Futex Scaling for Multi-core Systems
- 1. Futex Scaling for Multicore Systems ACM Applicative Conference – June 2016. New York, NY. Davidlohr Bueso <[email protected]> SUSE Labs.
- 2. 2 Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Implementing Futexes ● Overall architecture. ● Addressing performance bottlenecks. 3. Notes/Practises in Userspace.
- 3. 3 Introduction • Linux kernel (v2.5) functionality for userspace: “Fast userspace mutual exclusion” through the futex(2) interface: ‒ Method for a program to wait for a value at a given address to change, and a method to wake up anyone waiting on a particular address. ‒ A futex is in essence a userspace address.
- 4. 4 Introduction • Linux kernel (v2.5) functionality for userspace: “Fast userspace mutual exclusion” through the futex(2) interface: ‒ Method for a program to wait for a value at a given address to change, and a method to wake up anyone waiting on a particular address. ‒ A futex is in essence a userspace address. • Futexes are very basic and lend themselves well for building higher level locking abstractions such as POSIX threads: ‒ pthread_mutex_*(), pthread_rwlock_*(), pthread_barrier_*(), pthread_cond_wait(), etc.
- 5. 5 Introduction • In the uncontended cases, user locking implementations never need to exit from userspace, and the kernel is graciously unaware, nor cares. CAS is enough.
- 6. 6 Introduction • In the uncontended cases, user locking implementations never need to exit from userspace, and the kernel is graciously unaware, nor cares. CAS is enough. • In the case of sysv sems this is not true as jumping to kernel space is always required to handle the call. • Lock fastpaths therefore have a significant advantage using by futexes.
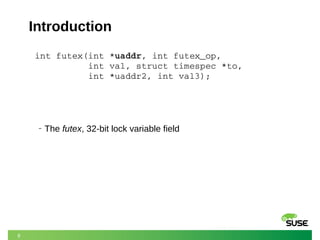
- 8. 8 Introduction int futex(int *uaddr, int futex_op, int val, struct timespec *to, int *uaddr2, int val3); ‒ The futex, 32-bit lock variable field
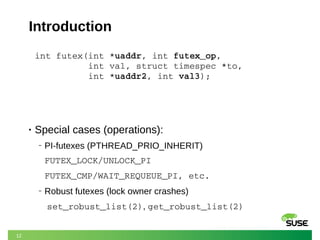
- 9. 9 Introduction int futex(int *uaddr, int futex_op, int val, struct timespec *to, int *uaddr2, int val3); ‒ What operation to do on the futex, ie: FUTEX_WAIT, FUTEX_WAKE
- 10. 10 Introduction int futex(int *uaddr, int futex_op, int val, struct timespec *to, int *uaddr2, int val3); ‒ What operation to do on the futex, ie: FUTEX_WAIT, FUTEX_WAKE, FUTEX_REQUEUE, etc.
- 11. 11 Introduction int futex(int *uaddr, int futex_op, int val, struct timespec *to, int *uaddr2, int val3); • Special cases (operations): ‒ PI-futexes (PTHREAD_PRIO_INHERIT) FUTEX_LOCK/UNLOCK_PI FUTEX_CMP/WAIT_REQUEUE_PI, etc.
- 12. 12 Introduction int futex(int *uaddr, int futex_op, int val, struct timespec *to, int *uaddr2, int val3); • Special cases (operations): ‒ PI-futexes (PTHREAD_PRIO_INHERIT) FUTEX_LOCK/UNLOCK_PI FUTEX_CMP/WAIT_REQUEUE_PI, etc. ‒ Robust futexes (lock owner crashes) set_robust_list(2), get_robust_list(2)
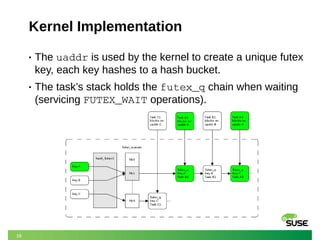
- 16. 16 Kernel Implementation • The uaddr is used by the kernel to create a unique futex key, each key hashes to a hash bucket. • The task’s stack holds the futex_q chain when waiting (servicing FUTEX_WAIT operations).
- 17. 17 Kernel Implementation • Wait queues are at the heart of futexes. ‒ Priority queues (high prio tasks first, otherwise FIFO). ‒ Governed by a chained global hash table.
- 18. 18 Kernel Implementation • Each bucket is serialized by a spinlock – all operations require holding the lock beforehand. • One or more futexes can share the queue (collisions).
