GIS - Lecture 4
- 1. 8/20/2010 GIS Data Structures and Models GE 517 – Geographic Information Systems Engr. Ablao Digital Geographic Data Numerical representations that d ib real-world f N i l i h describe l ld features and phenomena Must be encoded in digital form and organized as a geographic database to be useful to GIS This digital database creates our perception of the real world Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 1
- 2. 8/20/2010 Conventional Data vs. Digital Geographic Data Conventional Data: Paper map Static representation Represents a general-purpose snapshot of the real world at a given time only Digital Geographic Data: Dynamic representation Allows a range of functions for storing processing analyzing storing, processing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data Has tools that allow users to interact with the data to meet their objectives Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 FIGURE 1. Bringing real-world data into a GIS or a map requires several abstractions and/or conversions of the original data. (Freely adapted from Bernhardsen, 1992). Physical Real world Map / → → Data model → Database → reality model Report Actual Entity Object Object Symbol, line, phenomenon text • Properties • Type • Type • Type • Connection • Attributes • Attributes • Attributes s • Relationship • Relationship • Relationship • Geometry • Geometry • Quality • Quality Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 2
- 3. 8/20/2010 Figure 2 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 What is a Data Model? The h Th heart of any GIS f A way of representing data A set of constructs for describing and representing selected aspects of the real world in a computer l ld computer. Longley, Goodchild, Maguire & Rhind Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 3
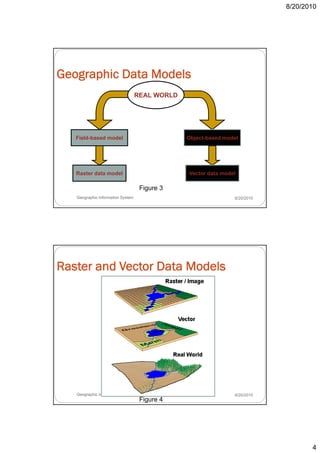
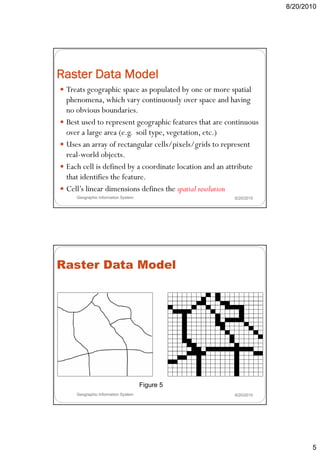
- 4. 8/20/2010 Geographic Data Models REAL WORLD Field-based model Object-based model Raster data model Vector data model Figure 3 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster and Vector Data Models Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Figure 4 4
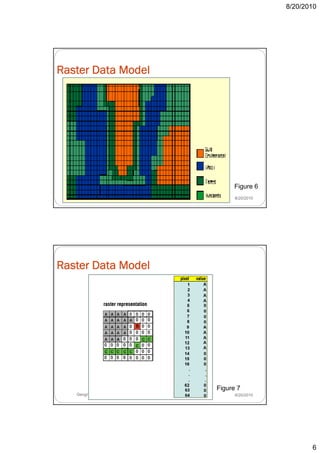
- 5. 8/20/2010 Raster Data Model Treats geographic space as populated by one or more spatial phenomena, phenomena which vary continuously over space and having no obvious boundaries. Best used to represent geographic features that are continuous over a large area (e.g. soil type, vegetation, etc.) Uses an array of rectangular cells/pixels/grids to represent real-world objects. real world objects Each cell is defined by a coordinate location and an attribute that identifies the feature. Cell’s linear dimensions defines the spatial resolution Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster Data Model Figure 5 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 5
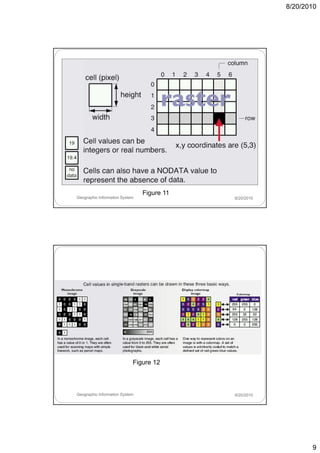
- 6. 8/20/2010 Raster Data Model Figure 6 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster Data Model Figure 7 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 6
- 7. 8/20/2010 A point is represented as a single cell. well tree rock Figure 8 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 A line is represented as a string of cells. river road canal Figure 9 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 7
- 8. 8/20/2010 An area is a contiguous block of cells. grassland barn forest Figure 10 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster Data Model The cell size determines the resolution of the data. The grid cell has an extent. When we map features onto the grid, there is sometimes an imperfect fit. Each grid cell can usually be “owned” by one feature, that is, the one whose attribute it holds (mixed pixels). Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 8
- 9. 8/20/2010 Figure 11 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Figure 12 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 9
- 10. 8/20/2010 Raster Data Compression A single raster file usually contains several million grid cells l d to a very l ll leading large d f l data file Therefore, data compression is very important in the digital representation of raster data! Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster Data Compression Based on the realization that cells representing the same ffeature type have identical values and that they h d l l d h h tend to be spatially clumped Examples of raster data compression techniques are: Run length encoding Wavelet compression Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 10
- 11. 8/20/2010 Raster Data Compression Run length encoding g g Adjacent cells along a row having the same value are treated as a group known as a ‘run’ instead of storing the similar cell values individually, the value is just stored once together with the number of cells that comprise the run b f ll th t i th Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Run length encoding Figure 13 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 11
