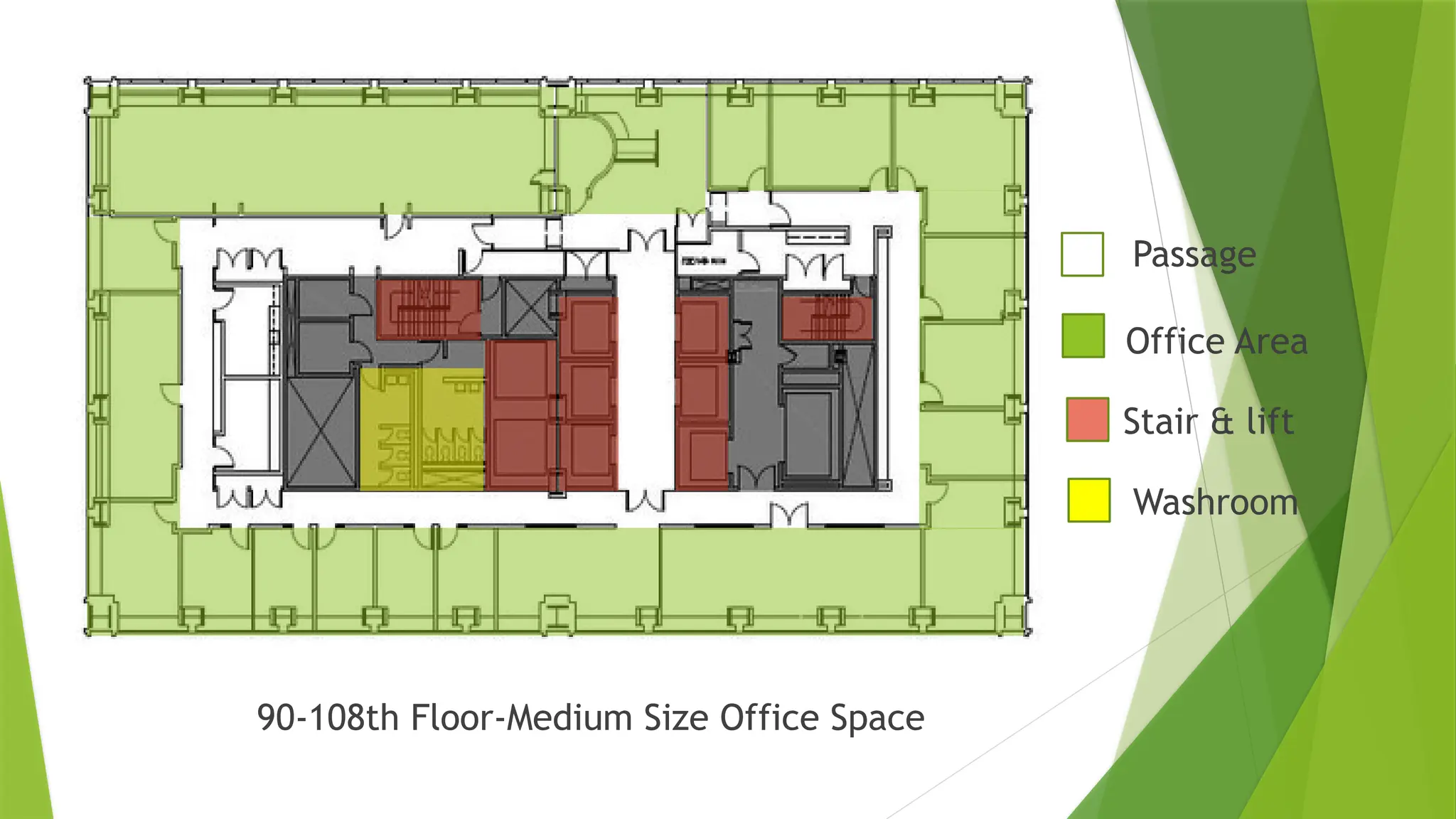
The document is a case study of the Willis Tower, focusing on its architectural design and various functional analyses including circulation, mechanical systems, and stack effect management. It emphasizes the building's height, significant features like the Skydeck, and advanced elevator and HVAC systems. Additionally, it discusses the stack effect phenomenon, its impact, and challenges in mitigating it within high-rise structures like the Willis Tower.