How to analyze and tune sql queries for better performance percona15
- 1. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Øystein Grøvlen Senior Principal Software Engineer MySQL Optimizer Team, Oracle April 16, 2015 How to Analyze and Tune MySQL Queries for Better Performance
- 2. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL cost-based optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 3. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 4. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL Optimizer SELECT a, b FROM t1, t2, t3 WHERE t1.a = t2.b AND t2.b = t3.c AND t2.d > 20 AND t2.d < 30; MySQL Server Cost based optimizations Heuristics Cost Model Optimizer Table/index info (data dictionary) Statistics (storage engine) t2 t3 t1 Table scan Range scan Ref access JOIN JOIN
- 5. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cost-based Query Optimization • Assign cost to operations • Compute cost of partial or alternative plans • Search for plan with lowest cost • Cost-based optimizations: General idea Access method Subquery strategyJoin order t2 t3 t1 Table scan Range scan Ref access JOIN JOIN
- 6. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. • IO-cost: – Estimates from storage engine based on number of pages to read – Both index and data pages • Schema: – Length of records and keys – Uniqueness for indexes – Nullability • Statistics: – Number of rows in table – Key distribution/Cardinality: • Average number of records per key value • Only for indexed columns • Maintained by storage engine – Number of records in an index range Input to Cost Model
- 7. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cost Model Example Table scan: • IO-cost: #pages in table • CPU cost: #rows * ROW_EVALUATE_COST Range scan (on secondary index): • IO-cost: #pages to read from index + #rows_in_range • CPU cost: #rows_in_range * ROW_EVALUATE_COST SELECT SUM(o_totalprice) FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1994-01-01' AND '1994-12-31';
- 8. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cost Model EXPLAIN SELECT SUM(o_totalprice) FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1994-01-01' AND '1994-12-31'; Example EXPLAIN SELECT SUM(o_totalprice) FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1994-01-01' AND '1994-06-30'; id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders ALL i_o_orderdate NULL NULL NULL 15000000 Using where Id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders range i_o_orderdate i_o_orderdate 4 NULL 2235118 Using index condition
- 9. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cost Model Example: Optimizer Trace join_optimization / row_estimation / table : orders / range_analysis "table_scan": { "rows": 15000000, "cost": 3.12e6 } /* table_scan */, "potential_range_indices": [ { "index": "PRIMARY", "usable": false, "cause": "not_applicable“ }, { "index": "i_o_orderdate", "usable": true, "key_parts": [ "o_orderDATE", "o_orderkey" ] } ] /* potential_range_indices */, … "analyzing_range_alternatives": { "range_scan_alternatives": [ { "index": "i_o_orderdate", "ranges": [ "1994-01-01 <= o_orderDATE <= 1994-12-31" ], "index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true, "rowid_ordered": false, "using_mrr": false, "index_only": false, "rows": 4489990, "cost": 5.39e6, "chosen": false, "cause": "cost" } ] /* range_scan_alternatives */, … } /* analyzing_range_alternatives */
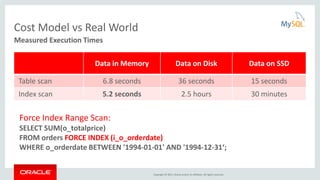
- 10. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cost Model vs Real World Data in Memory Data on Disk Data on SSD Table scan 6.8 seconds 36 seconds 15 seconds Index scan 5.2 seconds 2.5 hours 30 minutes Measured Execution Times Force Index Range Scan: SELECT SUM(o_totalprice) FROM orders FORCE INDEX (i_o_orderdate) WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1994-01-01' AND '1994-12-31‘;
- 11. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Performance Schema SELECT event_name, count_read, avg_timer_read/1000000000.0 “Avg Read Time (ms)”, sum_number_of_bytes_read “Bytes Read” FROM performance_schema.file_summary_by_event_name WHERE event_name='wait/io/file/innodb/innodb_data_file'; Disk I/O event_name count_read Avg Read Time (ms) Bytes Read wait/io/file/innodb/innodb_data_file 2188853 4.2094 35862167552 event_name count_read Avg Read Time (ms) Bytes Read wait/io/file/innodb/innodb_data_file 115769 0.0342 1896759296 Index Range Scan Table Scan
