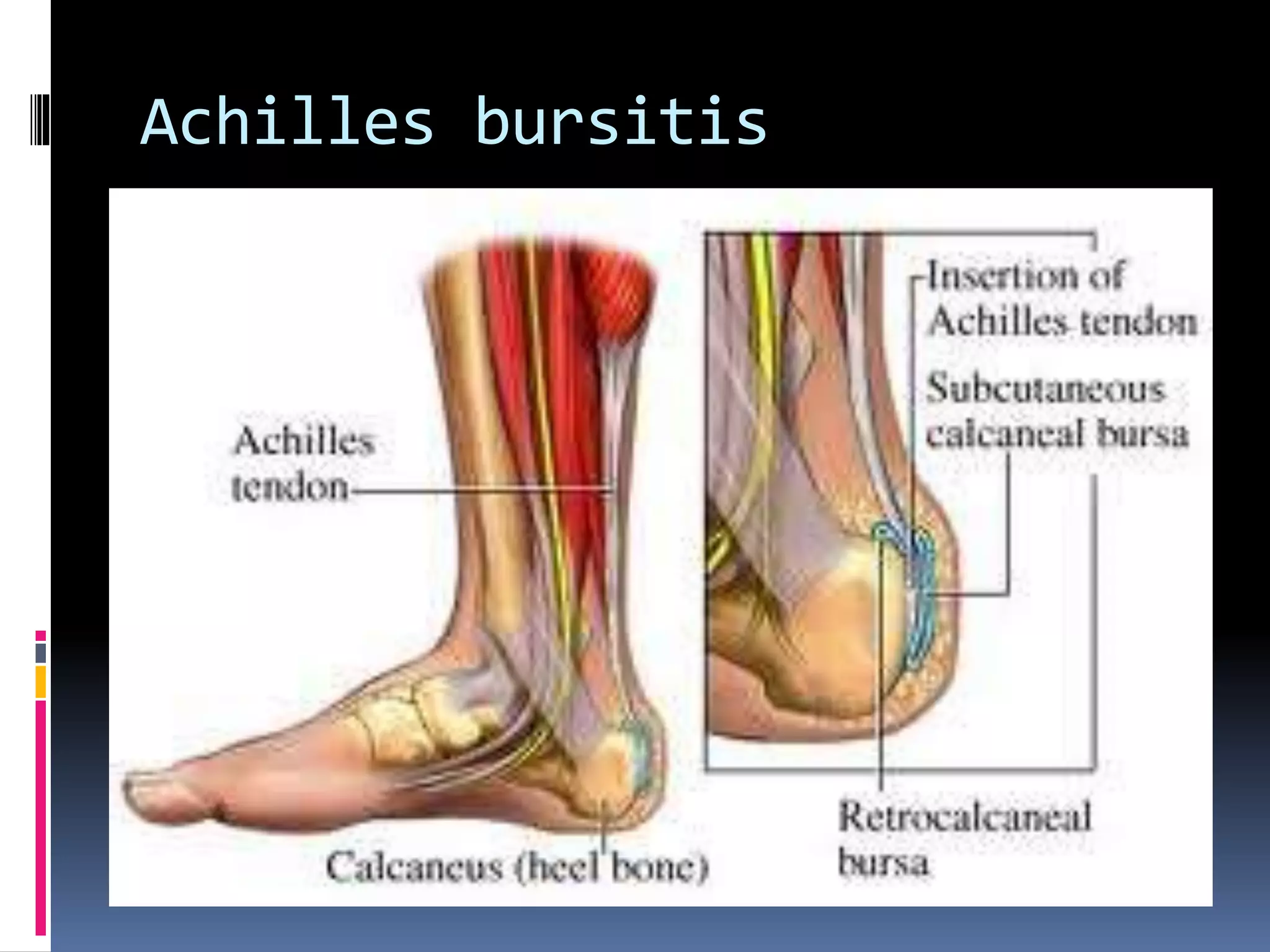
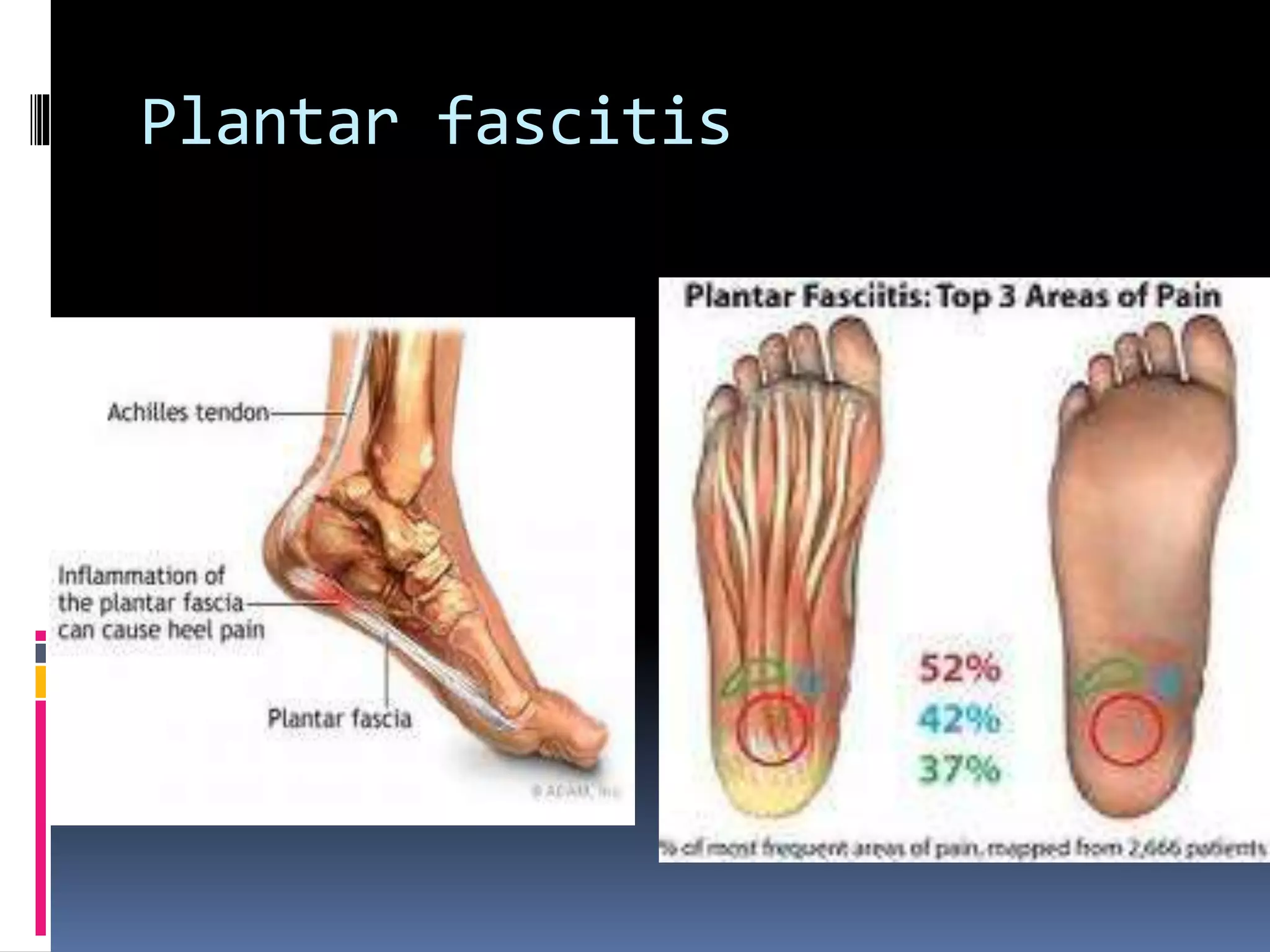
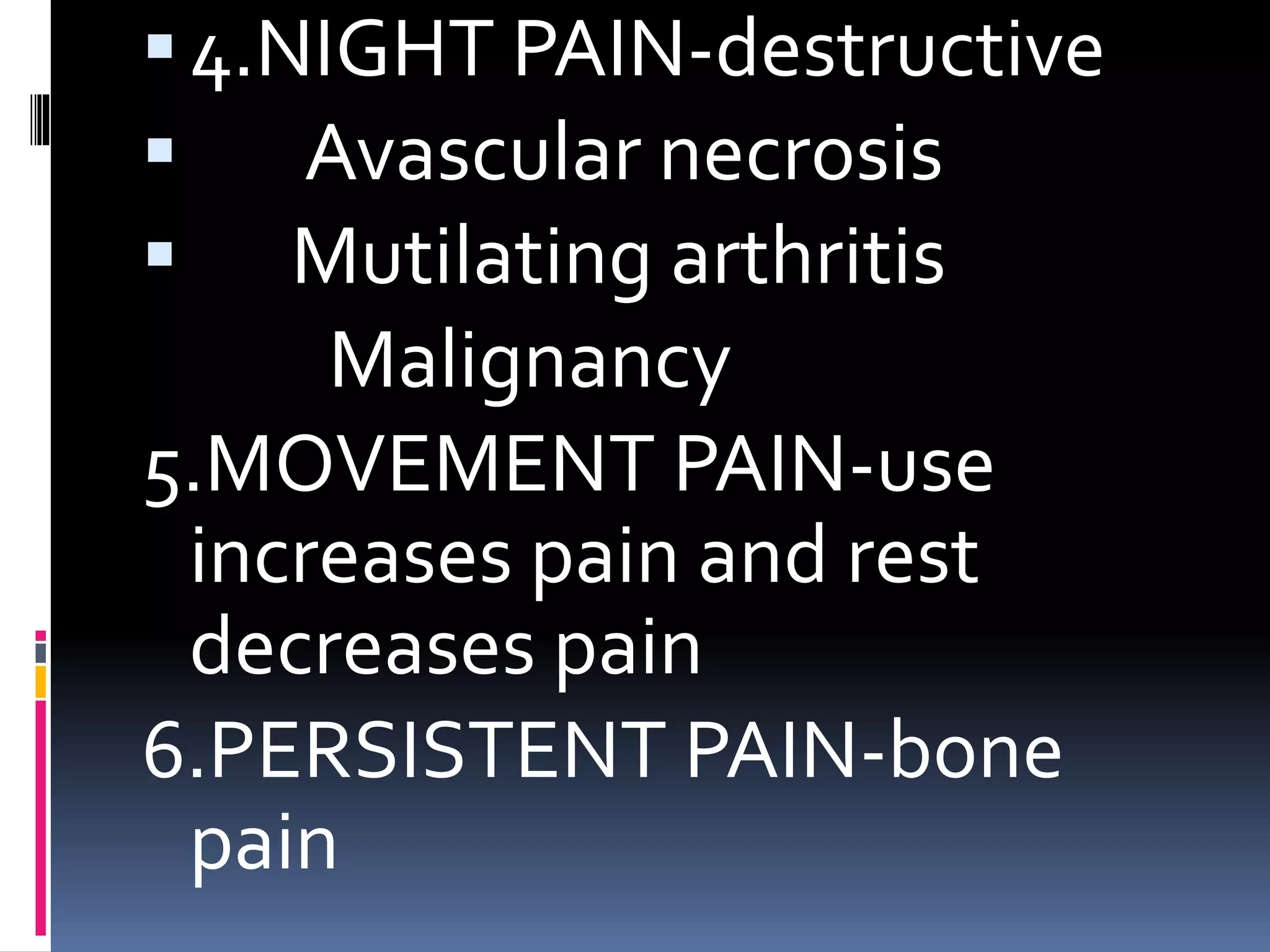
