Separate your object methods from your objects!
- 264. Example: Single vs Multiple Dispatch
- 265. Making Drum Noises
- 266. Making Drum Noises Drum, cymbal and stick classes
- 267. Making Drum Noises Drum, cymbal and stick classes When I hit something with the stick, it makes a noise
- 268. Making Drum Noises Drum, cymbal and stick classes When I hit something with the stick, it makes a noise Single Dispatch: drum.makeNoise(drumstick)
- 269. Making Drum Noises Drum, cymbal and stick classes When I hit something with the stick, it makes a noise Single Dispatch: drum.makeNoise(drumstick) cymbal.makeNoise(drumstick)
- 270. The verbs are owned by the nouns.
- 271. But what happens when I add a different stick class?
- 274. Now I will need to modify the drum and cymbal classes and add new methods to handle the mallets!
- 275. When two objects hit, the sound is function of both objects.
- 277. With multi-method functions hit(drumstick, cymbal) = crash
- 278. With multi-method functions hit(drumstick, cymbal) = crash hit(mallet, cymbal) = roar
- 279. With multi-method functions hit(drumstick, cymbal) = crash hit(mallet, cymbal) = roar hit(drumstick, drum) = bam
- 280. With multi-method functions hit(drumstick, cymbal) = crash hit(mallet, cymbal) = roar hit(drumstick, drum) = bam hit(mallet, drum) = bom
- 281. With multi-method functions hit(drumstick, cymbal) = crash hit(mallet, cymbal) = roar hit(drumstick, drum) = bam hit(mallet, drum) = bom hit(drumstick, drumstick) = click
- 282. With multi-method functions hit(drumstick, cymbal) = crash hit(mallet, cymbal) = roar hit(drumstick, drum) = bam hit(mallet, drum) = bom hit(drumstick, drumstick) = click hit(cymbal, cymbal) = loud crash
- 283. IMPORTANT: hit() is not a single function, but a collection of functions. (It is called a multi-method or generic function)
- 284. The particular function that is called is determined by the type of both of its arguments.
- 285. As you add more classes, just add more definitions of hit().
- 286. Part 3 Conclusion
- 287. Part 3 Conclusion Polymorphism is better done through interfaces than subtype inheritance.
- 288. Part 3 Conclusion Polymorphism is better done through interfaces than subtype inheritance. Functions do not require a heirarchy
- 289. Part 3 Conclusion Polymorphism is better done through interfaces than subtype inheritance. Functions do not require a heirarchy Functions allow simple multiple dispatch
- 290. The End
- 291. Any Questions?






























































































![x[t] = x0
x[t + 1] = x[t] + 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iit-2010-11-02-101130075324-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-with-Immutable-Data-Structures-94-320.jpg)












































































































![(defmacro and
([] true)
([x] x)
([x & rest]
‘(let [and# ~x]
(if and# (and ~@rest) and#))))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iit-2010-11-02-101130075324-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-with-Immutable-Data-Structures-206-320.jpg)