- 12. 8/20/2010 Raster Data Compression Wavelet Compression p More efficient compression Can achieve a ratio between 15:1 to 20:1 for 8-bit gray scale images and between 30:1 to 40:1 for 24- bit color images Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster File Formats BMP (bitmaps) – used by graphics in Microsoft Windows applications; no p compression DIB (Device Independent Bitmaps) GIF (Graphical Interchange Format) – widely used for images to be used on the World Wide Web TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) – non-proprietary, system-independent JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) – primarily for storage of photographic images and for the World Wide Web GeoTIFF – extension of the TIFF format that contains georeferencing information PNG (Portable Network Graphics) – patent-free; intended to replace the GIF format PCX – supported by many image scanners MrSID (Multi-resolution Seamless Image Database) GRID – proprietary format used by ESRI in ArcInfo and ArcView GIS Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 12
- 13. 8/20/2010 Quadtree Data Model A hierarchical field-based model that uses grid cells of variable sizes f i bl i Uses finer subdivisions in areas where finer detail occurs Geographic space is divided by the process of recursive decomposition More difficult compared to the simple raster model Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Quadtree Data Model Figure 14 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 13
- 14. 8/20/2010 Digital Elevation Model A raster-based representation of surface Figure 15 Geographic Information System Southwest Corner of the 8/20/2010 Morrison Quadrangle, Colorado Remotely sensed data are a special type of raster data. Figure 16 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 14
- 15. 8/20/2010 Other forms of raster data Scanned Aerial maps photos Pictures Converted data Figure 17 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Vector Data Model Treats geographic space as populated by discrete objects, which have identifiable b d i h id tifi bl boundaries or spatial extent ti l t t Each object in the real-world is represented as either point, line, or polygon features. characterized by the use of sequential points or vertices to define a linear segment, each vertex consisting of an X coordinate and a Y coordinate. Useful for representing discrete objects such as roads, buildings, rivers, boundaries, etc. Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 15
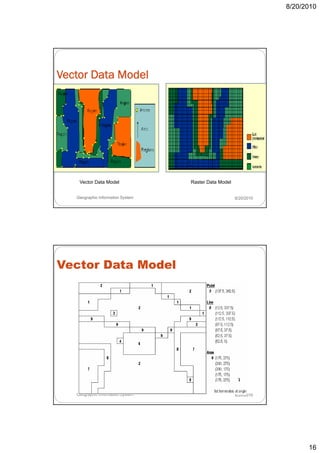
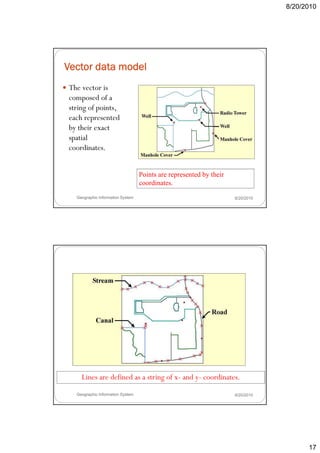
- 16. 8/20/2010 Vector Data Model Vector Data Model Raster Data Model Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Vector Data Model Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 16
- 17. 8/20/2010 Vector data model The vector is composed of a p string of points, each represented by their exact spatial coordinates. Points are represented by their coordinates. Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Vector data model Lines are defined as a string of x- and y- coordinates. Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 17
- 18. 8/20/2010 Vector data model Areas are a string of x- and y-coordinates that terminate at the origin. Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Types of Vector Data Model 1. Simple (spaghetti) data model p (pg ) 2. Topologic data model Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 18
- 19. 8/20/2010 Simple (Spaghetti) Data Model a one-for-one translation of the analog map Features (lines and polygons) may overlap No relationships between features/entities Generally used where analysis is not important (eg. Plotting) each entity is a single, logical record in the computer, coded as variable l th strings of x- and y- coordinate d d i bl length t i f d di t pairs Examples are digitized maps and CAD data Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Simple (Spaghetti) Data Model g Advantages: Easy to create and store Can be retrieved and rendered on screen very quickly Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 19
- 20. 8/20/2010 Simple (Spaghetti) Data Model Disadvantages: Spatial analysis (eg. Shortest path network analysis) cannot be performed easily due to lack of any connectivity relationships Redundant since the boundary segment between two polygons can be stored twice (once for each feature) Inflexible since it is difficult to dissolve common boundaries when joining polygons Cannot be used in certain applications such as land management because of overlapping features Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Topological Data Model spaghetti model but with topology! Essentially just a simple d model structured using E ll l data d l d topologic rules often referred to as an intelligent data structure because spatial relationships between geographic features are easily derived when using them Most commonly used variants is the arc node data arc-node model uses nodes (intersection of two lines; end point of line, and any point on line) and arcs (line connecting two nodes) System Geographic Information 8/20/2010 20