- 19. 19 Bottlenecks • There are some immediately apparent issues with the current futex architecture. ‒ Global hash table (really bad for NUMA). ‒ Hash table collisions. ‒ hb>lock contention/hold times.
- 20. 20 Bottlenecks • There are some immediately apparent issues with the current futex architecture. ‒ Global hash table (really bad for NUMA). ‒ Hash table collisions. ‒ hb>lock contention/hold times. • All of these can have disastrous effects on both performance, as systems increase in hardware capabilities, as well as determinism for real-time.
- 21. 21 Bottlenecks • There are some immediately apparent issues with the current futex architecture. ‒ Global hash table (really bad for NUMA). ‒ Hash table collisions. ‒ hb>lock contention/hold times. • All of these can have disastrous effects on both performance, as systems increase in hardware capabilities, as well as determinism for real-time. • Numerous efforts have been taken to mitigate some of these scalability problems.
- 22. 22 Keys and Hashing • Uses Jenkins hash function (lookup3). ‒ Fast and distributes hash values rather uniformly (on real workloads). • Keys for private vs shared futexes. ‒ Private simply use the current address space and the futex uaddr. ‒ Shared mappings require page pinning (gup), locks, RCU, ref counting, etc. Even worse if inode-backed. • For shared mappings, lockless get_futex_key() ‒ Avoids taking the page_lock (sleepable). ‒ Good for performance and RT.
- 23. 23 Keys and Hashing 52-core, 2 socket x86-64 (Haswell) nfutexes = nthreads * 1024
- 24. 24 Keys and Hashing • Avoiding collisions and therefore improving the parallelisation of different futexes is a major plus. ‒ Ie: two or more user locks can be operated on concurrently without being serialized by the same hb>lock. ‒ The perfect hash size will of course have one to one hb:futex ratio.
- 25. 25 Keys and Hashing • Futexes started out at 256 entry hash table, which caused havoc on multicore systems. Since then we scale by number of CPUs (and avoid false sharing). ‒ Improved raw hashing throughput by 80% to 800% in increasing futex counts.
- 26. 26 Per-process Hash Table • Recent patchset proposed upstream to address the NUMA issues of the global table for private futexes. • Dynamically sized: if a potential collision is detected the size of the hash table is doubled. • Hash table being on the same NUMA node as the task operating on the futex. • Addresses collisions by dedicating more hash table space per process.
- 28. 28 Hash Bucket Lock Contention • For a successful futex call to occur, intuitively, among others, the following work must occur while holding the the hb>lock ‒ Priority list handling. ‒ Block/wakeup(s). • It is not hard to find pathological contention on some hb>lock, when multiple operations are being done on the same futex/lock.
- 29. 29 Lockless Wakeups • Internally acknowledge that one or more tasks are to be awoken, then call wake_up_process() after releasing the bucket spinlock.
- 30. 30 Lockless Wakeups • Internally acknowledge that one or more tasks are to be awoken, then call wake_up_process() after releasing the bucket spinlock. • Lockless wake-queues respect the order given by the caller, hence wakeup fairness does not change whatsoever.
- 31. 31 Lockless Wakeups Works particularly well for batch wakeups of tasks blocked on a particular futex. ‒ Ie waking all reader-waiters that where blocked on some lock held for write. (Where N is a large number): futex(uaddr, FUTEX_WAKE, N, ...);
- 32. 32 Lockless Wakeups 16 32 48 64 80 96 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 parallel-wakeups no-batch batched time (ms) threads 26-core (HT), 2 socket x86-64 (Haswell)
- 33. 33 Queued/MCS Spinlocks (x86) • Bottlenecks in userspace can easily lead to severe contention on the hb>lock, and therefore exposed to the semantics of spinlocks.
- 34. 34 Queued/MCS Spinlocks (x86) • Bottlenecks in userspace can easily lead to severe contention on the hb>lock, and therefore exposed to the semantics of spinlocks. 58.32% 826174 xxx [kernel.kallsyms] [k] _raw_spin_lock _raw_spin_lock | |53.74% futex_wake | do_futex | sys_futex | system_call_fastpath |45.90% futex_wait_setup | futex_wait | do_futex | sys_futex | system_call_fastpath
- 35. 35 Queued/MCS Spinlocks (x86) • Replaced the regular ticket spinlock implementation. • Each lock waiter will be queued and spins on its own cacheline (per-cpu variable) rather than the lock itself. ‒ This occurs until the waiter becomes the head of the queue (next in line to take the lock). ‒ Eliminates much of the cacheline bouncing (inter-socket traffic) caused by contended ticket locks.
