Hadoop configuration & performance tuning
- 1. 1Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only 1 Hadoop 2.x Configuration & Map/Reduce Performance Tuning Suhas Gogate, Architect Hadoop Engg CF-Meetup, SFO (20th May 2014 )
- 2. A NEW PLATFORM FOR A NEW ERA
- 3. 3Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only About Me (https://www.linkedin.com/in/vgogate) Since 2008, active in Hadoop infrastructure and ecosystem components with lead Hadoop technology based companies – Yahoo, Netflix, Hortonworks, EMC-Greenplum/Pivotal Founder and PMC member/committer of the Apache Ambari project Contributed Apache “Hadoop Vaidya” – Performance diagnostics for M/R Prior to Hadoop, – IBM Almaden Research (2000-2008), CS Software & Storage systems. – In early days (1993) of my career, worked with a team that built first Indian super computer, PARAM (Transputer based MPP system) at Center for Development of Advance Computing (CDAC, Pune)
- 4. 4Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Agenda Introduction to Hadoop 2.0 – HDFS, YARN, Map/Reduce (M/R) Hadoop Cluster – Hardware selection & Capacity Planning Key Hadoop Configuration Parameters – Operating System, Local FS, HDFS, YARN Performance Tuning of M/R Applications – Hadoop Vaidya demo (MAPREDUCE-3202)
- 5. 5Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Introduction to Hadoop
- 6. 6Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop 1.0 -> 2.0 Image Courtesy Arun Murthy, Hortonworks
- 7. 7Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only HDFS Architecture
- 8. 8Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Map/Reduce 1.0
- 9. 9Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop YARN 2.0 Architecture
- 10. 10Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hardware selection & Capacity planning
- 11. 11Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Cluster: Hardware selection Hadoop runs on cluster of commodity machines – Does NOT mean unreliable & low-cost hardware – 2008: ▪ Single/Dual socket, 1+ GHz, 4-8GB RAM, 2-4 Cores, 2-4 1TB SATA drives, 1GbE NIC – 2014+: ▪ Dual socket 2+ GHz, 48-64GB RAM, 12-16 Cores, 12-16 1/3TB SATA drives, 2-4 bonded NICs Hadoop cluster comprises separate h/w profiles for, – Master nodes ▪ More reliable & available configuration ▪ Low storage/memory requirements compared to worker/data nodes (except HDFS Name node) – Worker nodes ▪ Not necessarily less reliable although not configured for high availability (e.g. JBOD not RAID) ▪ Resource requirements on storage, memory, CPU & network b/w are based on workload profile See Appliance/Reference architectures from EMC/IBM/Cisco/HP/Dell etc
- 12. 12Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Cluster capacity planning Initial cluster capacity is commonly based on HDFS data size & growth projection – Keep data compression in mind Cluster size – HDFS space per node = (Raw disk space per node – 20/25% non-DFS local storage) / 3 (RF) – Cluster nodes = Total HDFS space / HDFS space per node Start with balanced individual node configuration in terms of CPU/Memory/Number of disks – Keep provision for growth as you learn more about the workload – Guidelines for individual worker node configuration ▪ Latest generation processor(s) with 12/16 cores total, is a reasonable start ▪ 4 to 6 GB memory per core ▪ 1/1.5 disks per core ▪ 1 to 3 TB SATA disks per core ▪ 1GbE NIC Derive resource requirements service roles (typically Name node) – NN -> 4-6 cores, default 2GB + 1 GB roughly every 100TB of raw disk space, 1M Objects – RM/NN/DN -> 2GB RAM, 1 core (thumb rule)
- 13. 13Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Ongoing Capacity Planning Workload profiling – Make sure applications running on the cluster are well tuned to utilize cluster resources – Gather average CPU/IO/Mem/Disk utilization stats across worker nodes – Identify the resource bottlenecks for your workload and provision accordingly ▪ E,g, bump up more cores per node if CPU is bottleneck compared to other resources such as storage, I/O bandwidth ▪ E.g. If memory is a bottleneck (i.e. low utilization on CPU and I/O), then add more memory per node to let more tasks run per node. – HDFS storage growth rate & current capacity utilization Latency sensitive applications – Do planned project on-boarding ▪ Estimate resource requirement ahead of time (Capacity Calculator) – Use Resource Scheduler ▪ Schedule the jobs to maximize the resource utilization over the time
- 14. 14Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Cluster Configuration
- 15. 15Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Key Hadoop Cluster Configuration – OS Operating System (RHEL/CentOS 6.1+) – Mount disk volumes with NOATIME (speed up reads) – Disable transparent Huge page compaction ▪ # echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepages/defrag – Turn off caching on disk controller – vm.swappiness = 0 – vm.overcommit_memory = 1 – vm.overcommit_ratio = 100 – net.core.somaxconn=1024 (default socket listen queue size 128) – Choice of Linux I/O scheduler Local File System – Ext3 (reliable and recommended) vs Ext4 vs XFS – Default max open file descriptors per user (default 1K may change to 32K) – Reduce FS reserve blocks space (default 5% -> 0% on non-os partitions) BIOS – Disable BIOS power saving options may boost node performance