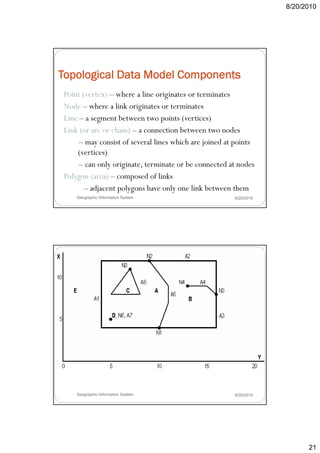
- 21. 8/20/2010 Topological Data Model Components Point (vertex) – where a line originates or terminates Node – where a link originates or terminates Line – a segment between two points (vertices) Link (or arc or chain) – a connection between two nodes – may consist of several lines which are joined at points (vertices) – can only originate, terminate or be connected at nodes Polygon (area) – composed of links – adjacent polygons have only one link between them Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 21
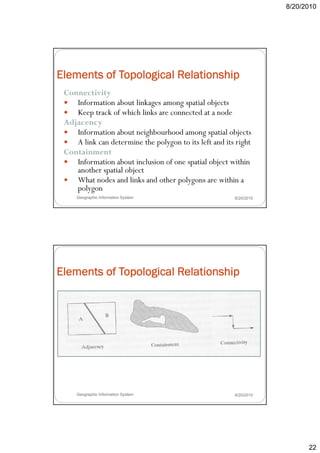
- 22. 8/20/2010 Elements of Topological Relationship Connectivity Information about linkages among spatial objects I f ti b t li k ti l bj t Keep track of which links are connected at a node Adjacency Information about neighbourhood among spatial objects A link can determine the polygon to its left and its right Containment Information about inclusion of one spatial object within another spatial object What nodes and links and other polygons are within a polygon Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Elements of Topological Relationship Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 22
- 23. 8/20/2010 Topological Map Explains the concept of topological relationships A map that contains explicit topological information on top of the geometric information expressed in coordinates (Masry and Lee, 1988) All spatial entities are decomposed and represented in the form of the three basic graphical elements (point, line, polygon) Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Concept of a Topological Map Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 23
- 24. 8/20/2010 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 24
- 25. 8/20/2010 Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Arc-node Data Model Stores graphical elements rather than graphical entities Explicitly stores spatial relationships between the graphical elements, and relationships between the arcs and respective nodes Stored t l i l l ti hi ll St d topological relationships allow graphical hi l entities to be constructed using the basic graphical elements Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 25
- 26. 8/20/2010 Arc-node Data Model Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Network Data Model A special type of topologic model p yp p g Shows how lines connect with each other at nodes Applications: Load analysis over an electric network y Vehicle routing over a street network Pollution tracing over a river network Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 26
- 27. 8/20/2010 Use of Topological Relationship Areas in GIS wherein topological relationships are applied are: 1. Data input and representation 2. Spatial search 3. Construction of complex spatial objects from basic graphical elements b h l l 4. Integrity checks in database creation Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Data input and representation Creating a topologic geographic database is extremely time-consuming and error-prone Possible to adopt the spaghetti digitization for graphical data input and then later on let the computer refine and structure them using topological relationships Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 27
- 28. 8/20/2010 Data input and representation Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Spatial search GIS uses topological relationships to perform spatial searches efficiently h ffi i tl For example, the land parcels surrounding a particular parcel can be located immediately using adjacency information Polygons that share a common boundary with the parcel of interest are identified Their IDs are used to retrieve the descriptive data from the database Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 28
- 29. 8/20/2010 Spatial search Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Construction of complex spatial objects Complex objects are represented as complex polygons in a geographic d b l h database Two types of complex polygons are: Those containing one or more holes (or islands/enclaves) constructed from vector lines using topological information Those d Th made up of two or more polygons th t are not ft l that t physically connected constructed using a common identifier Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 29
- 30. 8/20/2010 Construction of complex spatial objects Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Integrity checks Graphical data must be topologically cleaned before using them in GIS applications Must not contain any topological errors During topology building, the computer detects topological errors and marks them immediately Operator can then decide what to do with the hat ith errors Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 30
