Https interception proxies
- 1. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Jeff Jarmoc Dell SecureWorks Counter Threat Unit℠ Threat Intelligence Presented at Black Hat Europe – March 14, 2012. Introduction Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) [1] and its successor Transport Layer Security (TLS) [2] have become key components of the modern Internet. The privacy, integrity, and authenticity [3] [4] provided by these protocols are critical to allowing sensitive communications to occur. Without these systems, ecommerce, online banking, and business-to-business exchange of information would likely be far less frequent. Threat actors have also recognized the benefits of transport security, and they are increasingly turning to SSL to hide their activities. Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attackers [5], botnets [6], and even commodity web attacks can leverage SSL encryption to evade detection. To counter these tactics, organizations are increasingly deploying security controls that intercept endto-end encrypted channels. Web proxies, data loss prevention (DLP) systems, specialized threat detection solutions, and network intrusion prevention systems (NIPS) offer functionality to intercept, inspect, and filter encrypted traffic. Similar functionality is present in lawful intercept systems and solutions enabling the broad surveillance of encrypted communications by governments. Broadly classified as “SSL/TLS interception proxies,” these solutions act as a “man in the middle,” violating the end-to-end security promises of SSL. This type of interception comes at a cost. Intercepting SSL-encrypted connections sacrifices a degree of privacy and integrity for the benefit of content inspection, often at the risk of authenticity and endpoint validation. Implementers and designers of SSL interception proxies should consider these risks and understand how their systems operate in unusual circumstances. Background Before exploring the methods and associated risks of intercepting and inspecting encrypted communications, it is important to understand the inner workings of the relevant protocols. The governing specifications for SSL [1], TLS [2], and X.509 [7] provide much greater detail. History The SSL and TLS protocols are very similar mechanisms and share a common history. Netscape originally proposed the SSL protocol as a v2.0 draft specification [1] in 1994. SSLv2.0 was then updated to become SSLv3.0 [8], which formed the basis of the standardized TLS protocol v1.0 [9]. TLS has since been revised to v1.1 [10] and v1.2 [2]. Modern implementations generally support both TLSv1.0 and TLSv1.1, with TLSv1.2 support still somewhat limited. However, the original name “SSL” has become part the common lexicon. In this analysis, the terms SSL and TLS are used interchangeably and generally refer to the specification for TLSv1.1 with differences highlighted where relevant.
- 2. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust SSL/TLS handshake The SSL handshake process is illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. Sample two-party TLS handshake. Broadly, the SSL protocol and its handshake serve the following purposes: • • • • Exchange version and extension compatibility information. Secure exchange of identity certificates and cryptographic key materials. Negotiate a cipher suite to be used for encryption. Establish a secure transport layer for use by higher layer protocols. Of specific note is that the TLS protocol itself does not validate endpoint identity. This is a function left to companion protocols. In practice, this task commonly falls to X.509. [7] A server can also request that the client provide its own identity certificate via a client certificate message. This scenario, known as ”mutual authentication” or ”client certificate authentication,” poses special challenges to interception. It generally causes mutually authenticated sessions to bypass inspection. This analysis focuses primarily on HTTP over TLS [11], though other application-layer protocols leverage TLS similarly. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 2 of 21
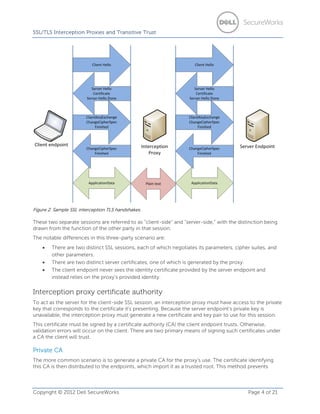
- 3. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust X.509 certificate validation The authenticity component of SSL stems from the ability to validate an endpoint’s certificate. The X.509 specification [7] governs the format of these certificates, as well as considerations necessary for validating their integrity and suitability for a given purpose. RFC5280 goes into much greater detail, but the validation process consists of the following points: • • • • • • Validating the digital signature of a certificate. Following the certificate chain to determine relevant certificate authorities. o Validating any/all intermediate certificates encountered. Determining if the root CA is trusted. Confirming certificate temporal validity by checking issuance and expiration dates. Determining the subject for which the certificate applies, for comparison with the higher layer protocol’s expectation. Determining if the certificate has been revoked. In the X.509 specification, the only defined means of checking for certificate revocation is through a certificate revocation list (CRL). However, the specification leaves room for other extensions to expand upon this standard. One extension that has gained broad support is the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) [12]. Failures in certificate validation result in a failure of SSL’s authenticity. Failure of SSL’s authenticity allows for identity spoofing and, by extension, attacks against end-to-end integrity. SSL / TLS interception proxies To inspect plain-text contents of communications over SSL, interception proxies insert themselves in the flow of traffic and terminate the client’s request. The interception proxy makes a second request on behalf of the client to the server. This behavior causes what was an end-to-end session to instead be two separate, but related, point-to-point sessions. The goal is to allow access to the plain-text session contents while transferring between the two encrypted sessions. Interception proxies may be implemented in several ways, depending on their purpose and the type of inspection they perform. Perhaps the most common scenario is to integrate with an existing HTTP or SOCKS proxy. However, Deep Packet Inspection devices, next-generation firewalls, application-aware firewalls, and data loss prevention (DLP) systems are other possible points. Interception may also reside on the client itself as part of an endpoint protection suite, or even as a web-browser plugin. Despite the wide variance in how the interception proxies access to the SSL session, they all operate the same way once they’ve reached the session. They terminate two separate sessions and act as a man in the middle (MITM) to exchange the contents between the two sessions. Unless otherwise indicated, the term ”proxy” in this analysis refers to this exchange between two SSL sessions and should not be confused with an HTTP or TCP proxy. As shown in Figure 2, SSL interception TLS handshakes build on the simple handshake of Figure 1 by including the interception proxy and additional session. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 3 of 21