- 12. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 13. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Selecting Access Method • For each table, find the best access method: – Check if the access method is useful – Estimate cost of using access method – Select the cheapest to be used • Choice of access method is cost based Finding the optimal method to read data from storage engine Main access methods: Table scan Index scan Ref access Range scan Index merge Loose index scan
- 14. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Ref Access EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM customer WHERE c_custkey = 570887; Single Table Queries id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE customer const PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 const 1 NULL EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate = ‘1992-09-12’; id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders ref i_o_orderdate i_o_orderdate 4 const 6271 NULL
- 15. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Ref Access Join Queries EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders JOIN customer ON c_custkey = o_custkey WHERE o_orderdate = ‘1992-09-12’; Id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders ref i_o_orderdate, i_o_custkey i_o_orderdate 4 const 6271 Using where 1 SIMPLE customer eq_ref PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 dbt3.orders. o_custkey 1 NULL
- 16. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Ref Access Join Queries, continued EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders JOIN customer ON c_custkey = o_custkey WHERE c_acctbal < -1000; Id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE customer ALL PRIMARY NULL NULL NULL 1500000 Using where 1 SIMPLE orders ref i_o_custkey i_o_custkey 5 dbt3.customer. c_custkey 7 NULL
- 17. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Optimizer • Goal: find the “minimal” ranges for each index that needs to be read • Example: SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE (key1 > 10 AND key1 < 20) AND key2 > 30 • Range scan using INDEX(key1): • Range scan using INDEX(key2): 10 20 30
- 18. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Optimizer "analyzing_range_alternatives": { "range_scan_alternatives": [ { "index": "i_a", "ranges": [ "10 < a < 11", "11 < a < 19", "19 < a < 25" ], "index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true, "rowid_ordered": false, "using_mrr": false, "index_only": false, "rows": 3, "cost": 6.61, "chosen": true }, { "index": "i_b", "ranges": [ "NULL < b < 5", "10 < b" ], "index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true, "rowid_ordered": false, … Optimizer Trace show ranges SELECT a, b FROM t1 WHERE a > 10 AND a < 25 AND a NOT IN (11, 19)) AND (b < 5 OR b > 10);
- 19. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Optimizer: Case Study SELECT * FROM orders WHERE YEAR(o_orderdate) = 1997 AND MONTH(o_orderdate) = 5 AND o_clerk = 'Clerk#000001866'; Why table scan? id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders ALL NULL NULL NULL NULL 15000000 Using where Index not considered mysql> SELECT * FROM orders WHERE year(o_orderdate) = 1997 AND MONTH(… ... 15 rows in set (8.91 sec)
- 20. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Some Reasons Why Index can not be Used • Indexed column is used as argument to function YEAR(o_orderdate) = 1997 • Looking for a suffix: name LIKE ’%son’ • First column(s) of compound index NOT used b = 10 when index defined over (a, b) • Type mismatch my_string = 10 • Character set / collation mismatch t1 LEFT JOIN t2 ON t1.utf8_string = t2. latin1_string 20
- 21. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Optimizer: Case Study SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND '1997-05-31' AND o_clerk = 'Clerk#000001866'; Rewrite query to avoid functions on indexed columns id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders range i_o_orderdate i_o_orderdate 4 NULL 376352 Using index condition; Using where mysql> SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND … ... 15 rows in set (0.91 sec)
- 22. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Optimizer: Case Study CREATE INDEX i_o_clerk ON orders(o_clerk); SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND '1997-05-31' AND o_clerk = 'Clerk#000001866'; Adding another index id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders range i_o_orderdate, i_o_clerk i_o_clerk 16 NULL 1504 Using index condition; Using where mysql> SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND … ... 15 rows in set (0.01 sec)
