GUI Programming in JAVA (Using Netbeans) - A Review
- 2. After studying this lesson the students will be able to: 1. Identify, name and state the usage of the different components of the NetBeans IDE. 2. Identify and name the various methods and properties associated with the various form controls 3. Create simple applications in Java using NetBeans IDE. 4. Create GUI applications using the concepts of variables and control structures.
- 3. NetBeans is an integrated development environment (IDE) for developing primarily with Java, but also with other languages, in particular PHP, C/C++, and HTML5. It is also an application platform framework for Java desktop applications and others. The NetBeans IDE is written in Java and can run on Windows, OS X, Linux, Solaris and other platforms supporting a compatible JVM. The NetBeans Platform allows applications to be developed from a set of modular software components called modules. Applications based on the NetBeans Platform (including the NetBeans IDE itself) can be extended by third party developers.
- 5. The various componets of Netbeans IDE are: 1. Title Bar 2. Menu Bar 3. Toolbars 4. GUI builder 5. Palette 6. Inspector Window 7. Properties Window 8. Code Editor Window
- 6. Components (also known as "widgets") are the basic interface elements the user interacts with: jlabels, jbuttons, jtextfields etc. Components are placed on a container like the jFrame). There are two types of controls : 1. Parent Controls: They act as a background for other controls. For example-Frame. When we delete a parent control, all its child controls get deleted. When we move a parent control all its child controls also move along with it. 2. Child Control: controls placed inside a container control are called child controls. For example-Text Field, Label, Button etc.
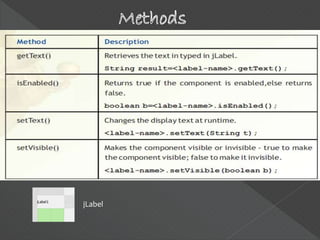
- 7. Properties of an object are used to specify its appearance on the form. For example to set the background colour of a textfield you change its background property; to set its font you change its font property; and so on. Methods are used to perform some action on the object. For example to display something in a textfield you can use its setText() method, to extract the contents of a textfield you can use its getText() method. Methods can be divided into two categories getters and setters. Events are the actions which are performed on controls. Examples of events are: mouseClick, mouseMoved,keyPressed etc. When the user performs any action on a control, an event happens and that event invokes (sends a call to) the corresponding part of the code and the application behaves accordingly.
- 8. We will be looking at the methods and properties of various componets. They are : 1.jFrameForm 2.jButton 3.jTextField 4.jLabel 5.jTextArea 6.jPassword 7.jRadioButton 8.jCheckBox 9.jComboBox 10.jList
- 9. jFrame in Navigator Window
- 10. jButton
- 11. jTextField
- 14. jLabel
- 16. jTextArea
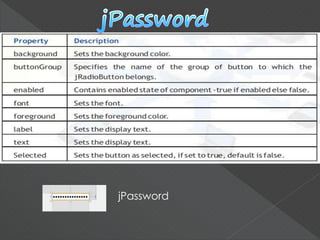
- 17. jPassword
- 21. jCheckBox
- 23. jComboBox
- 25. jList
- 26. In computer programming, a variable or scalar is a storage location and an associated symbolic name (an identifier) which contains some known or unknown quantity or information, a value. The variable name is the usual way to reference the stored value; this separation of name and content allows the name to be used independently of the exact information it represents. The characteristics of a variable are: 1. It has a name. 2. It is capable of storing values. 3. It provides temporary storage.
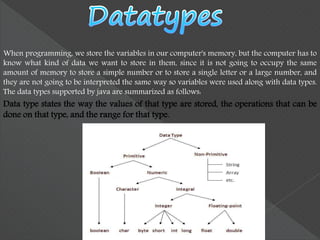
- 27. When programming, we store the variables in our computer's memory, but the computer has to know what kind of data we want to store in them, since it is not going to occupy the same amount of memory to store a simple number or to store a single letter or a large number, and they are not going to be interpreted the same way so variables were used along with data types. The data types supported by java are summarized as follows: Data type states the way the values of that type are stored, the operations that can be done on that type, and the range for that type.