- 16. 16Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Key Hadoop Cluster Configuration - HDFS Use multiple disk mount points – dfs.datanode.data.dir (use all attached disks to data node) – dfs.namenode.name.dir (NN metadata redundancy on disk) DFS Block size – 128MB (you can override it while writing new files with different block size) Local file system buffer – io.file.buffer.size = 131072 (128KB) – Io.sort.factor = 50 to 100 (number merge streams while sorting file) NN/DN concurrency – dfs.namenode.handler.count (100) – dfs.datanode.max.transfer.threads (4096) Datanode Failed volumes tolerated – dfs.datanode.failed.volumes.tolerated
- 17. 17Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Key Hadoop Cluster Configuration - HDFS Short circuit read – dfs.client.read.shortcircuit = true – dfs.domain.socket.path JVM options (hadoop-env.sh) – export HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS=” ▪ -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Xms${dfs.namenode.heapsize.mb}m ▪ -Xmx${dfs.namenode.heapsize.mb}m ▪ -Dhadoop.security.logger=INFO,DRFAS ▪ -Dhdfs.audit.logger=INFO,RFAAUDIT ▪ -XX:ParallelGCThreads=8 ▪ -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC ▪ -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:ErrorFile=${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/hs_err_pid%p.log $HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS” – export HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS=” ▪ -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote ▪ -Xms${dfs.datanode.heapsize.mb}m ▪ -Xmx${dfs.datanode.heapsize.mb}m ▪ -Dhadoop.security.logger=ERROR,DRFAS $HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS"
- 18. 18Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Key Hadoop Cluster Configuration - YARN Use multiple disk mount points on the worker node – yarn.nodemanager.local-dirs – yarn.nodemanager.log-dirs Memory allocated for node manager containers – yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb ▪ Total memory on worker node allocated for all the containers running in parallel – yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb ▪ Minimum memory requested for map/reduce task container. ▪ Based on CPU cores and available memory on the node, this parameter can limit number of max containers per node – yarn.nodemanager.maximum-allocation-mb ▪ Default to yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb – yarn.mapreduce.map.memory.mb, yarn.mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb ▪ Default values for map/reduce task container memory. User can override them through job configuration – yarn.nodemanager.vmem-pmem-ratio = 2.1
- 19. 19Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Key Hadoop Cluster Configuration - YARN Use Yarn log aggregation – yarn.log-aggregation-enable RM/NM JVM options (yarn-env.sh) – export YARN_RESOURCEMANAGER_HEAPSIZE=2GB – export YARN_NODEMANAGER_HEAPSIZE=2GB – YARN_OPTS="$YARN_OPTS -server – -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true – -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC – -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError – -XX:ErrorFile=${YARN_LOG_DIR}/hs_err_pid%p.log"
- 20. 20Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Configuration Advisor - Tool Given – Data size, Growth rate, Workload profile, Latency/QoS requirements Suggests – Capacity requirement for Hadoop cluster (reasonable starting point) ▪ Resource requirements for various services roles ▪ Hardware profiles for master/worker nodes (No specific h/w vendor ) – Cluster services topology i.e. placement of service roles to nodes – Optimal services configuration for given hardware specs
- 21. 21Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Performance Tuning of M/R applications
- 22. 22Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Map/Reduce - WordCount
- 23. 23Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Optimizing M/R applications – key features Speculative Execution Use of Combiner Data Compression – Intermediate: LZO(native)/Snappy, Output: BZip2, Gzip Avoid map side disk spills – io.sort.mb Increased replication factor for out-of-band Hdfs access Distributed cache Map output partitioner Appropriate granularity for M/R tasks – Mapreduce.map.minsplitsize – Mapreduce.map.maxsplitsize – Optimal number of reducers
- 24. 24Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Performance Benchmark – Teragen Running teragen out-of-box will not utilize the cluster hardware resources Determine number of map tasks to run on each node to exploit max I/O bandwidth – Depends on number of disks on each node Example – 10 nodes, 5 disks/node, per node memory for m/r tasks 50GB – Hadoop jar hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.x.x.jar teragen – -Dmapred.map.tasks=50 -Dmapreduce.map.memory.mb=10GB – 10000000000 /teragenoutput
