Handout-Normal Forms-Db Indexescombo.pptx
- 2. 2 NORMAL FORMS • At the end of this lesson students should be able to i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 3. NORMAL FORMS • Normal Form (NF) is a set of rules or guidelines used to structure and organize the data within database tables to minimize data redundancy, improve data integrity, and reduce database anomalies. The normal forms are: 1NF - First Normal Form 2NF - Second Normal Form 3NF - Third Normal Form BCNF - Boyce-Codd Normal Form 5NF - Fifth Normal Form i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 4. 4 FIRST NORMAL FORM (1NF) 1. Every field in 1NF must be atomic, that is, indivisible. In other words, there must be no “multi-valued” field 2. Every record must be unique (i.e. have a primary key) 3.There should be no repeating columns like vehicle1, vehicle2, vehicle3… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jgUeOjImOOw&feature=youtu.be T1 i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 5. 5 1NF EXAMPLE Id Name Age Interests 1 John 14 Soccer, Programming 2 Garba 15 3 Daniel 13 Music Id Name Age Interests 1 John 14 Soccer 1 John 14 Programming 2 Garba 15 3 Daniel 13 Music SOLUTION i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 6. 6 MENTION THE THREE MOST WIDELY USED NORMAL FORMS i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 7. 7 EXAMPLE: ORDER TABLE (T3) Item Colour Price Tax T-shirt Red, blue 12.00 0.60 Polo Red, yellow 12.00 0.60 Sweatshirt Blue, black 25.00 1.25 The table is not in first normal form.Why? 1. Multi-valued fields. 2. No primary key. i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 8. RESOLVED: ORDER TABLE (T4) • Resolve the multi-values. • Concatenate two fields to form composite key or concatenated primary key. • We now have the table in 1NF Item Colour Price Tax T-shirt Red 12.00 0.60 T-shirt Blue 12.00 0.60 Polo Red 12.00 0.60 Polo Yellow 12.00 0.60 Sweatshirt Blue 25.00 1.25 Sweatshirt Black 25.00 1.25 i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 9. 9 SECOND NORMAL FORM 1. The table must FIRST be in 1NF 2. All non-key fields must depend on all components of the primary key. Item Colour Price Tax T-shirt Red 12.00 0.60 T-shirt Blue 12.00 0.60 Polo Red 12.00 0.60 Polo Yellow 12.00 0.60 Sweatshirt Blue 25.00 1.25 Sweatshirt Black 25.00 1.25 In table T4, Price depends on item but not on colour. T4
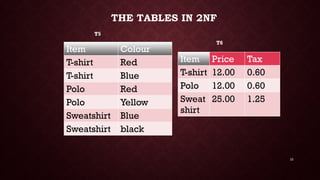
- 10. 10 THE TABLES IN 2NF Item Colour T-shirt Red T-shirt Blue Polo Red Polo Yellow Sweatshirt Blue Sweatshirt black Item Price Tax T-shirt 12.00 0.60 Polo 12.00 0.60 Sweat shirt 25.00 1.25 T5 T6
- 11. 3NF • The table must FIRT be in 2NF • No non-key field depends upon another. All non- key fields must depend ONLY on the primary key. • Table T6 below is not in 3NF….Why? Item Colour T-shirt Red T-shirt Blue Polo Red Polo Yellow Sweatshirt Blue Sweatshirt black Item Price Tax T-shirt 12:00 0.60 Polo 12:00 0.60 Sweatshirt 25:00 1.25 T6 T5 i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 12. 12 TABLES IN 3NF Price Tax 12.00 0.60 25.00 1.25 Item Colour T-shirt Red T-shirt Blue Polo Red Polo Yellow Sweatshirt Blue Sweatshirt black T5 Item Price T-shirt 12.00 Polo 12.00 Sweats hirt 25.00 T7 T8 i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 13. 13 CLASS WORK 1. With the aid of a table vividly explain composite key? 2. Normalise the table below to 1NF and 2NF. Item Colour Price Tax Huawei PSmart White,Yellow 16.00 0.50 Iphone Yellow, blue 19.00 0.70 Galaxy Blue, Red 17.00 0.25 i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 14. 14 SOLUTION i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
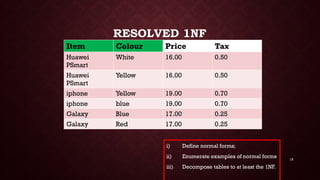
- 15. 15 RESOLVED 1NF Item Colour Price Tax Huawei PSmart White 16.00 0.50 Huawei PSmart Yellow 16.00 0.50 iphone Yellow 19.00 0.70 iphone blue 19.00 0.70 Galaxy Blue 17.00 0.25 Galaxy Red 17.00 0.25 i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 16. 16 RESOLVED TO 2NF Item Price Tax Huawei PSmart 16.00 0.50 iphone 19.00 0.70 Galaxy 17.00 0.25 Item Colour Huawei PSmart White Huawei PSmart Yellow iphone Yellow iphone blue Galaxy Blue Galaxy Red i) Define normal forms; ii) Enumerate examples of normal forms iii) Decompose tables to at least the 1NF.