- 4. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 2. Sample SSL interception TLS handshakes. These two separate sessions are referred to as ”client-side” and ”server-side,” with the distinction being drawn from the function of the other party in that session. The notable differences in this three-party scenario are: • • • There are two distinct SSL sessions, each of which negotiates its parameters, cipher suites, and other parameters. There are two distinct server certificates, one of which is generated by the proxy. The client endpoint never sees the identity certificate provided by the server endpoint and instead relies on the proxy’s provided identity. Interception proxy certificate authority To act as the server for the client-side SSL session, an interception proxy must have access to the private key that corresponds to the certificate it’s presenting. Because the server endpoint’s private key is unavailable, the interception proxy must generate a new certificate and key pair to use for this session. This certificate must be signed by a certificate authority (CA) the client endpoint trusts. Otherwise, validation errors will occur on the client. There are two primary means of signing such certificates under a CA the client will trust. Private CA The more common scenario is to generate a private CA for the proxy’s use. The certificate identifying this CA is then distributed to the endpoints, which import it as a trusted root. This method prevents Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 4 of 21
- 5. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust errors from occurring on client endpoints that are appropriately configured, but it may pose a logistical challenge for the implementing organization. Public SubCA A SubCA is an intermediate signing authority authorized by a trusted root. Organizations that can convince a trusted public root CA to issue them a SubCA certificate can use this certificate for interception proxy purposes. This method eases the deployment process because existing endpoints will already trust these certificates that chain to a trusted root. Recent controversy The practice of using public SubCAs for SSL interception proxies has drawn attention and debate [14]. SubCAs have the technical ability to sign certificates that will be considered valid by most endpoints on the Internet, not just those configured explicitly as in a private CA scenario. Therefore, exposure of the signing certificates, private keys, or generated certificates presents a significant risk for the implementing organization and for all Internet users who trust the root CA that issued the certificates. Trustwave recently announced that it has issued this type of SubCA certificate in the past [13], but the organization changed its stance, revoked the certificate in question, and pledged never to issue such certificates in the future. This announcement led to significant debate [14] regarding what actions, including the possibility of root trust revocation, should be taken in response. Other CAs have been suspected of having similar programs, though the programs are rarely advertised. Dan Kaminsky noted in 2009 that ”at least two companies offer this, probably more.” [15] At Black Hat USA 2011, Moxie Marlinspike [16] highlighted GeoTrust’s GeoRoot program [17] as a very public example of this practice. It’s widely believed [18] that other such programs exist; however, because they aren’t publicly discussed and disclosed, the extent of this practice remains mostly unknown. In response to the Trustwave disclosure, Mozilla issued a communication to trusted roots CAs asking them to revoke and disclose such certificates, and clarifying that trusted roots should not issue SubCAs for interception purposes [19]. As of this writing, it remains to be seen what impact this request will have and whether other browser manufacturers will follow Mozilla’s lead or take related action. Risks introduced by interception proxies Interception proxies introduce several new avenues of possible risk into the environments they protect. This analysis focuses on the risks introduced through transitive trust relationships. Other risks summarized in the following sections include possible legal exposures, an increased threat surface, and the possibility of decreased cipher strength. Legal exposure When implementing an SSL interception proxy, an organization may face increased legal exposure as a result of inspecting communications intended to be encrypted and private. Implementing organizations should carefully consider the legal risks. Employees’ expectations of privacy when using encrypted protocols may affect the employer’s rights and obligations. For this reason, organizations should develop a clear use policy, explicitly outlining handling of encrypted communications, and present it to all employees. Microsoft highlights this concern with a warning in the installation screen for the Forefront Threat Management Gateway HTTPS interception functions (see Figure 3), as well as in its documentation [20]. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 5 of 21