- 31. 8/20/2010 Integrity checks Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) Data Model Creates and represents surfaces in GIS Surface i S f is represented as contiguous, non-overlapping t i l t d ti l i triangles Size of triangles may be adjusted to reflect the relief of the surface being modelled Larger triangles for relatively flat terrain Smaller triangles for rugged terrain Manages information about the nodes that comprise each triangle and the neighbors of each triangle Applications: Volumetric calculations for road design Drainage studies Landslide studies Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 31
- 32. 8/20/2010 Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) Data Model Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Advantages of TIN Data Model Incorporates original sample points so the accuracy of the model can be checked Efficient way of storing surface representations because the size of triangles can be varied according to the terrain Data t t D t structure makes it easy t calculate elevation, k to l l t l ti slope, aspect, and line-of-sight between points Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 32
- 33. 8/20/2010 Vector File Formats GDF/DIME (Geographic Base File/Dual Independent Map Encoding) – originally used for storing street maps TIGER (Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing System) – improvement for GDF/DIME DLG (Digital Line Graphs) – USGS topographic maps AutoCAD DXF (Data Exchange Format) – widely used as an export format in many GIS IGDS (Intergraph Design System) – widely used in mapping ArcInfo Coverage – stores vector graphical data using topological structure explicitly defining spatial relationships ArcInfo E00 – export format of ArcInfo p Shapefiles – format of ArcView GIS; defines geometry and attribute of geographically referenced objects using the main file, index file and database table CGM (Computer Graphics Metafile) – ISO standard for vector data format; widely used in PC-based computer graphics applications Page Description Languages (PDL’s) Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Considerations in choosing between Raster and Vector source and type of data analytical procedures to be used intended use of data Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 33
- 34. 8/20/2010 Raster vs. Vector Raster Data Model Advantages: Simple data structure Easy to conceptualize space representation Easy data collection and processing Easy and efficient overlaying High spatial variability is efficiently represented Easier and efficient for surface modelling, wherein individual features are not that important Allows easy integration of i All i i f image d ( lli remotely-sensed, data (satellite, l d etc.) Pixel values can be modified individually or in a group by using a palette Simple for own programming Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster vs. Vector Raster Data Model Disadvantages: Do not provide precise locational and area computation information due to grid cells Requires large storage capacity, based on size and number of colors No topological processing Limited tt ib t data handling Li it d attribute d t h dli Inefficient projection transformations Loss of information when using large cells “Blocky” appearance when image is viewed in detail Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 34
- 35. 8/20/2010 Raster vs. Vector Vector Data Model Advantages: Far more efficient in storage than grids Compact data structure Provides precise locational information of points Can represent point, line, and area features very accurately, leading to more accurate measurements and map outputs Topological models enable many types of analysis Sophisticated attribute data handling Efficient for network analysis Efficient projection transformation Work well with pen and light-plotting devices and tablet digitizers Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster vs. Vector Vector Data Model Disadvantages: Complex data structure Difficult overlay operations High spatial variability is inefficiently represented Not compatible with RS imagery Expensive data collection Not good at continuous coverages or plotters that fill areas Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 35
- 36. 8/20/2010 Representation of a line using raster and vector model Raster representation Vector representation Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 Raster vs. Vector Raster Vector Data collection Rapid Slow Data volume Large Small Graphic treatment Average Good Data structure Simple Complex Area analysis Good Average Network analysis Poor Good Generalization Simple Complex Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 36
- 37. 8/20/2010 Integrating raster and vector data Geographic Information System 8/20/2010 37