- 28. These data types are used to store integer values only i.e. whole numbers only. The storage size and range is listed below :
- 29. These data types are used to store numbers having decimal points i.e. they can store numbers having fractional values.
- 30. With the introduction of variables and constants there arose a need to perform certain operations on them. We performed operations on variables and constants using operators. The operators available in java are summarized below: Assignment Operator : One of the most common operator is the assignment operator "=" which is used to assign a value to a variable. We assign the value given on the right hand side to the variable specified on the left hand side. The value on the right hand side can be a number or an arithmetic expression. For example:
- 31. Arithmetic Operators : These operators perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These symbols are similar to mathematical symbols. The only symbol that is different is "%“, which divides one operand by another and returns the remainder as its result. Relational Operator : A relational operator is used to test for some kind of relation between two entities. A mathematical expression created using a relational operator forms a relational expression or a condition. The following table lists the various relational operators and their usage:
- 32. Logical Operator : A logical operator denotes a logical operation. Logical operators and relational operators are used together to form a complex condition. Logical operators are: Unary Operators : The unary operators perform different kind of operations on a single operand .The operations performed are increasing/decreasing a value, negating a value/ expression, or inverting a Boolean value.
- 33. Control structures allow us to control the flow of our program's execution. If left unchecked by control-flow statements, a program's logic will flow through statements from top to bottom. We can have some control on the flow of a program by using operators to regulate precedence of operations, but control structures provide the power to change statement order and govern the flow of control in a program.
- 34. Simple if Statement - The if statement allows selection (decision making) depending upon the outcome of a condition. If the condition evaluates to true then the statement immediately following if will be executed and otherwise if the condition evaluates to false then the statements following the else clause will be executed. The selection statements are also called conditional statements or decision statements.
- 35. Nested if . . . else - These control structures are used to test for multiple conditions as against the simple if statement which can be used to test a single condition. The syntax of nested if else is as follows:
- 36. Switch Statement - This selection statement allows us to test the value of an expression with a series of character or integer values. On finding a matching value the control jumps to the statement pertaining to that value and the statement is executed, till the break statement is encountered or the end of switch is reached. The expression must either evaluate to an integer value or a character value. It cannot be a string or a real number. The syntax of the switch statement is as follows:
- 37. These statements are used to perform a set of instructions repeatedly while the condition is true. Iteration statements are also called looping statements. for loop - The loop has four different elements that have different purposes. These elements are: a) Initialization expression: Before entering in a loop, its variables must be initialized. b) Test Expression: The test expression decides whether the loop body will be executed or not. If the test condition is true, the loop body gets executed otherwise the loop is terminated. c) Increment/Decrement Expression: The Increment/Decrement expression changes the value of the loop variable. d) The Body of the loop: The statements, which are executed repeatedly while the test expression evaluates to true form the body of the loop. The syntax of the for loop is:
- 38. While Loop – The while loop is an entry-controlled loop. It means that the loop condition is tested before executing the loop body. If the loop condition is initially false, for the first iteration, then loop may not execute even once. The main characteristic of the while loop is that it can be used in both cases i.e. when the number of iterations is known as well as when it is unknown. The syntax of the while loop is as follows:
- 39. Do..While Loop - Do..While loop is an exit-controlled loop. In the do..while loop, the test occurs at the end of the loop. This ensures that the do..while loop executes the statements included in the loop body at least once. After the first execution of the statement, it evaluates the test expression. If the expression evaluates to true, then it executes the statements of the loop body again. Like if and while statements, the condition being checked must be included between parenthesis. The while statement must end with a semicolon. The syntax of the loop is as follows:
- 40. NetBeans is an IDE using which we can develop GUI applications in Java. NetBeans provides various components used to create a GUI front-end interface. GUI components' appearance and behavior is controlled by their properties and methods. We should use meaningful names for controls on the form and variables in the code. It makes programming convenient. Some useful Data Types supported in Java are: int, double, char and boolean. String is an Object (reference) type supported in Java. A variable must be declared before it can be used. Different types of operators are available in Java. Operators are used to perform various operations on data. Control Statements available in java are: if..else, switch..case, for, while, do..while.