- 23. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Access for Multi-Column Index • Table: • INDEX idx(a, b, c); • Logical storage layout of index: Example table with multi-column index 10 1 2 3 4 5 10 11 1 2 3 4 5 12 1 2 3 4 5 13 1 2 3 4 5 a b c 11 12 pk a b c
- 24. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Range Optimizer: Case Study CREATE INDEX i_o_clerk_date ON orders(o_clerk, o_orderdate); SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND '1997-05-31' AND o_clerk = 'Clerk#000001866'; Create multi-column index id select type table type possible keys key key len ref row s extra 1 SIMPLE orders range i_o_orderdate, i_o_clerk, i_o_clerk_date i_o_clerk_date 20 NULL 14 Using index condition mysql> SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND … ... 15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 25. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Performance Schema: Query History UPDATE performance_schema.setup_consumers SET enabled='YES' WHERE name = 'events_statements_history'; mysql> SELECT sql_text, (timer_wait)/1000000000.0 “Time(ms)”, rows_examined Rows FROM performance_schema.events_statements_history ORDER BY timer_start; +---------------------------------------------------------------+----------+------+ | sql_text | Time(ms) | Rows | +---------------------------------------------------------------+----------+------+ | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 8.1690 | 1505 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 7.2120 | 1505 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 8.1613 | 1505 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 7.0535 | 1505 | | CREATE INDEX i_o_clerk_date ON orders(o_clerk,o_orderdate) |82036.4190 | 0 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 0.7259 | 15 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 0.5791 | 15 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 0.5423 | 15 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 0.6031 | 15 | | SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' … | 0.2710 | 15 | +---------------------------------------------------------------+----------+------+ MySQL 5.7: Enabled by default
- 26. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 27. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Join Optimizer • Goal: Given a JOIN of N tables, find the best JOIN ordering • Strategy: – Start with all 1-table plans – Expand each plan with remaining tables • Depth-first – If “cost of partial plan” > “cost of best plan”: • “prune” plan – Heuristic pruning: • Prune less promising partial plans • May in rare cases miss most optimal plan (turn off with set optimizer_prune_level = 0) ”Greedy search strategy” t1 t2 t2 t2 t2 t3 t3 t3 t4t4 t4 t4t4 t3 t3 t2 t4t2 t3
- 28. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Complexity and Cost of Join Optimizer Heuristics to reduce the number of plans to evaluate: • Use optimizer_search_depth to limit the number of tables to consider • Pre-sort tables on size and key dependency order (Improved in MySQL 5.6) • When adding the next table to a partial plan, add all tables that it has an equality reference to (New in MySQL 5.6) Join of N tables: N! possible plans to evaluate
- 29. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Join Optimizer: Case study SELECT o_year, SUM(CASE WHEN nation = 'FRANCE' THEN volume ELSE 0 END) / SUM(volume) AS mkt_share FROM ( SELECT EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o_orderdate) AS o_year, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) AS volume, n2.n_name AS nation FROM part JOIN lineitem ON p_partkey = l_partkey JOIN supplier ON s_suppkey = l_suppkey JOIN orders ON l_orderkey = o_orderkey JOIN customer ON o_custkey = c_custkey JOIN nation n1 ON c_nationkey = n1.n_nationkey JOIN region ON n1.n_regionkey = r_regionkey JOIN nation n2 ON s_nationkey = n2.n_nationkey WHERE r_name = 'EUROPE’ AND o_orderdate BETWEEN '1995-01-01' AND '1996-12-31’ AND p_type = 'PROMO BRUSHED STEEL' ) AS all_nations GROUP BY o_year ORDER BY o_year; DBT-3 Query 8: National Market Share Query
- 30. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Join Optimizer: Case Study MySQL Workbench: Visual EXPLAIN Execution time: 3 min. 28 sec.