- 17. 17 DATABASE INDEXES • At the end of this lesson students should be able to i) Describe database index; ii) State the advantages of database index; iii) Enumerate and explain the various types of indexes; iv) Create database index using MS Access.
- 18. 18 DATABASE INDEXES See the index at the end of a book. Why would you use a book index? Why do you need Database indexes. Indexes make it faster to find specific records in a database.
- 19. 19 DATABASE INDEXING What is DATABASE INDEX? • A database index is a list of keys (or keywords), each of which identifies a unique record. • Index File: an index file is a table with two columns: one stores a sorted list of the values in the field being indexed and the second stores pointers that give the location of each record in the table. • That is, an index is a file which consists of records (called index entries) of the form… search key value pointer to block in data file i) Describe database index; ii) State the advantages of database index; iii) Enumerate and explain the various types of indexes; iv) Create database index using MS Access.
- 20. 20 INDEX FILE
- 21. 21 TYPES OF INDEX 1. Primary Index: Primary index is defined on an ordered data file.The data file is ordered on a key field.The key field is generally the primary key of the relation. E.g. Employee ID or RegNo as in the table below.
- 22. 22 2. Secondary (Non-clustering) index : An index that is defined on a non-ordering field of the data file. A Secondary index may be generated from a field which is a candidate key and has a unique value in every record, or a non-key with duplicate values. That is, indexing is done on a set of attributes different from the primary key
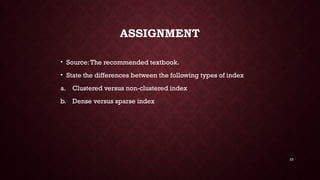
- 23. 23 ASSIGNMENT • Source:The recommended textbook. • State the differences between the following types of index a. Clustered versus non-clustered index b. Dense versus sparse index
- 24. 24 CREATING A SINGLE-FIELD INDEX IN MS ACCESS • In the Navigation Pane, right-click the name of the table that you want to create the index in, and then click DesignView on the shortcut menu. • Click the Field Name for the field that you want to index. • Under Field Properties, click the General tab. • In the Indexed property, click Yes (Duplicates OK) if you want to allow duplicates, or Yes (No Duplicates) to create a unique index. • To save your changes, click Save
Editor's Notes
- #3: There are five normal forms. The first three are the most widely used normal forms.
- #9: Though this is in 1NF, it fails the rule. Solution: Break the erroneous table into parts: Item and Price tables
- #10: Table resolved to 2NF
- #11: Tax depends on item instead of price. Normalize table two further
- #15: SS3C to form a note on this for been noisy.
- #18: See video: What is an index Read pages 1 and 2: Understanding data processing for SSS 3 by Dinehin Victoria - Definitions, Advantages, Search key, table scan, Disadvantages of table scan
- #19: See the image in next slide
- #21: Online: A primary index is an index on a set of fields that includes the unique primary key for the field and is guaranteed not to contain duplicates. Also called clustered index. E.g. Employee ID. In the example here, the search key or ordering key field in the index table is the registration number which is the primary key of the students table.
- #22: Point 1: Source: Data Processing for senior secondary school book 3. Page 7 Point 2: http://www.tutorialspoint.com/dbms/dbms_indexing.htm Point 3: Gege