Fundamentals or Basics of Cloud Computing.pdf
- 1. FUNDAMENTALS OF CLOUD COMPUTING by Amol S. Gaikwad Lecturer Government Polytechnic Gadchiroli Maharashtra
- 2. Learning Outcomes Explain characteristics of Cloud computing Compare Cloud deployment models on the given services Explain the given service offered by identified Cloud service model Explain components of Cloud computing architecture
- 3. Introduction To Cloud Computing Cloud computing uses internet and servers to support applications and data User can use these applications and data on the cloud from any workstation (computers) using internet Cloud computing means providing on demand computing facilities, IT infrastructure and services using internet. Cloud computing defined by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) is as below - “Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand, access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (eg- networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minmal management effort or service provider interaction”
- 4. According to this definition cloud computing provides various resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services over some network like internet Introduction To Cloud Computing Cloud users are not required to know about the details of the cloud like its infrastructure or cloud site. Users can access(use) cloud applications using various interfaces like desktop, mobiles, web-browsers etc. Business data and applications are stored on cloud servers. Cloud computing performs task at faster rates Cloud is a set or collection of hardware, network, storage, services and interfaces that facilitates the service
- 5. Basic Structure of Cloud Computing Facilities (Paas+SaaS+IaaS) Cloud user 1 (using mobile) Cloud user 2 (using desktop) Cloud user 3 (using laptop) Cloud computing Cloud providers (offers facilities)
- 6. Cloud providers provide various facilities services to the users Various users use these services from different locations and devices like - mobiles, desktop computers and laptops Basic Structure of Cloud Computing
- 7. Cloud consumer - An individual person or organisation using services provided by cloud provider as their business relationship Terminologies used in Cloud Computing Cloud provider - An individual person or organisation who provides service and responsible for those services to those who demand it Cloud auditor - A party that checks (evaluates) cloud services such as performance, working (operation) on various systems, security etc. Cloud broker - Management between cloud providers and cloud consumers, they present and deliver various services Cloud mediator - Responsible for connectivity and transport of cloud services from service providers to cloud consumers
- 8. Due to following challenges there is need of cloud computing - Need of Cloud Computing Software licensing and support - In data centre licensing is required for every application but in cloud computing only a single licensing is required. Scalability - Conventional infrastructure cannot be extend easily at a particular time how much to scale (expand) also changes with time Accountability - Conventional infrastructure don’t have accountability (responsibility) Modifiability - When changes are needed, its cost extra charges for changing applications
- 9. Physical Security - Maintaining physical security is a difficult task Need of Cloud Computing Cost-effective management - To make the application available for users all the time, replication of data is required from time to time which is very costly for organisations
- 10. Cloud computing reduces cost of companies for storing data. Reduces total investment in hardware and software for an organisation Benefits (Advantages) of Cloud Computing Improves operational expenses, renewing charges and capital expenses of an organisation Hotmail, gmail, yahoo mail are all examples of cloud computing - software and servers of these emails are on the cloud and users can access them from any where Reduced costs - Expenses of maintenance and upgradation are handled by the cloud providers. Cloud reduces server’s cost, maintenance fees, data centre space, software licences etc, many cloud computing applications are provided free.
- 11. Scalability - Cloud computing permits businesses to pay as per work and and other resources they use. RAM space, storage space etc are simple to use and expand which can be done in hours rather than days. Businesses pay as per their demand, pay more for more demand and less for less demand Remote Access - Data can be easily synchronised and effortlessly shared between international offices, any tool can be used any time and at any place (isolated access) Isolated access - 1) Streaming of data - online radio station or movie 2) Web application interface - online store / search engine 3) Desktop sharing and isolated control software Benefits (Advantages) of Cloud Computing
- 12. Disaster Relief - Cloud virtualization techniques permit restoration, backup and flawless migration of application and protects from natural calamities like earthquakes, floods, internal troubles and wars. Ease of implementation - cloud applications do not need to be upgraded, fixed or downloaded, easy to learn, cost free trail and small enterprises (businesses) Skilled Vendors - Cloud computing suppliers maintains professional workers with them Response time - Response time is faster when compared to normal hardware and servers Benefits (Advantages) of Cloud Computing
- 13. Easy to customize - customization of resources is possible upto some level as per need. Pre-configured operating system, committed IP addresses for cloud servers, conversion between servers of similar cloud free and at high speed, allocation/replication at many remote sites Virtual Provisioning - Storage space is allocated on demand to various devices on the virtual storage network. Virtualized network for controlling, monitoring and maintaining physical disk storage connected with virtual machines Fully Automated Storage Tiering (FAST) - Shifts active data to storage tiers with high performance computing and stationary data to different storage spaces at low cost Benefits (Advantages) of Cloud Computing
- 14. Pay as per use - pay for only those resources which are required and release them after use. Benefits of Cloud Computing Accessibility from anywhere - Resources can be used (accessed) from any location and any device Increased scalability - resources can be easily scaled (expand) without much time, cost and efforts Increased availability and reliability - Resources are available all the time and whenever any component fails, it is immediately separated and replaced by cloud provider Dynamic provision - It is perception (imagination) of having unlimited computing resources available on demand and no need to plan for it.