- 31. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Join Optimizer: Case Study SELECT o_year, SUM(CASE WHEN nation = 'FRANCE' THEN volume ELSE 0 END) / SUM(volume) AS mkt_share FROM ( SELECT EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o_orderdate) AS o_year, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) AS volume, n2.n_name AS nation FROM part STRAIGHT_JOIN lineitem ON p_partkey = l_partkey JOIN supplier ON s_suppkey = l_suppkey JOIN orders ON l_orderkey = o_orderkey JOIN customer ON o_custkey = c_custkey JOIN nation n1 ON c_nationkey = n1.n_nationkey JOIN region ON n1.n_regionkey = r_regionkey JOIN nation n2 ON s_nationkey = n2.n_nationkey WHERE r_name = 'EUROPE’ AND o_orderdate BETWEEN '1995-01-01' AND '1996-12-31’ AND p_type = 'PROMO BRUSHED STEEL' ) AS all_nations GROUP BY o_year ORDER BY o_year; Force early processing of high selectivity predicates Highest selectivity part before lineitem
- 32. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Join Optimizer: Case Study Improved join order Execution time: 7 seconds
- 33. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL 5.7: Cost Information in Structured EXPLAIN Accumulated cost Total query cost Cost per table Improvements to Query 8 in MySQL 5.7: • Filtering on non-indexed columns are taken into account – No need for hint to force part table to be processed early • Merge derived tables into outer query – No temporary table
- 34. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 35. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. ORDER BY Optimizations • General solution; “Filesort”: – Store query result in temporary table before sorting – If data volume is large, may need to sort in several passes with intermediate storage on disk • Optimizations: – Take advantage of index to generate query result in sorted order – For ”LIMIT n” queries, maintain priority queue of n top items in memory instead of filesort. (New in MySQL 5.6)
- 36. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Filesort SELECT * FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice ; SELECT c_name, o_orderkey, o_totalprice FROM orders JOIN customer ON c_custkey = o_custkey WHERE c_acctbal < -1000 ORDER BY o_totalprice ; id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE customer ALL PRIMARY NULL NULL NULL 1500000 Using where; Using temporary; Using filesort 1 SIMPLE orders ref i_o_custkey i_o_custkey 5 ... 7 NULL id select type table type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 SIMPLE orders ALL NULL NULL NULL NULL 15000000 Using filesort
- 37. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Filesort Status variables related to sorting: mysql> SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Sort%'; +-------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------+--------+ | Sort_merge_passes | 1 | | Sort_range | 0 | | Sort_rows | 136170 | | Sort_scan | 1 | +-------------------+--------+ Status variables >0: Intermediate storage on disk. Consider increasing sort_buffer_size Number of sort operations (range scan or table/index scans) Number of rows sorted
- 38. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Filesort Sorting status per statement available from Performance Schema mysql> SELECT sql_text,sort_merge_passes,sort_range,sort_rows,sort_scan FROM performance_schema.events_statements_history ORDER BY timer_start DESC LIMIT 1; +--------------+-------------------+------------+-----------+-----------+ | sql_text | sort_merge_passes | sort_range | sort_rows | sort_scan | +--------------+-------------------+------------+-----------+-----------+ | SELECT ... | 1 | 0 | 136170 | 1 | +--------------+-------------------+------------+-----------+-----------+ Performance Schema
- 39. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. mysql> FLUSH STATUS; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM ( SELECT * FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000) td; +-------------------+ | AVG(o_totalprice) | +-------------------+ | 398185.986158 | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (24.65 sec) mysql> SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Sort%'; +-------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------+--------+ | Sort_merge_passes | 1432 | | Sort_range | 0 | | Sort_rows | 100000 | | Sort_scan | 1 | +-------------------+--------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) Filesort: Case Study Unnecessary large data volume! Many intermediate sorting steps!
