How Android Architecture Components can Help You Improve Your App’s Design?
- 2. How Android Architecture Components can Help You Improve Your App’s Design? With so many app architectures around weren’t you confused when it came to picking the right pattern for your app? Whether to choose Model View Presenter (MVP), Model View Controller (MVC), Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM), some other pattern, or even no architectural pattern at all?
- 3. Until Google I/O 2017, there was no clue from Google too! Or rather, the tech giant never made any recommendations on any specific architecture for Android app development. However, in response to popular demand from Android app developers, the Android Framework team has come out with an opinionated guide to architecting Android apps. Along with the guide they have developed a companion set of architecture components. In today’s post we would be talking about Android architecture components, why you need them and how they help you to improve your apps. So let’s get started!
- 4. Why do you need architecture components? Well, according to Lyla, developer advocate at Android, the architecture components can help you with common development challenges. These components can: persist data; manage lifecycle; make your app modular; help you avoid memory leaks; prevent you from writing boilerplate code. You can either use these components separately or together. A very simple app needs a database and a robust app UI that modifies, requests or generates data for database and also displays data from the database. So, the new components make this process that is required to make a basic app, function, quite easy. Moreover, these components are designed to work together like building blocks. With the release of Android P Developer Preview 1, Google is trying to make the app design more systematic with the new architecture components.
- 5. A brief introduction to the architecture components and how they can enable you to enhance your app’s design So, what are Android architecture components? Well, a set of libraries that would enable you to design robust, testable and maintainable apps. The components are as follows: Room LiveData Lifecycle-aware components ViewModel Paging
- 6. Room Room is a robust SQL object-mapping library that you can use to tackle the database. In order to set up the tables using Room, you can define a Plain Old Java Object, or a POJO and then mark this POJO with an @Entity annotation as shown below: @Entity public class Trail { public @PrimaryKey String id; public String name; public double kilometers; public int difficulty; } Now for each POJO you would need to define a DAO or a Database Access Object. The annotated methods represent the SQLite commands you would need to interact with your POJO’s data. (Android Developers official website is the source of all the screenshots or images used within this article.)
- 7. Room Along with providing a fluent database access, Room also perform the following two important functions: It automatically converts your POJO objects into the corresponding database tables and back again. It verifies your SQLite at compile time, so that if you make a mistake like referencing a column that is not actually in the database, it will throw a helpful error. Now that you have a Room database, you can use another new architecture component, called LiveData, to monitor changes in the database.
- 8. Live Data LiveData is an observable data holder. It implies that LiveData holds data and lets you know by a notification when the data changes so that you can change the UI accordingly. It is an abstract class that you can extend or for simple cases you can use the MutableLiveData class. Whenever you update the value of the MutableLiveData with a call to set value, it would then trigger and update in your UI. Room is designed for supporting LiveData and this a very powerful feature indeed. In case, you want to use them together, just modify your DAO to return objects that are wrapped with the LiveData class. Room will create a LiveData object observing the database. Now, to update your UI using LiveData and Room, you can write code as follows:
- 9. Live Data The final outcome is that every time your Room database updates, the data in your LiveData changes simultaneously which in turn automatically triggers UI updates. This reminds us of another astounding feature of LiveData, that is, it is a Lifecycle-aware component.
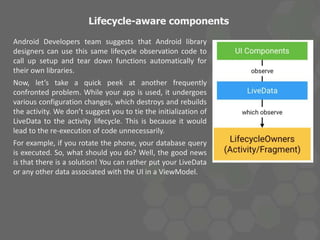
- 10. Lifecycle-aware components According to the definition in Android developers’ site, Lifecycle-aware components perform actions in response to a change in the lifecycle status of another component, such as activities and fragments. These components help you produce better-organized, and often lighter-weight code, that is easier to maintain. Now, LiveData is Lifecycle-aware because it can find out when your activity is on-screen, off-screen or destroyed through the power of lifecycle observation. Thus, it makes sure that it does not send database updates to an inactive UI. Lifecycle-aware components have two interfaces: 1. Lifecycle Owner; and 2. Lifecycle Observer. 3. Lifecycle Owners: These are objects with lifecycles, such as, activities and fragments. 4. Lifecycle Observers: This interface, on the other hand, observes Lifecycle Owners and are informed of lifecycle changes.
- 11. Lifecycle-aware components Let’s put a quick glance at the simplified code for LiveData that is a Lifecycle observer too. The methods that are annotated with @OnLifecycleEvent manage initialization and decimate when the associated Lifecycle Owner starts or stops. This in turn enables LiveData objects to manage their own setup and tear down; this allows the UI components to observe the LiveData, and the LiveData components to observe the Lifecycle Owners.
- 12. Lifecycle-aware components Android Developers team suggests that Android library designers can use this same lifecycle observation code to call up setup and tear down functions automatically for their own libraries. Now, let’s take a quick peek at another frequently confronted problem. While your app is used, it undergoes various configuration changes, which destroys and rebuilds the activity. We don’t suggest you to tie the initialization of LiveData to the activity lifecycle. This is because it would lead to the re-execution of code unnecessarily. For example, if you rotate the phone, your database query is executed. So, what should you do? Well, the good news is that there is a solution! You can rather put your LiveData or any other data associated with the UI in a ViewModel.
- 13. ViewModel ViewModels are objects that provide data for UI components and remain unaffected by configuration changes. Every time you want to create a ViewModel object, you would need to extend the ViewModel class. Then, you have to put all the data needed for your activity UI into the ViewModel as shown in the screenshot below: Now on, if your activity is recreated owing to a configuration change, your app won’t re- query the database because you have already cached data for the UI within the ViewModel.
- 14. ViewModel If you need to create your activity or fragment, you can now get a reference to the ViewModel and use it (see screenshot below). When you create an activity a ViewModel is generated for your activity for the first time. When you request again a ViewModel, the original ViewModel with the UI data cache is received. This ensures that there is no database calls needlessly anymore.
- 15. Paging Now let’s assume that we have a list of users instead of a single user. Many applications require loading a lot of information from the database. Database queries can take a long time to run and consume a lot of memory. To address all of these issues, Google recently released an architecture component, called Paging, which streamlines the process of requesting data as and when you need it. The main components of the Paging library are: 1. PagedList Adapter; 2. PagedList; 3. DataSource; and 4. LivePageListBuilder You can get a detailed view of the Paging library at the Android developers site.
- 16. Summing up Hope you too are super excited to know about this new architecture shininess, which will enable you to enhance the design of your applications. Do you have any Android app idea? You can talk with our Android app development experts to transform it into reality. Originally Published at: https://goo.gl/mRBq7w