- 15. Data lock-in - Shifting of data and application is challenging to the cloud provider provider particularly for big organizations Limitations/disadvantages of Cloud Computing Data Segregation - Separating cloud users from one another is difficult as it is difficult to separate memory or storage among different users Privilege Neglect - malicious insider with access to confidential data is threat to data security of companies Cloud does not scale up (expand) resources rapidly Data location - Geographical locations of data is challenging as different countries may have different rules and strategies.
- 16. Deletion of data - If the data is not deleted properly or not migrated completely from the cloud then that data may be used by malicious user Limitations/disadvantages of Cloud Computing Recovery of data - Keeping the data of consumer safe at different locations for easy recovery and backup is a big challenge Internet connection is required for using cloud services, which may not safe and feasible (practical) Unpredictable performance - Cloud performance depends on many aspects and the end user has no control on many of them
- 17. Cloud Architecture Client infrastructure Application Service Cloud Runtime Storage Infrastructure Management Security front end back end Internet Fig : Cloud Architecture
- 18. Cloud architecture can be divided into two main parts - front end and back end Cloud Architecture Front end - It is client side of cloud computing and includes all the interfaces and applications client uses to access cloud resorces, for ex- web browsers Back end - It is cloud itself and contains many resources like storage, virtual applications, virtual machines, security, management, networking etc. Different components of cloud architecture are as below - 1) Client Infrastructure - It is a part of front end, it contains user interfaces (GUI) and applications require to interact with cloud. 2) Application - It is a backend part. It is a software or application used by client. It provides service to client as per its requirements.
- 19. 3) Services - It refers to services and their management provided in the back end like PaaS, SaaS and IaaS Cloud Architecture 4) Runtime Cloud - It is backend part and provides runtime platform/environment to virtual machines 5) Storage - It provides scalable storage devices and management of stored in the backend 6) Infrastructure - It is a back end part and refers to hardware and software components of cloud like - servers, storages, network devices, virtualization software etc. 7) Management - It refers to the management of backend components like storage, infrastructure, applications , services, runtime cloud, security mechanisms etc.
- 20. 8) Security - It is a backend components and it provides different mechanisms to cloud users for secure access to cloud resources, files, storage, infrastructure etc Cloud Architecture 9) Database - Database at the back end is used for storing structured data like SQL, NOSQL. Amazon SQL, Microsoft Azure SQL, Google cloud SQL are examples of database services 10) Networking - It is a backend part. It provides networking infrastructure to cloud applications like - load balancing, DNS and Virtual Private Network (VPN) 11) Internet - It connects the front end to the back end of cloud. Cloud users use all the resources and services of the cloud using internet
- 21. Cloud infrastructure means all the hardware and software components reuired to creat a complete cloud system Infrastructure components of Cloud Computing Management Software Deployment Software Hypervisor Network Server Storage Fig : Infrastructure Components of cloud Compunting
- 22. Management Software - It helps in maintaining and configuring of cloud infrastructure. It controls and optimizes resources such as data, applications and services Infrastructure components of Cloud Computing Deployment Software - It helps to deploy and integrate the application on cloud Hypervisor - It is a firmware (low level program) which divides and allocates cloud resources to several customers. It monitors and manages cloud resources hence it is also called as Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) or Virtual Machine Manager (VMM)
- 23. Network - It connects the cloud with customers (internet) or different internal components of cloud with each other Infrastructure components of Cloud Computing Server - Servers provides services such as resource sharing, allocation and deallocation of resources, managing, monitoring and security Storage - It refers to the tools which saves the data. Which storage to use depends on the amount of data and time period it is to be saved
- 24. On-demand self-service Characteristics of Cloud Computing - Cloud customers can use, manage, monitor, provision cloud resources without requirement of humans interference - Customers can scale up or scale down services as per their demand (on- demand) Broad Network Access - Cloud services can be used (accessible) by many tools like mobile, PCs, laptop computers etc. - Cloud applications and services are available over the network
- 25. Resource Pooling Characteristics of Cloud Computing - Computing resources of the cloud are grouped together and shared among customers as per their requirments. - Resources such as memory, storage, processing, network bandwidth, mail services, virtual machines are shared among customers Quick Elasticity - Computing resources should be flexible, they should scale out (expand) when uses increases and scale in when usage decreases
