Functions in Pythons UDF and Functions Concepts
- 1. Working With Functions Class 12 CBSE Krish_Info_Tech
- 2. What Is a function? •A function is a subprogram that acts on data and often returns a value. Krish_Info_Tech
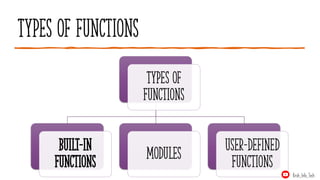
- 3. Types of functions Types of Functions Built-in Functions Modules User-Defined Functions Krish_Info_Tech
- 4. Built-in functions • These are predefined function in python and are used as and when there is need by simply calling them. • Example: • int( ) • float( ) • str( ) • min( ) • max( ) • print( ) ...etc Krish_Info_Tech
- 5. modules Eg: If u want to use pre-defined function sin( ) , you need to first import the module math. These functions are pre-defined in particular modules and can only be used when the corresponding module is imported. Krish_Info_Tech
- 6. How to import? •Syntax: import module_name •Example: import math Krish_Info_Tech
- 7. User defined functions These are defined by the programmer. As programmers you can create your own functions. Krish_Info_Tech
- 8. Syntax for user defined function def <function name> ( [ parameters ] ) : < statement > .......................... [ < statement > ] . . . [ return ] Krish_Info_Tech
- 9. Syntax for user defined function •where, odef means a function definition starting oFunction name is the name of the function and it is an identifier oParameters are the value to collect the values passed during function call oThe colon (:) at the end of the def line, means it requires a block. oThe return statement returns the computed result Krish_Info_Tech
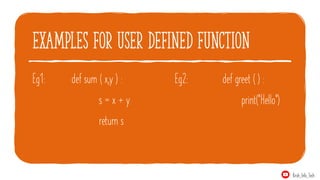
- 10. examples for user defined function Eg1: def sum ( x,y ) : s = x + y return s Eg2: def greet ( ) : print("Hello") Krish_Info_Tech
- 11. Calling/invoking/using a function <function_name> ( <value-to-be-passed-to-argument> ) Example sum(10,20) Krish_Info_Tech
- 12. Define the terms • The first line of the function definition that begins with keyword def and ends with a colon ( : ), specifies the name of the function and its parameters. Function Header • Variables that are listed within the parameters of a function header. Parameters • The block of statements beneath function header that defines the action performed by the function. Function Body • The blank space in the beginning of a statement within a block. All statements within same block have same indentation. Indentation Krish_Info_Tech
- 13. Flow of execution The flow of execution refers to the order in which statements are executed during a program run. A function body is a block which is executed as a unit and is executed in an execution frame. An execution frame contains: • Some internal information • Name of the function • Values passed to function • Variables created within function • Information about the next instruction to be executed. Krish_Info_Tech
- 14. How a function works def function( ): ....................................... ....................................... return #main ( ) - control begins …................................. function( ) #function call print(…...............) Control moves from function call to function header Send the control from where the function was called Krish_Info_Tech
- 16. Arguments and parameters • Two types of values which are passed and received during the function and the function definition are: oArguments – refers to the values being passed oParameters – refers to the values being received • Eg: def func1( ): ............................... ............................... func1( ) Parameters Arguments Krish_Info_Tech
- 17. Actual and formal parameters The alternate names for argument are Actual parameters and for parameter it is Formal parameters. Krish_Info_Tech
- 18. Passing parameters Types of formal arguments Positional Arguments ( Required Arguments) Default Arguments Keyword or Named Arguments Krish_Info_Tech
- 19. Positional Arguments (Required Arguments) When the function call statement must match the number and order of arguments as defined in the function definition, this is called positional arguments. Eg1: def func1( a,b ): c=a * b print ( c ) func1( "12A",5 ) Eg2: def func1( a,b ): c=a + b return c print( func1(10,20)) Krish_Info_Tech
- 20. Default arguments • Python allows as to assign default value your function's parameter which is useful in case a matching argument is not passed in the function called statement. • The default values are specified in the function header of function definition. • Eg: def func1(a,b,c=20): d=a+b+c return d print(funct1(10,20)) Krish_Info_Tech
- 21. Default arguments •A parameter having default value in the function header is known as default parameter. •Require parameters should be before default parameters. •The default values for parameters are considered only if no value is provided for that parameter in the function call statement. Krish_Info_Tech
- 22. Keyword arguments • Python offers a way of writing function call where you can write any argument in any order provided you name the argument when calling the function. • Eg1: def interest(p=10000,n=20,r=35): i=(p*n*r)/100 print I Interest() • Eg2: def interest(n=20,p=10000,r=35): • Eg3: def interest(r=35,p=10000,n=20): Krish_Info_Tech
- 23. Rules for combining all three types of arguments •Python states that in a function call statement oAn argument list must first contain positional arguments followed by any keyword arguments. oKeyword arguments should be taken from the required arguments preferably. oYou cannot specify a value for an argument more than once. Krish_Info_Tech
- 24. Function call – legal / illegal Function call statement legal / illegal interest(prin=3000, cc=5) Legal interest(rate=0.12, prin=3000, cc=5) Legal interest(cc=5, rate=0.12, prin=3000) Legal interest(5000, 3, rate=0.05) Legal interest(rate=0.05, 5000, 3) illegal interest(5000, prin=300, cc=2) illegal interest(5000, principal=300, cc=2) illegal interest(5000, time=2, rate=0.05) illegal Krish_Info_Tech
