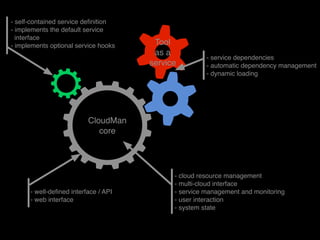
This document discusses deploying bioinformatics tools and pipelines using CloudMan and CloudBioLinux on cloud infrastructure. It outlines how to launch an instance on the cloud using CloudMan, customize the instance by installing additional tools, and share the customized instance platform with other users. Key concepts discussed include how CloudMan manages cloud resources, tools as services, and building and deploying CloudMan machine images.












![Accessing an instance over ssh
Use the terminal (or install Secure Shell for Chrome extension)
SSH using user ubuntu and the password you chose when
launching an instance:
[local machine]$ ssh ubuntu@<instance IP address>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8scypvqmuoiqwyymckqp-140630133905-phpapp02/85/GCC-2014-scriptable-workshop-13-320.jpg)


![Use the new tool in the cluster mode
1. Create a new sample shell file to run the tool; call it job_script.sh
with the following content:
#$ -cwd
/mnt/galaxy/export/dnaclust_linux_release3/dnaclust -l -s
0.9 /mnt/workshop-data/mtDNA.fasta
2. Submit single job to SGE queue
qsub job_script.sh
3. Check the queue: qstat -f
4. Job output will be in the local directory in file job_script.sh.o#
5. Submit the same job a number of times:
qsub job_script.sh (*10)
watch qstat ‒f
1. See all jobs lined up
6. [optional] See auto-scaling in action (if enabled) [1.5-2 mins]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8scypvqmuoiqwyymckqp-140630133905-phpapp02/85/GCC-2014-scriptable-workshop-16-320.jpg)


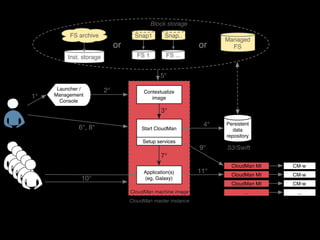




![Launcher /
Management
Console
Application(s)
(eg, Galaxy)
1°
2°
3°
6°, 8°
9°
Persistent
data
repository
Start CloudMan
Setup services
5°
4°
7°
10°
CM-w
CM-w
CM-w
...
FS 1 FS ...
Block storage
Contextualize
image
CloudMan MI
CloudMan MI
...
CloudMan MI
CloudMan machine image
11°
S3/Swift
CloudMan master instance
Snap1 Snap..
Managed
FS
Inst. storage
or or
FS archive
Troubleshooting
/mnt/galaxy[Indices]
/mnt/cm/paster.log cm-<hash>
/usr/bin/ec2autorun.log
/tmp/cm/cm_boot.log
/mnt/cm/paster.log
2
1
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8scypvqmuoiqwyymckqp-140630133905-phpapp02/85/GCC-2014-scriptable-workshop-26-320.jpg)