- 36. 36 Queued/MCS Spinlocks (x86) • Replaced the regular ticket spinlock implementation. • Each lock waiter will be queued and spins on its own cacheline (per-cpu variable) rather than the lock itself. ‒ This occurs until the waiter becomes the head of the queue (next in line to take the lock). ‒ Eliminates much of the cacheline bouncing (inter-socket traffic) caused by contended ticket locks. • This really matters on systems with > 4-sockets, but can bring 8 or 16-socket machines to its knees. ‒ Experiments show improvements in throughput of up to 2.4x on 80 core machines. ‒ Reports of lockups for futexes on 240-core systems.
- 37. 37 Queued/MCS Spinlocks (x86) • qspinlocks outperform ticket locks in the uncontended case. Ie avg single threaded lock+unlock: • Therefore smaller systems under non-pathological (normal case) workloads can also benefit. Time (ns) Ticket lock (unlock: CAS) 17.63 Queued lock (unlock: store) 9.54 (2.6Ghz x86-64)
- 38. 38 PI-Futexes • Futexes make use of rt-mutexes to support priority- inheritance (PTHREAD_PRIO_INHERIT) semantics. ‒ pi_state is attached to the waiter’s futex_q ‒ The pi_state>pi_mutex top-waiter (highest priority waiter) has been optimized for both lockless wakeups and avoid blocking if current lock owner is running.
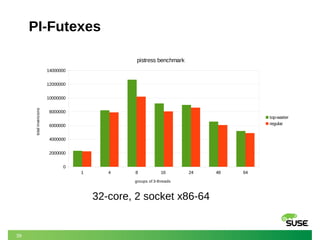
- 39. 39 PI-Futexes 1 4 8 16 24 48 64 0 2000000 4000000 6000000 8000000 10000000 12000000 14000000 pistress benchmark top-waiter regular groups of 3-threads totalinversions 32-core, 2 socket x86-64
- 41. 41 General Notes • The performance optimizations at the Kernel side are only one part of the picture. Using futexes is just as important. • As with any system call, there really is no single recipe to make good use of futexes in userspace. The kernel simply obliges. • Locking algorithms can play a huge factor in performance on large-scale machines. ‒ Contention on a 240-core system is much more severe than on a 40-core machine.
- 42. 42 General Notes • Locks in both the kernel and in userspace can be exposed to the same architectural difficulties: cacheline contention and NUMA-awareness. • Many applications today are developed/tuned for certain amount of CPUs. ‒ Scaling based only on the number of CPUs is likely to introduce significant lock and cacheline contention. • Unsurprisingly similar optimizations and tools to obtain data for analysis (perf, tracing, etc) can be taken from this presentation and applied to your locks.
- 43. 43 Best Practises • Data partitioning. ‒ Cacheline contention within a single NUMA node can be significantly less severe than among cores from different NUMA nodes. • Lock granularity. • Data layout ‒ structure organization, avoiding false sharing. ‒ Cacheline bouncing can occur when there are multiple hb>lock residing on the same cacheline and different futexes hash to adjacent buckets. • Avoid futex(2) calls unless necessary ‒ Ie: make sure there are waiters to wakeup.
- 44. 44 References • man 2 futex • Hart, Darren. “A futex overview and update”. lwn.net. Nov 2009. • Drepper, Ulrich. “Futexes are Tricky”. Nov 2011. • Hart, D. “Requeue-PI: Making Glibc Condvars PI-Aware”. Proc. RT Linux Summit 2011. • Bueso, D. Norton, S. “An Overview of Kernel Lock Improvements”. Linux Con. 2014. Chicago, IL.
- 45. Thank you.
- 46. 46































![34
Queued/MCS Spinlocks (x86)
• Bottlenecks in userspace can easily lead to severe
contention on the hb>lock, and therefore exposed
to the semantics of spinlocks.
58.32% 826174 xxx [kernel.kallsyms] [k] _raw_spin_lock
_raw_spin_lock
|
|53.74% futex_wake
| do_futex
| sys_futex
| system_call_fastpath
|45.90% futex_wait_setup
| futex_wait
| do_futex
| sys_futex
| system_call_fastpath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbueso-applicative16-futex-160602193613/85/Futex-Scaling-for-Multi-core-Systems-34-320.jpg)