- 40. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Filesort: Case Study mysql> SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000) td; +-------------------+ | AVG(o_totalprice) | +-------------------+ | 398185.986158 | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (8.18 sec) mysql> SELECT sql_text, sort_merge_passes FROM performance_schema. events_statements_history ORDER BY timer_start DESC LIMIT 1; +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ | sql_text | sort_merge_passes | +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ | SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice | 229 | +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ Reduce amount of data to be sorted
- 41. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Filesort: Case Study mysql> SET sort_buffer_size = 1024*1024; mysql> SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000) td; +-------------------+ | AVG(o_totalprice) | +-------------------+ | 398185.986158 | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (7.24 sec) mysql> SELECT sql_text, sort_merge_passes FROM performance_schema. events_statements_history ORDER BY timer_start DESC LIMIT 1; +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ | sql_text | sort_merge_passes | +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ | SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice | 57 | +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ Increase sort buffer (1 MB) Default is 256 kB
- 42. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Filesort: Case Study mysql> SET sort_buffer_size = 8*1024*1024; mysql> SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000) td; +-------------------+ | AVG(o_totalprice) | +-------------------+ | 398185.986158 | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (6.30 sec) mysql> SELECT sql_text, sort_merge_passes FROM performance_schema. events_statements_history ORDER BY timer_start DESC LIMIT 1; +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ | sql_text | sort_merge_passes | +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ | SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice | 0 | +----------------------------------------------------+-------------------+ Increase sort buffer even more (8 MB)
- 43. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Use Index to Avoid Sorting CREATE INDEX i_o_totalprice ON orders(o_totalprice); SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM (SELECT o_totalprice FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000) td; id select type table Type possible keys key key len ref rows extra 1 PRIMARY <derived2> ALL NULL NULL NULL NULL 100000 NULL 2 DERIVED orders index NULL i_o_totalprice 6 NULL 15000000 Using index mysql> SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM ( SELECT o_totalprice FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000) td; ... 1 row in set (0.06 sec)
- 44. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 45. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Useful tools • MySQL Enterprise Monitor (MEM), Query Analyzer – Commercial product • Performance schema, MySQL SYS schema • EXPLAIN • Structured EXPLAIN (FORMAT=JSON) • Visual EXPLAIN (MySQL Workbench) • Optimizer trace • Slow log • Status variables (SHOW STATUS LIKE ’Sort%’)
- 46. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL Enterprise Monitor, Query Analyzer
- 47. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Query Analyzer Query Details
- 48. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Performance Schema • events_statements_history events_statements_history_long – Most recent statements executed • events_statements_summary_by_digest – Summary for similar statements (same statement digest) • file_summary_by_event_name – Interesting event: wait/io/file/innodb/innodb_data_file • table_io_waits_summary_by_table table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage – Statistics on storage engine access per table and index Some useful tables