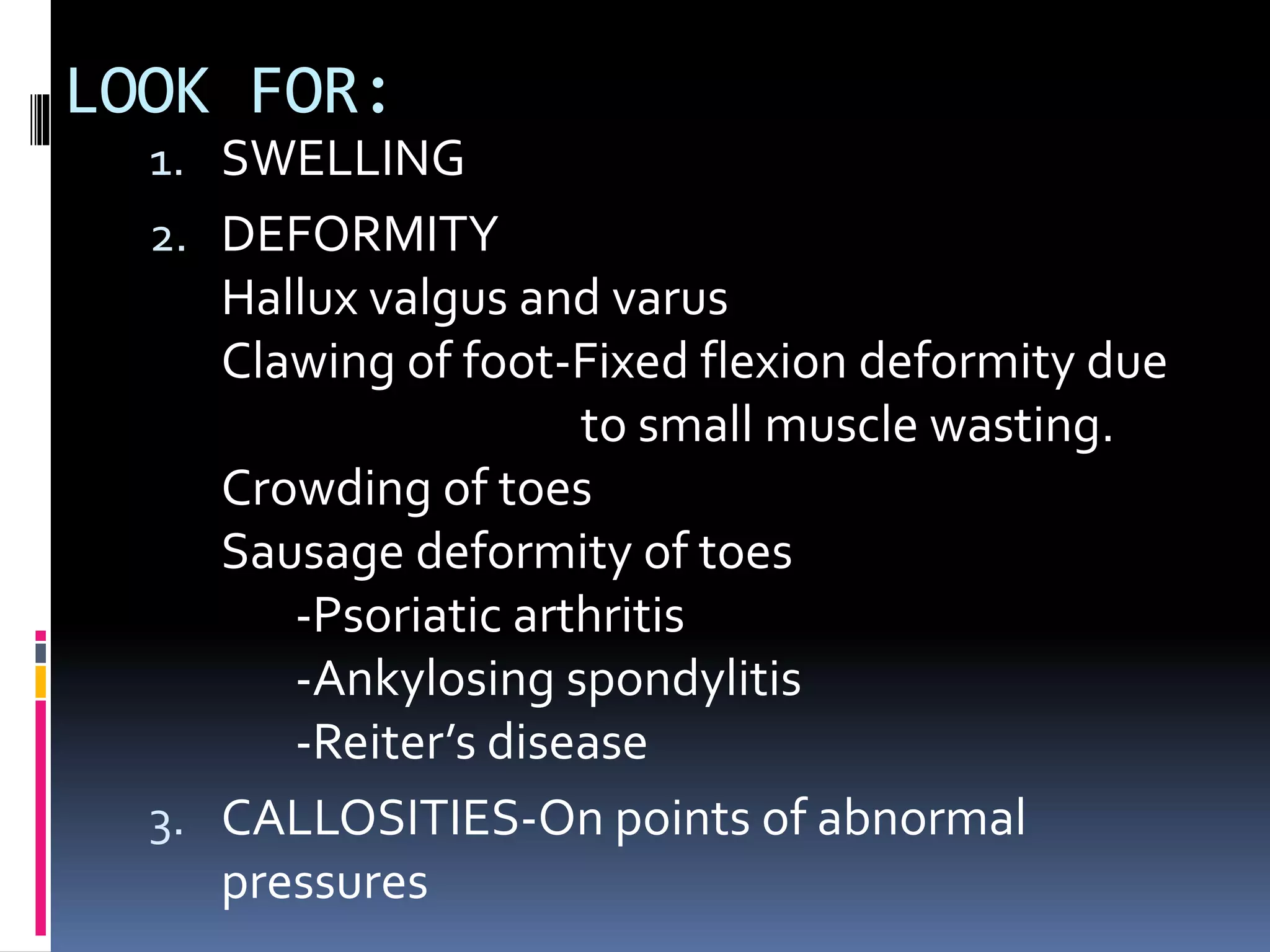
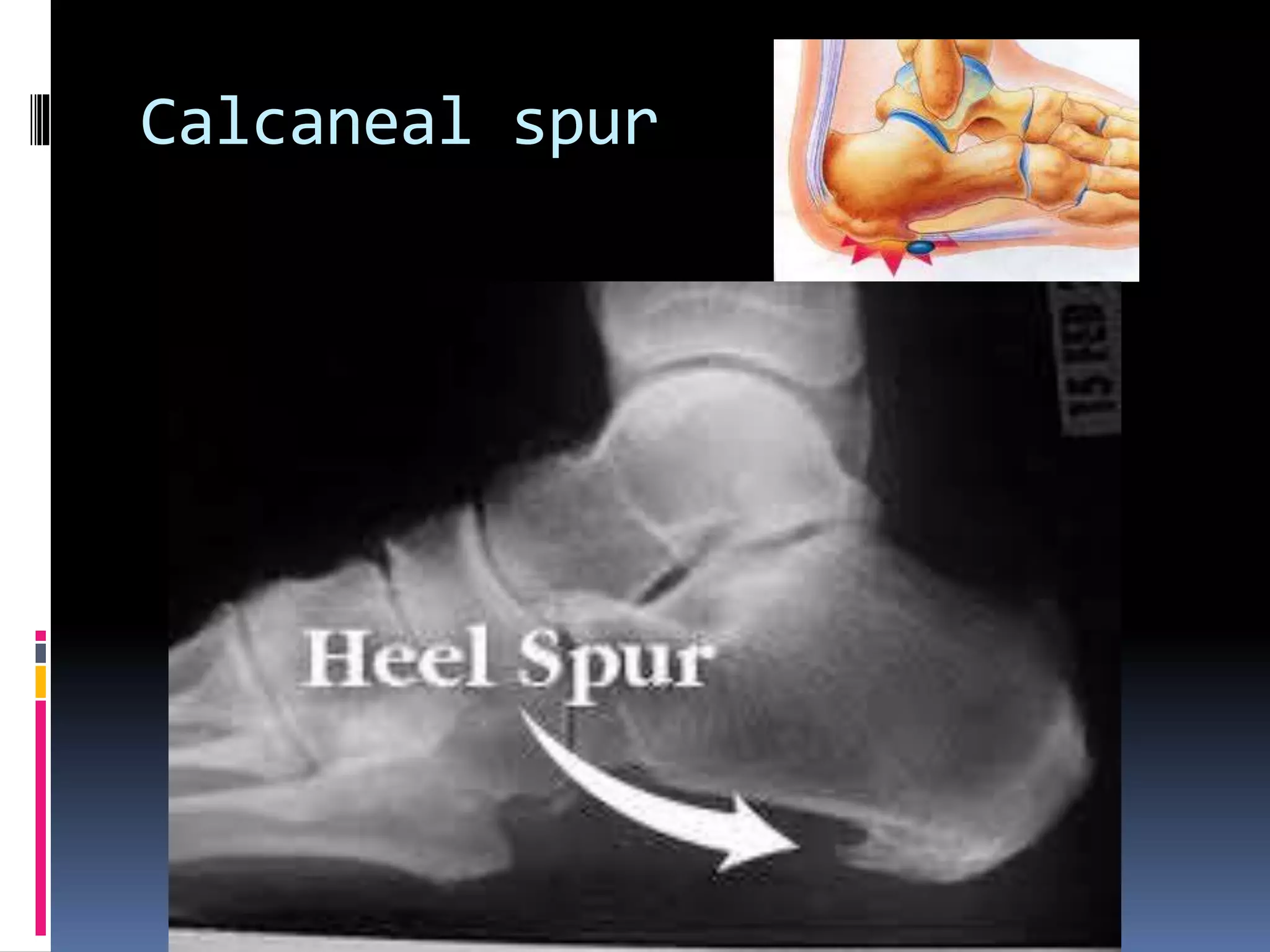
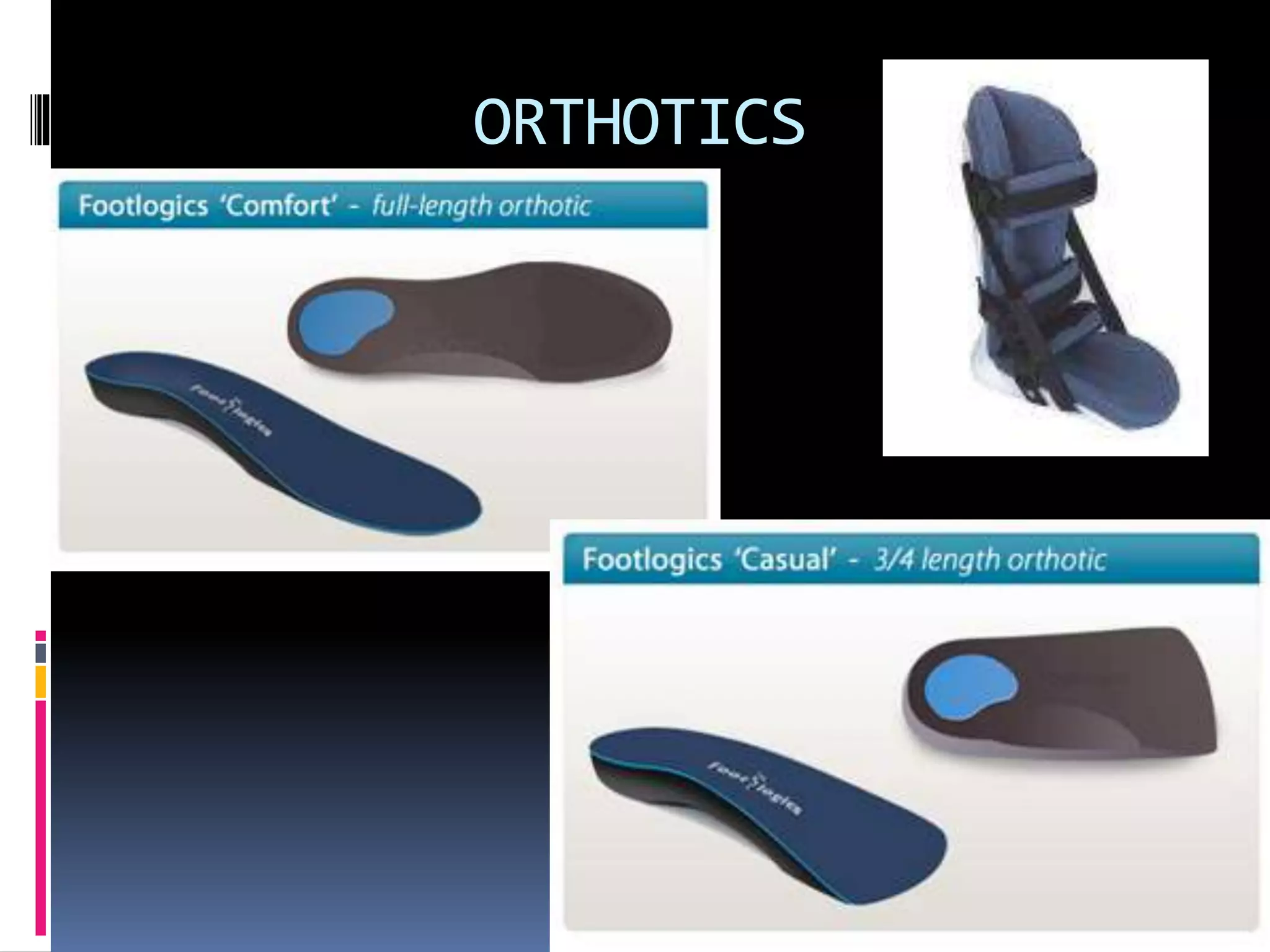
This document discusses various causes of heel pain and approaches to evaluation and treatment. The most common causes are Achilles enthesitis, Achilles tendinitis, Achilles bursitis, and plantar fasciitis. Less common causes include Achilles tendon rupture and bone issues. Evaluation involves taking a history, clinical examination, and potential investigations. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include rest, exercises, ice, anti-inflammatories, orthotics, and orthotics.