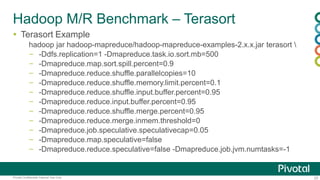
- 25. 25Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop M/R Benchmark – Terasort Terasort Example hadoop jar hadoop-mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.x.x.jar terasort – -Ddfs.replication=1 -Dmapreduce.task.io.sort.mb=500 – -Dmapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent=0.9 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.shuffle.parallelcopies=10 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.shuffle.memory.limit.percent=0.1 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.shuffle.input.buffer.percent=0.95 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.input.buffer.percent=0.95 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.shuffle.merge.percent=0.95 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.merge.inmem.threshold=0 – -Dmapreduce.job.speculative.speculativecap=0.05 – -Dmapreduce.map.speculative=false – -Dmapreduce.reduce.speculative=false -Dmapreduce.job.jvm.numtasks=-1
- 26. 26Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop M/R Benchmark – Terasort – -Dmapreduce.job.reduces=84 -Dmapreduce.task.io.sort.factor=100 – -Dmapreduce.map.output.compress=true – -Dmapreduce.map.output.compress.codec= ▪ org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec – -Dmapreduce.job.reduce.slowstart.completedmaps=0.4 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.merge.memtomem.enabled=false – -Dmapreduce.reduce.memory.totalbytes=12348030976 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.memory.mb=12288 – -Dmapreduce.reduce.java.opts= ▪ "-Xms11776m -Xmx11776m -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+CMSIncrementalMode - XX:+CMSIncrementalPacing -XX:ParallelGCThreads=4" – -Dmapreduce.map.memory.mb=4096 – -Dmapreduce.map.java.opts="-Xmx1356m" – /terasort-input /terasort-output
- 27. 27Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Vaidya: Performance diagnostic tool
- 28. 28Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Vaidya: Rule based performance diagnostic tool • Rule based performance diagnosis of M/R jobs – Set of pre-defined diagnostic rules – Diagnostic rules execution against job config & Job History logs – Targeted advice for discovered problems • Extensible framework – You can add your own rules, • Based on a rule template and published job counters – Write complex rules using existing simpler rules Vaidya: An expert (versed in his own profession , esp. in medical science) , skilled in the art of healing , a physician
- 29. 29Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Vaidya: Diagnostic Test Rule <DiagnosticTest> <Title>Balanaced Reduce Partitioning</Title> <ClassName> org.apache.hadoop.vaidya.postexdiagnosis.tests.BalancedReducePartitioning </ClassName> <Description> This rule tests as to how well the input to reduce tasks is balanced </Description> <Importance>High</Importance> <SuccessThreshold>0.40</SuccessThreshold> <Prescription>advice</Prescription> <InputElement> <PercentReduceRecords>0.85</PercentReduceRecords> </InputElement> </DiagnosticTest>
- 30. 30Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Vaidya: Report Element <TestReportElement> <TestTitle>Balanaced Reduce Partitioning</TestTitle> <TestDescription> This rule tests as to how well the input to reduce tasks is balanced </TestDescription> <TestImportance>HIGH</TestImportance> <TestResult>POSITIVE(FAILED)</TestResult> <TestSeverity>0.69</TestSeverity> <ReferenceDetails> * TotalReduceTasks: 4096 * BusyReduceTasks processing 0.85% of total records: 3373 * Impact: 0.70 </ReferenceDetails> <TestPrescription> * Use the appropriate partitioning function * For streaming job consider following partitioner and hadoop config parameters * org.apache.hadoop.mapred.lib.KeyFieldBasedPartitioner * -jobconf stream.map.output.field.separator, -jobconf stream.num.map.output.key.fields </TestPrescription> </TestReportElement>
- 31. 31Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Vaidya: Example Rules Balanced Reduce Partitioning – Check if intermediate data is well partitioned among reducers. Map/Reduce tasks reading HDFS files as side effect – Checks if HDFS files are being read as side effect and causing the access bottleneck across map/reduce tasks Percent Re-execution of Map/Reduce tasks Granularity of Map/Reduce task execution Map tasks data locality – This rule detects % data locality for Map tasks Use of Combiner & Combiner efficiency – Checks if there is a potential in using combiner after map stage Intermediate data compression – Checks if intermediate data is compressed to lower the shuffle time
- 32. 32Pivotal Confidential–Internal Use Only Hadoop Vaidya: Demo Thank you! • For Hadoop Vaidya demo • Download Pivotal HD single node VM (https://network.gopivotal.com/products/pivotal-hd) • Run M/R job • After job completed, go Resource Manager UI • Select Job History • To look at the diagnostic report click on “Vaidya Report” link in left menu • Vaidya Patch submitted to Apache Hadoop • https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/MAPREDUCE-3202
- 33. A NEW PLATFORM FOR A NEW ERA