- 49. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Performance Schema • Normalization of queries to group statements that are similar to be grouped and summarized: SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_custkey=10 AND o_totalprice>20 SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_custkey = 20 AND o_totalprice > 100 SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_custkey = ? AND o_totalprice > ? • events_statements_summary_by_digest DIGEST, DIGEST_TEXT, COUNT_STAR, SUM_TIMER_WAIT, MIN_TIMER_WAIT, AVG_TIMER_WAIT, MAX_TIMER_WAIT, SUM_LOCK_TIME, SUM_ERRORS, SUM_WARNINGS, SUM_ROWS_AFFECTED, SUM_ROWS_SENT, SUM_ROWS_EXAMINED, SUM_CREATED_TMP_DISK_TABLES, SUM_CREATED_TMP_TABLES, SUM_SELECT_FULL_JOIN, SUM_SELECT_FULL_RANGE_JOIN, SUM_SELECT_RANGE, SUM_SELECT_RANGE_CHECK, SUM_SELECT_SCAN, SUM_SORT_MERGE_PASSES, SUM_SORT_RANGE, SUM_SORT_ROWS, SUM_SORT_SCAN, SUM_NO_INDEX_USED, SUM_NO_GOOD_INDEX_USED, FIRST_SEEN, LAST_SEEN Statement digest
- 50. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Performance Schema • Tables: events_statements_current (Current statement for each thread) events_statements_history (10 most recent statements per thread) events_statements_history_long (10000 most recent statements) • Columns: THREAD_ID, EVENT_ID, END_EVENT_ID, EVENT_NAME, SOURCE, TIMER_START, TIMER_END, TIMER_WAIT, LOCK_TIME, SQL_TEXT, DIGEST, DIGEST_TEXT, CURRENT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_TYPE, OBJECT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_NAME, OBJECT_INSTANCE_BEGIN, MYSQL_ERRNO, RETURNED_SQLSTATE, MESSAGE_TEXT, ERRORS, WARNINGS, ROWS_AFFECTED, ROWS_SENT, ROWS_EXAMINED, CREATED_TMP_DISK_TABLES, CREATED_TMP_TABLES, SELECT_FULL_JOIN, SELECT_FULL_RANGE_JOIN, SELECT_RANGE, SELECT_RANGE_CHECK, SELECT_SCAN, SORT_MERGE_PASSES, SORT_RANGE, SORT_ROWS, SORT_SCAN, NO_INDEX_USED, NO_GOOD_INDEX_USED, NESTING_EVENT_ID, NESTING_EVENT_TYPE Statement events
- 51. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL SYS Schema / ps_helper • Started as a collection of views, procedures and functions, designed to make reading raw Performance Schema data easier • Implements many common DBA and Developer use cases • MySQL 5.7.7: Included by default • Bundled within MySQL Workbench • Also available on GitHub – https://github.com/MarkLeith/mysql-sys • Examples of very useful functions: – format_time() , format_bytes(), format_statement()
- 52. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL SYS Schema statement_analysis: Lists a normalized statement view with aggregated statistics, mimics the MySQL Enterprise Monitor Query Analysis view, ordered by the total execution time per normalized statement mysql> select * from statement_analysis limit 1G *************************** 1. row *************************** query: INSERT INTO `mem__quan` . `nor ... nDuration` = IF ( VALUES ( ... db: mem full_scan: exec_count: 1110067 err_count: 0 warn_count: 0 total_latency: 1.93h max_latency: 5.03 s avg_latency: 6.27 ms Example lock_latency: 00:18:29.18 rows_sent: 0 rows_sent_avg: 0 rows_examined: 0 rows_examined_avg: 0 tmp_tables: 0 tmp_disk_tables: 0 rows_sorted: 0 sort_merge_passes: 0 digest: d48316a218e95b1b8b72db5e6b177788! first_seen: 2014-05-20 10:42:17
- 53. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. EXPLAIN { "query_block": { "select_id": 1, "ordering_operation": { "using_filesort": false, "grouping_operation": { "using_temporary_table": true, "using_filesort": true, "table": { "table_name": "lineitem", "access_type": "ALL", "possible_keys": [ "i_l_shipdate” ], "rows": 2829575, "filtered": 50, "attached_condition": "(`dbt3`.`lineitem`.`l_shipDATE` <= <cache>(('1998-12-01' - interval '118' day)))" } /* table */ } /* grouping_operation */ } /*ordering_operation */ } /*query_block */ } Structured EXPLAIN EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON SELECT l_returnflag, l_linestatus, SUM(l_quantity) FROM lineitem WHERE l_shipdate <= DATE_SUB('1998-12-01', INTERVAL '118' DAY) GROUP BY l_returnflag,l_linestatus ORDER BY l_returnflag, l_linestatus; FORMAT=JSON