- 26. Calculated Services Characteristics of Cloud Computing - Cloud computing resources can be controlled and reported, providing transparency of the used service to both customer and cloud providers - Cloud computing services use metering facility - it means just like electricity, IT services are also charged as per the usage , more usage more pay and less usage less pay Multi-persistant - Customers from different companies or from different business entities of different management departments can share same infrastructure between them
- 27. Dynamic computing Infrastructure Characteristics of Cloud Computing - Cloud providers use virtualisation technology which abstracts hardware resources and present them as logical resorces to the customers IT Service-centric Approach - Cloud users may effortlessly access strong, predefined, computing situations designed particularly around their service - The IT service centric method allows user acceptance and business flexibility
- 28. Self-service Based Usage Model Characteristics of Cloud Computing - It offers users the ability to assemble, upload, plan, install, control, and report on their company service on demand - A self service cloud offers simple-to-use, normal user interface, which allows users to effectively control the life cycle of service delivery - It saves time, money and less participation of management teams Self-managed platforms - Clouds provides self-administration through software automation - Tasks such as managing, configuring, planning, accessing and reporting are done through software automation
- 29. Standardized Interfaces Characteristics of Cloud Computing - Cloud services should have consistent APIs that decides how two data sources or applications can work with each other - A consist interface allows cloud users to connect to cloud services together - API - Application Programming Interface
- 30. Service Models of Cloud SaaS PaaS IaaS SaaS ( Email, virtual desktop, games ) PaaS ( Database, web server, development tools ) IaaS (Servers, storage, virtual machines, network, etc) Layer-3 Layer-2 Layer-1
- 31. In SaaS applications are hosted (provided) by vendors or cloud providers and made available to customers over internet Software as a Service (SaaS) It is responsibility of cloud suppliers to manage and control the software in cloud Cloud users do not manage the cloud platform and infrastructure on which the app is working There is no requirement to deploy and operate the application on personal computers of cloud users Cloud applications are multi-tenant, it means one machine can serve lagre number of cloud users
- 32. In SaaS applications are hosted (provided) by vendors or cloud providers and made available to customers over internet Software as a Service (SaaS) Some applications of SaaS are - Complaint resolution system Employee management system E-police, E-court Water board, billing, payment systems District management solutions Service desk
- 33. Size of SaaS infrastructure is large compared to client-server architecture technology Software as a Service (SaaS) Physical resources Cloud provider Virtual resources Software Cloud client Fig : Software as a Service
- 34. Examples of SaaS - Gmail, Google Apps, Netflix, Microsoft Office 365, Photoshop, Google docs, Dropbox etc. Software as a Service (SaaS) Advantages of SaaS - Straightforward expenses are nil It doesn’t require hardware purchase or software installation, only webs browser required to access the application Quick operation service Extremely scalable (expandable) Multi-tenant (multi-user) design Technical modernisation is efforlessly incorporated by the cloud supplier
- 35. Characteristics of SaaS Its applications are not complicate to manage and simple to use Applications are service oriented and modular Product sold to customer is the access to the application SaaS applications have integrated invoicing service Applications are centrally managed Data of every consumer is saved and protected Applications require offering complicated business procedure arrangement for customers Examples of SaaS providers - NetSuite, Financial Force.com, Cuopa Software, AT & T
- 36. Software as a Service (SaaS) Advantages of SaaS - Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) pricing Service level improvement rapid implementation Lessens licensing charge Disadvantages of SaaS Security - data is stored on cloud, so security of data is an issue Latency issue - As applications and data are stored on cloud the response time (latency) may increase while interacting with application Without internet SaaS applications can be used Switching between SaaS is difficult because of transferring and importing of large data files over internet
- 37. Platform as a Service (PaaS) Platform in computing is hardware architecture, operating system and runtime libraries which are used together to create and run programs PaaS model provides all the facilities to the programmer to develop, test , manage and deploy applications Cloud suppliers in the PaaS model provides computing platform which includes database, operating system, web server, programming language implementations etc. Application developers do not require to purchase basic software and harwdware required to buit applications Examples of PaaS - Heroku, Amazon Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure Mendix etc.
