Genetic programming
- 2. What is Genetic Programming? • Genetic Programming (GP) is an Evolutionary Computation (EC) technique that automatically solves problems without requiring the user to know or specify the form or structure of the solution in advance, • At the most abstract level, GP is a systematic, domain-independent method for getting computers to solve problems automatically starting from a high-level statement of what needs to be done
- 3. Why Genetic Programming • It saves time by freeing the human from having to design complex algorithms, • Not only designing the algorithms but creating ones that give optimal solutions
- 4. How Genetic Programming? The basic control flow for genetic programming, where survival of the fittest is used to find solutions, is shown below:
- 5. The basic steps in a GP system Algorithm
- 6. The basic steps in a GP system • GP finds out how well a program works by running it, and then comparing its behavior to some ideal (line 3), • We might be interested, for example, in how well a program predicts a time series or controls an industrial process, • This comparison is quantified to give a numeric value called fitness, • Those programs that do well are chosen to breed (line 4) and produce new programs for the next generation (line 5)
- 7. The basic steps in a GP system • The primary genetic operations that are used to create new programs from existing ones are: Crossover: The creation of a child program by combining randomly chosen parts from two selected parent programs, Mutation: The creation of a new child program by randomly altering a randomly chosen part of a selected parent program
- 9. Representation of Solutions in a GP System The tree representation of the program: max(x+x,x+3*y)
- 10. In more advanced forms of GP
- 14. Representation of Solutions in a GP System • In GP, programs are usually expressed as syntax trees rather than as lines of code, • The variables and constants in the program (x, y and 3) are leaves of the tree and in GP they are called terminals, whilst the arithmetic operations (+, * and max) are internal nodes called functions, • The sets of allowed functions and terminals together form the primitive set of a GP System • In more advanced forms of GP, programs can be composed of multiple components (e.g., subroutines), • In this case, the representation used in GP is a set of trees grouped together under a special root node that acts as glue. • The (sub)trees are called branches and the number and type of the branches in a program, together with certain other features of their structure, form the architecture of the program. • It is common in the GP literature to represent expressions in a prefix notation, • For example, max(x+x,x+3*y) becomes (max (+ x x) (+ x (* 3 y))), • This notation often makes it easier to see the relationship between (sub)expressions and their corresponding (sub)trees, • The trees and their corresponding prefixnotation expressions are used interchangeably
- 16. Initializing the Population • In GP, the individuals in the initial population are typically randomly generated, • There are a number of different approaches for generating this random initial population, • Next, two of the simplest (and earliest) methods (the full and grow methods), and a widely used combination of the two known as Ramped half-and-half
- 17. The Full Method • The next slide shows a series of snapshots of the construction of a full tree of depth 2, • The children of the * and / nodes must be leaves or otherwise the tree would be too deep, • Thus, at both steps t = 3, t = 4, t = 6 and t = 7 a terminal must be chosen (x, y, 1 and 0, respectively). • Creation of a full tree having maximum depth 2 using the full initialization method (t = time)
- 18. The Full Method Initialization Example
- 19. The Full Method Initialization Example
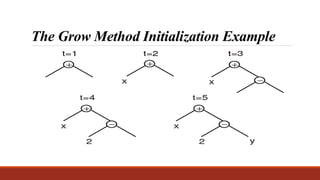
- 20. Initializing the Population: Grow Method • The grow method, on the contrary, allows for the creation of trees of more varied sizes and shapes, • Nodes are selected from the whole primitive set (i.e., functions and terminals) until the depth limit is reached, • Once the depth limit is reached only terminals may be chosen (just as in the full method), • The next slide illustrates this process for the construction of a tree with depth limit 2 • Creation of a five node tree using the grow initialisation method with a maximum depth of 2 (t = time) • A terminal is chosen at t = 2, causing the left branch of the root to be closed at that point even though the maximum depth had not been reached
- 21. The Grow Method Initialization Example
- 23. Initializing the Population: half-and-half Method Because neither the grow or full method provide a very wide array of sizes or shapes on their own, a combination called ramped half-and- half proposed, • Half the initial population is constructed using full and half is constructed using grow, • This is done using a range of depth limits (hence the term “ramped”) to help ensure that we generate trees having a variety of sizes and shapes
- 24. Recombination and Crossover • The most commonly used form of crossover is subtree crossover, • Given two parents, subtree crossover randomly selects a crossover point (a node) in each parent tree, • It creates the offspring by replacing the subtree rooted at the crossover point in a copy of the first parent with a copy of the subtree rooted at the crossover point in the second parent, for example
- 26. Recombination and Mutation • The most commonly used form of mutation in GP (called subtree mutation) randomly selects a mutation point in a tree and substitutes the subtree rooted there with a randomly generated subtree, • This is illustrated by the example of the next slide
- 29. Applying GP System to a Problem
- 30. Examples of primitives in GP function and terminal sets
- 31. The development of the topology and the sizing of an electrical circuit
- 32. Function development for appraising brittleness of intact rocks using genetic programming and non-linear multiple regression models
- 33. Proposed model Training Testing R 2 RMSE VAF R 2 RMSE VAF NLMR 0.817 4.382 80.231 0.882 3.602 86.701 GP 0.909 2.862 90.648 0.904 3.509 88.943 R2 :Coefficient of determination RMSE: Root Mean Square Error VRF: Variance account for
- 35. GP is much more power full than GA. The output of the GA is a quantity, while output of GP is a another computer program. Where there is no ideal solution, GP works best (ex. A program that drives a car).