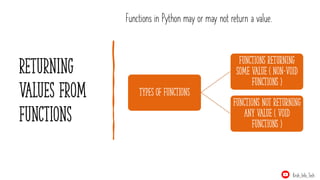
- 26. Returning values from functions Functions in Python may or may not return a value. Types of functions functions returning some value ( non-void functions ) Functions not returning any value ( void functions ) Krish_Info_Tech
- 27. Functions returning some value ( non-void functions ) The functions that return some computed result in terms of a value, fall in this category. The computer value is returned using return statement. return Syntax return <value> Example return 5 return 6+4 retuen (a+8**2)/b Krish_Info_Tech
- 28. Example program def sum(x,y): s = x + y return s result = sum ( 5 , 3 ) Krish_Info_Tech
- 29. Where to use return statement • The returned value of a function should be used in the caller function/program inside an expression or a statement. • if you do not use their value in any of the following ways and just give a standalone function call, Python will not report an error but their return value is completely wasted: add_result = sum ( a , b ) print ( sum ( 3 , 4 ) ) Krish_Info_Tech
- 30. Another use of return statement The return statement ends a function execution even if it is in the middle of the function. def check ( a ) : a = a**2 return a print ( a ) check(-15) Krish_Info_Tech
- 31. Functions not returning any value ( void functions ) • The functions that perform some action or do some work but do not return any computed value or final value to the caller are called void functions. • A void function may or may not have a return statement, then it takes the following form: return that is, keyword return without any value or expression. def greet ( ) : print ( "hello" ) def greet ( ) : print ( "hello" ) return Krish_Info_Tech
- 32. Fruitful and non- fruitful functions • Functions returning a value are known as fruitful function. • A void function, sometimes called non fruitful function, returns legal empty value of Python i.e., None to its caller. Krish_Info_Tech
- 33. Possible combinations of functions • non void functions without any arguments • non void functions with some arguments • void functions without any arguments • void functions with some arguments Krish_Info_Tech
- 34. Returning multiple values • Python lets you return more than one value from a function. • to return multiple values from a function, you have to ensure following things: oThe return statement inside a function body should be of the form given below: return <value1>,<value2>,..... oThe function call statement should receive or use the returned values in one of the following ways: ▪ either receive the returned values in form of tuple variable t=squared(2,3,4) ▪ or you can directly unpack the received values of tuple by specifying the same number of variables on the left hand side of the assignment in function call. v1,v2,v3=squared(2,3,4) Krish_Info_Tech
- 35. Scope of variables Parts of program within which a name is legal and accessible, is called scope of the name. Krish_Info_Tech
- 36. Types of scopes global scope • A name declared in top level segment i.e., the main program is set to have global scope and is usable inside the whole program and all blocks contained within the program. local scope • A name declared in a function body is set to have local scope that is it can be used only within this function and the other blocks contained under it. Krish_Info_Tech
- 38. • Variables defined outside all functions are global variables Krish_Info_Tech
- 39. Name resolution When you access a variable from within a program or function, Python follows name resolution rule, also known as LEGB rule. Local environment Enclosing environment Global environment Built in environment Krish_Info_Tech
- 40. Local environment • It checks within its local environment if it has a variable with the same name; if yes, python uses its value. If not then it moves to next step. enclosing environment • Python now checks the enclosing environment that is if whether there is a variable with the same name otherwise it repeats this step to the higher level enclosing environment if not then it moves to step 3. global environment • Python now checks the global environment whether there is a variable with the same name; if yes Python uses its value, if not then it moves to Step 4. built an environment • Python checks its built in environment that contains all built in variables and functions of Python, if there is a variable with the same name; if S Python uses its value. otherwise Python reports an error; name< variable> not defined. Krish_Info_Tech
- 41. Built-in Namespace Global Namespace Enclosing Namespace Local Namespace 1 2 3 4 Krish_Info_Tech
- 42. Mutable / immutable properties of passed data objects Krish_Info_Tech
- 43. Properties • Pythons variables are not storage containers, rather Python variables are like memory references; they refer to the memory address where the value is stored. • Depending upon the mutability/ immutability of its data type, a variable behaves differently. That is, if a variable is referring to an immutable type then any change in its value will also change the memory address it is referring to, but if a variable is referring to mutable type then any change in the value of mutable type will not change the memory address of the variable. Krish_Info_Tech
- 44. Mutability / immutability of arguments / parameters and function calls • Mutability of arguments / parameters affects the change of value in caller function. oPassing an immutable type value to a function. oPassing an mutable type value to a function. Krish_Info_Tech






![Syntax for
user defined
function
def <function name> ( [ parameters ] ) :
< statement >
..........................
[ < statement > ]
.
.
.
[ return ]
Krish_Info_Tech](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionsinpython-240719035651-a62f8219/85/Functions-in-Pythons-UDF-and-Functions-Concepts-8-320.jpg)