- 38. Operating System Web-application Database Platform as a Service (PaaS) Layer-2 Fig : Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- 39. Platform as a Service (PaaS) Advantages or Features of PaaS Application expansion structure - Cloud users can customize the application as per the requirement Simplicity to use - PaaS is user friendly, provides drag and drop options and helps rapid development of application Accessibility - Platform is reachable and available anywhere, anytime Scalability - Platform is able to control and manage the infrastructure and application loads Comprehensiveness - The platform offers the facility to insert and incorporate other applications set up on similar platforms
- 40. Platform as a Service (PaaS) Advantages or Features of PaaS Application expansion structure - Cloud users can customize the application as per the requirement Portability - The platform works with any any basic infrastructure and corporations (organisations) can shift application from one IaaS to other Porting devices - Porting devices are used for effortless data migration from on-premise applications to other Properly documented - It has properly documented API for for tasks such as user verification, recovery, saving of files and calls to database
- 41. Platform as a Service (PaaS) Disadvantage of PaaS Vendor lock-in - Applications are written according to platform provided by PaaS vendors, so migrating applications to another PaaS vendor is problematic Data Safety - Organisation data will be available on the cloud so there is risk of data privacy Integration with other applications - Using data from local application with data which is in cloud can be complicated Examples of PaaS providers - Google App Engine, PivotalLab, AppScale, Flexiscale etc.
- 42. Platform as a Service (PaaS) Features of PaaS for Application developers - A virtual development environment - Application principles based on developers requirements - An interface with tools ‘virtual development’ - A ready to use tool for public application developers
- 43. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) IaaS provides computer infrastructure as a service It provides computing resources as physical or virtual machines form Resources provided by IaaS clouds includes virtual machines, storage,server, network, software collections, firewalls, IP addresses, Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) Cloud users install applications and operating system images on the cloud Cloud user is responsible for patching (updating) the application and operating system both. Cloud users pay only for the amount of resources allotted and used by them
- 44. IaaS provides tools to access a fully virtualized infrastructure IaaS is a combination of hardware and software resources IaaS has a software called as ‘hypervisor’ which responsible for keeping record of hardware resources and and distributing resources to different users called as resource pooling Hypervisor runs independent of operating system (does not depend on operating system. Hypervisor also known as virtual machine manager (VMM) provides guests operating systems virtual operating platform and also controls implementations of these guests operating system Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- 45. Hypervisor are generally organised on server hardware Examples of IaaS - Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, Rackspace cloud, RightScale etc. Physical resources (server) Virtual resource cloud client Storage Fig : Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Cloud provider Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- 46. Advantages of IaaS - Cloud user can configure and select computing resources like storage, network, server, CPU etc as per their needs - IaaS cloud services are very easy to access (use) - Corporations (organisation) do not need to invest on large IT infrastructure, IaaS reduces their expenses on IT infrastructure - Cloud infrastructure is managed and controlled by cloud providers - Cloud users are charged according to resources allotted and utilized by them Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- 47. Disadvantages of IaaS - Data security - cloud providers may have access to organisations important data - To access (use) IaaS clouds internet facility is required - Depends on the availability of virtualisation services Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- 48. Cloud Deployment Models Cloud deployment means who will own, manage, control and where the cloud infrastructure will be placed Company select different cloud models depending on their requirements There are generally four types of cloud deployment models as below Public cloud Private cloud Community cloud Hybrid cloud
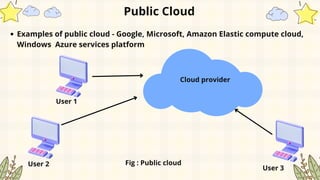
- 49. Public Cloud Public cloud infrastructure can be used by general public Public cloud may be owned, managed, controlled and operated, business, government organisations , academic organisations or combination of these organisations Public cloud infrastructure is located on the cloud providers place Public cloud is not free, it charges some amount for usage It is flexible and less expensive of establishing cloud services Physical infrastructure of the cloud is possessed by the cloud provider Cloud infrastructure, services and computing resources are available for all
- 50. Public Cloud Examples of public cloud - Google, Microsoft, Amazon Elastic compute cloud, Windows Azure services platform User 1 User 2 User 3 Cloud provider Fig : Public cloud
- 51. Public Cloud Advantages of Public cloud : - No initial investment is required to use any service from the cloud - Cloud infrastructure is managed by the cloud provider - Public cloud is highly scalable, companies can scale up or down the resources easily as per their requirements - Public cloud are reliable, if one resource fails other resource can be made available quickly - Public cloud is less expensive as it charges very amount at a lesser rate
- 52. Public Cloud Disadvantages of Public cloud : - Public cloud are less secure as information and data are on public platform - It cannot be customized as per our requirements
- 53. Private Cloud In private cloud, cloud infrastructure is exclusively used by a single organisation. Multiple departments or units within that organisation can use that cloud It is owned, managed, controlled and operated by the organisation or third party or combination of both Cloud infrastructure may located on the premises of organisation or some where else Cloud infrastructure may located on the premises of organisation or some where else Growth and information are managed inside the private cloud without restrictions on system bandwidth, authorization requirement and disclosure of security procedures
- 54. Private Cloud In private cloud, cloud infrastructure is exclusively used by a single organisation. Multiple departments or units within that organisation can use that cloud In private cloud user can control the cloud infrastructure Infrastructure is accessed only by the members of the organisation and granted by third party Private cloud is hosted in the data centre of the company Private cloud is owned by the organisation but it is constructed, deployed and directed by third party
- 55. Private Cloud A new concept of ‘virtual private cloud’ is launched in which a private cloud is provided inside public cloud infrastructure In private clouds safety is stricter than in public cloud Businesses which has safety concerns may use the power of private cloud When applications or data need to follow some standards then organisations may prefer private cloud for it Examples of private cloud - Eucalyptus, Vmware, Microsoft, Elastra private cloud etc.