- 54. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. • attached_condition "attached_condition": "(`test`.`t1`.`b` <> 30)" • index_condition “index_condition": "(`test`.`t1`.`c` = 10)” • used_key_parts "used_key_parts": [ "o_clerk", "o_orderDATE" ], • rows_examined_per_join (5.7) "rows_examined_per_scan": 1, "rows_produced_per_join": 3, • Cost (5.7) "query_block": { "select_id": 1, "cost_info": { "query_cost": "6.41" } /* cost_info */, ... "table": { … "cost_info": { "read_cost": "3.00", "eval_cost": "0.60", "prefix_cost": "6.41", "data_read_per_join": "24" } /* cost_info */, Structured EXPLAIN Additional information compared to traditional EXPLAIN
- 55. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Optimizer Trace: Query Plan Debugging • EXPLAIN shows the selected plan • TRACE shows WHY the plan was selected: – Alternative plans – Estimated costs – Decisions made • JSON format
- 56. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Optimizer Trace: Example SET optimizer_trace= “enabled=on“, end_markers_in_json=on; SELECT * FROM t1, t2 WHERE f1=1 AND f1=f2 AND f2>0; SELECT trace INTO DUMPFILE <filename> FROM information_schema.optimizer_trace; SET optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; QUERY SELECT * FROM t1,t2 WHERE f1=1 AND f1=f2 AND f2>0; TRACE “steps”: [ { "join_preparation": { "select#": 1,… } … } …] MISSING_BYTES_BEYOND_MAX_MEM_SIZE 0 INSUFFICIENT_PRIVILEGES 0
- 57. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 5 Program Agenda Introduction to MySQL optimizer Selecting data access method Join optimizer Sorting Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries Influencing the optimizer 1 2 3 4 6
- 58. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Influencing the Optimizer • Add indexes • Force use of specific indexes: – USE INDEX, FORCE INDEX, IGNORE INDEX • Force specific join order: – STRAIGHT_JOIN • Adjust session variables – optimizer_switch flags: set optimizer_switch=“index_merge=off” – Buffer sizes: set sort_buffer=8*1024*1024; – Other variables: set optimizer_prune_level = 0; When the optimizer does not do what you want
- 59. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL 5.7: New Optimizer Hints • Ny hint syntax: – SELECT /*+ HINT1(args) HINT2(args) */ … FROM … • New hints: – BKA(tables)/NO_BKA(tables) – BNL(tables)/NO_BNL(tables) – MRR(table indexes)/NO_MRR(table indexes) – NO_ICP(table indexes) – NO_RANGE_OPTIMIZATION(table indexes) – QB_NAME(name) • Finer granularilty than optimizer_switch session variable 59
- 60. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Optimizer Hints • Hints for subquery / semi-join execution: SELECT /*+ SEMIJOIN(@subq1 LOOSESCAN) NO_SEMIJOIN(@subq2 DUPSWEEDOUT) */ a, b FROM t1 WHERE a IN (SELECT /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) c FROM t2 WHERE d > 10) AND b IN (SELECT /*+ QB_NAME(subq2) e FROM t3); • Other hints to consider – Enable/disable merge of views and derived tables – Force/ignore index_merge alternatives – Join order: LEADING(t1 t2 ...) • Plan to reimplement existing hints in new syntax 60 Future hints
- 61. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. MySQL 5.7: Query Rewrite Plugin • Rewrite problematic queries without the need to make application changes – Add hints – Modify join order – Much more … • Add rewrite rules to table: INSERT INTO query_rewrite.rewrite_rules (pattern, replacement ) VALUES ("SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a > ? AND b = ?", "SELECT * FROM t1 FORCE INDEX (a_idx) WHERE a > ? AND b = ?"); • New pre and post parse query rewrite APIs – Users can write their own plug-ins 61
- 62. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. More information • My blog: – http://oysteing.blogspot.com/ • Optimizer team blog: – http://mysqloptimizerteam.blogspot.com/ • MySQL Server Team blog – http://mysqlserverteam.com/ • MySQL forums: – Optimizer & Parser: http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?115 – Performance: http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?24
- 63. Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Q&A Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.








![Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Cost Model Example: Optimizer Trace
join_optimization / row_estimation / table : orders / range_analysis
"table_scan": {
"rows": 15000000,
"cost": 3.12e6
} /* table_scan */,
"potential_range_indices": [
{
"index": "PRIMARY",
"usable": false,
"cause": "not_applicable“
},
{
"index": "i_o_orderdate",
"usable": true,
"key_parts": [ "o_orderDATE", "o_orderkey" ]
}
] /* potential_range_indices */,
…
"analyzing_range_alternatives": {
"range_scan_alternatives": [
{
"index": "i_o_orderdate",
"ranges": [ "1994-01-01 <= o_orderDATE <= 1994-12-31"
],
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": false,
"using_mrr": false,
"index_only": false,
"rows": 4489990,
"cost": 5.39e6,
"chosen": false,
"cause": "cost"
}
] /* range_scan_alternatives */,
…
} /* analyzing_range_alternatives */](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoanalyzeandtunesqlqueriesforbetterperformance-percona15-150417094220-conversion-gate02/85/How-to-analyze-and-tune-sql-queries-for-better-performance-percona15-9-320.jpg)







![Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Range Optimizer
"analyzing_range_alternatives": {
"range_scan_alternatives": [
{
"index": "i_a",
"ranges": [
"10 < a < 11",
"11 < a < 19",
"19 < a < 25"
],
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": false,
"using_mrr": false,
"index_only": false,
"rows": 3,
"cost": 6.61,
"chosen": true
},
{
"index": "i_b",
"ranges": [
"NULL < b < 5",
"10 < b"
],
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": false,
…
Optimizer Trace show ranges
SELECT a, b FROM t1
WHERE a > 10
AND a < 25
AND a NOT IN (11, 19))
AND (b < 5 OR b > 10);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoanalyzeandtunesqlqueriesforbetterperformance-percona15-150417094220-conversion-gate02/85/How-to-analyze-and-tune-sql-queries-for-better-performance-percona15-18-320.jpg)


































![Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
EXPLAIN
{ "query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"ordering_operation": {
"using_filesort": false,
"grouping_operation": {
"using_temporary_table": true,
"using_filesort": true,
"table": {
"table_name": "lineitem",
"access_type": "ALL",
"possible_keys": [
"i_l_shipdate”
],
"rows": 2829575,
"filtered": 50,
"attached_condition":
"(`dbt3`.`lineitem`.`l_shipDATE` <=
<cache>(('1998-12-01' - interval '118' day)))"
} /* table */
} /* grouping_operation */
} /*ordering_operation */
} /*query_block */ }
Structured EXPLAIN
EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON
SELECT l_returnflag, l_linestatus, SUM(l_quantity)
FROM lineitem
WHERE l_shipdate <=
DATE_SUB('1998-12-01', INTERVAL '118' DAY)
GROUP BY l_returnflag,l_linestatus
ORDER BY l_returnflag, l_linestatus;
FORMAT=JSON](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoanalyzeandtunesqlqueriesforbetterperformance-percona15-150417094220-conversion-gate02/85/How-to-analyze-and-tune-sql-queries-for-better-performance-percona15-53-320.jpg)
![Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
• attached_condition
"attached_condition": "(`test`.`t1`.`b` <> 30)"
• index_condition
“index_condition": "(`test`.`t1`.`c` = 10)”
• used_key_parts
"used_key_parts": [
"o_clerk",
"o_orderDATE"
],
• rows_examined_per_join (5.7)
"rows_examined_per_scan": 1,
"rows_produced_per_join": 3,
• Cost (5.7)
"query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"cost_info": {
"query_cost": "6.41"
} /* cost_info */,
...
"table": { …
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "3.00",
"eval_cost": "0.60",
"prefix_cost": "6.41",
"data_read_per_join": "24"
} /* cost_info */,
Structured EXPLAIN
Additional information compared to traditional EXPLAIN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoanalyzeandtunesqlqueriesforbetterperformance-percona15-150417094220-conversion-gate02/85/How-to-analyze-and-tune-sql-queries-for-better-performance-percona15-54-320.jpg)

![Copyright © 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Optimizer Trace: Example
SET optimizer_trace= “enabled=on“, end_markers_in_json=on;
SELECT * FROM t1, t2 WHERE f1=1 AND f1=f2 AND f2>0;
SELECT trace INTO DUMPFILE <filename>
FROM information_schema.optimizer_trace;
SET optimizer_trace="enabled=off";
QUERY SELECT * FROM t1,t2 WHERE f1=1 AND f1=f2 AND f2>0;
TRACE “steps”: [ { "join_preparation": { "select#": 1,… } … } …]
MISSING_BYTES_BEYOND_MAX_MEM_SIZE 0
INSUFFICIENT_PRIVILEGES 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoanalyzeandtunesqlqueriesforbetterperformance-percona15-150417094220-conversion-gate02/85/How-to-analyze-and-tune-sql-queries-for-better-performance-percona15-56-320.jpg)