- 56. Private Cloud Different resources available Cloud provider Fig : Private cloud User 1 User 2
- 57. Private Cloud Advantages of private cloud - - Organisation have better control on the cloud infrastructure, they can manage and operate the cloud - Organisation can customize the cloud as per their needs - private cloud provides high data security and privacy as only the members of the organisation can access it Disdvantages of private cloud - - Private clouds are costlier than public as it needs infrastructure expense as in IT infrastructure - Private clouds are less scalable as the its resources are limited
- 58. Community Cloud In community model, many corporations share the cloud infrastructure with similar needs, strategy and agreement considerations It reduces cloud cost as it is shared by a bigger group or cluster Community cloud falls between private and public cloud category When numerous consumers have similar requirements and necessities, they may share infrastructure and also administration and arrangements of cloud Cloud administration could be made by third party or by themselves Community or groups can interconnected aim like non-competitive company objectives, safety of resources etc.
- 59. Community Cloud Community cloud network Community members User 1 User 2 User 3 Fig : Community cloud
- 60. Community Cloud The physical infrastructure can be located on any location or third party location Advantages of community cloud - - As the cloud is shared by a community or group it is less expensive - Cloud resources and infrastructure is shared with multiple organisations - Better control as the cloud is controlled and administered by the community or group - Provides better security than public cloud
- 61. Community Cloud Disadvantages of community cloud - - Community cloud can be sometimes more expensive than private cloud - Running community cloud is difficult because of changing or undefined responsibility and control - Customization is difficult as changes required by one organisation may affect other organisation
- 62. Hybrid Cloud Hybrid cloud is a combination two or more clouds (community, private and public cloud) which is mutually dependant on one another In hybrid cloud model resources are provided on both on-premises and on isolated server based cloud infrastructure It provides flexibility of internal applications and scalability and error tolerance features of cloud services In hybrid deployment model, corporations may install less important software applications on public cloud, where as critical (important) applications are installed on private cloud located on premises Hybrid cloud provides benefits of protected data and application on private cloud and reduced cost by sharing data and applications on public cloud
- 63. Hybrid Cloud This model is also used to manage loads, where private cloud is used to support emergency loads, managing load between private and public cloud without any trouble to users Hybrid cloud can be consist of private and public clouds but it is administered or managed as a single unit Different clouds in hybrid model are bound by standardized technology that enables data and application portability between them
- 64. Hybrid Cloud Resources available on private cloud Resources available on public cloud Public cloud Private cloud Organisation using hybrid cloud network (both private and public cloud ) Fig : Hybrid cloud
- 65. Hybrid Cloud Advantages of hybrid cloud - hybrid cloud are scalable as it provides features of public cloud - hybrid cloud provides better security as important data and applications are installed on private cloud - As hybrid cloud also uses public cloud it becomes more cost effective disadvantages of hybrid cloud - As hybrid cloud uses combination of different clouds networking becomes complicated - hybrid cloud are complex that may make data insecure and cause security issue
- 66. Vendors of Cloud Computing Vendors means companies which provides some services or product Vendors of cloud computing provides cloud computing services to customers Some popular examples of popular cloud computing vendors are - Amazon Web Services - IaaS Google - SaaS, PaaS Microsoft Azure Services Platform - PaaS