- 6. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 3. Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway legal warning. Implementers of any SSL interception proxy should consider these issues and consult their legal teams. Increased threat surface Interception proxies are meant to inspect plain-text contents of what would otherwise be encrypted traffic. Encrypted traffic is often highly valued by attackers. Therefore, providing a single point where all encrypted sessions can be viewed in plain text may make that point a high-value target. Compromising an interception proxy would allow an attacker to inspect and potentially modify plain-text contents of any encrypted sessions that are subject to the proxy’s interception. Because the CA used by the inspection proxy is trusted by client endpoints, it is also a highly valuable target for attackers. If the CA signing keys are compromised, then it is trivial to spoof communications to client endpoints that trust that CA. With interception proxies using public SubCAs, the risks of CA signing key exposure are greater. The risks extend to all client endpoints on the Internet that trust the issuing root. Similarly, exposure of generated private keys can allow for spoofing attacks involving the website for which they’re valid. These issues combine to increase the sensitivity of the interception proxy system. Vulnerabilities on this system present an increased risk to all clients who trust it. Decreased cipher strength The introduction of an interception proxy results in two point-to-point encrypted sessions. Because these sessions negotiate their cipher suites independently, there is a possibility that either the client-side or server-side sessions may use a weaker cipher than a session directly between the client endpoint and server endpoint. As an example, consider SSL sessions involving Google’s web properties. Google recently took the step of preferring cipher suites that support forward secrecy [21]. Forward secrecy [22], also known as Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS), is a cryptographic property of certain cipher suites. It seeks to reduce the impact of key exposures by using the endpoint’s keys to derive another key, used to encrypt data in transit. This second key is valid only for a short period of time, typically a single session. The result of this process is Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 6 of 21
- 7. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust that a compromise of the server’s private key would not allow previously generated content to be decrypted. In high-security environments, this property is valuable as a hedge against the possibility of an attacker collecting large amounts of ciphertext with hopes of later recovering the keys. While valuable in many cases, cipher suites supporting PFS are not commonly preferred in practice due to performance and implementation complexities. As a result, a proxy may not support cipher suites necessary for PFS. If this is the case, then both the client-side and server-side sessions may revert to weaker cipher suites lacking PFS, despite the support of the endpoints involved. Other scenarios are possible in any case where the interception proxy does not support stronger cipher suites that both endpoints support. The resulting cipher suite might be less secure than if negotiated without the proxy’s interception. Transitive trust The differences in the establishment of an SSL session when interception is introduced create a phenomenon called “transitive trust.” Similar to the mathematic transitive property “if a=b and b=c, then a=c,” transitive trust relationships can be described with the following statement: “if the client trusts the proxy and the proxy trusts the server, then the client trusts the server.” This property can manifest itself in several flaws. Transitive root trust A Dell SecureWorks blog post [23] titled “Transitive Trust and SSL Certificate Validation” discussed transitive trust, using transitive root trust as the prime example. Because interception proxies create two SSL sessions, the proxy must act as the client for the server-side session and validate the trustworthiness of the root CA that signed the server endpoint’s certificate. This process leaves the client unable to make its own decision about the trustworthiness of the server endpoint’s root CA. As a result, in cases where the interception proxy trusts a CA that the client endpoint does not, the client inherits the interception proxy’s trust decision. Consider the compromise of DigiNotar’s CA [24]. As a result of the compromise, all major browser manufacturers, including Google [25], Mozilla [26], and Microsoft [27], rapidly revoked trust in DigiNotar’s CA roots. As illustrated in Figure 4, these browsers no longer trust certificates signed by DigiNotar’s roots. Figure 4. Untrusted root. However, when connecting through an interception proxy that trusts the server’s root CA, a transitive root trust is formed (see Figure 5). Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 7 of 21
- 8. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 5. Transitive root trust. This example of transitive root trust highlights the need to manage trust roots on the interception proxy itself, because the proxy masks the roots configured on the client endpoint. A similar transitive root trust can manifest in cases where the interception proxy accepts certificates from unknown root CAs. Self-signed certificates Self-signed certificates are similar to certificates signed by an untrusted root. The only difference is that the certificate is its own root. Because anyone can create self-signed certificates and there’s no external verification of their root, these certificates generally should not be accepted as valid. For this reason, browsers typically present a warning dialog asking the user how to proceed. This warning gives the user an opportunity to check the certificate’s status via some other means, such as verifying the expected certificate fingerprint out of band with the server’s operator, prior to proceeding. Interception proxies that accept self-signed certificates on the server-side session and sign the clientsession certificate under the trusted CA certificate improperly elevate this certificate to trusted status from the client’s perspective. This elevation of status allows for spoofing the server endpoint identity of encrypted communications. Expired certificates X.509 certificate validation calls for checking the certificate’s issuance and expiry date stamps, verifying that the current time falls within this period. Proxies that fail to check for certificate expiration prior to generating new client-session certificates elevate expired certificates to trusted status from the client’s perspective. Revoked certificates Certificate revocation is necessary to invalidate certificates in cases of theft or loss of key materials. There are two major mechanisms for certificate revocation commonly deployed: the checking of Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) and Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responders. Interception proxies that do not properly perform CRL and/or OCSP checks on server-side session certificates may improperly elevate trust in these certificates from the client endpoint’s perspective. CRL checking In the X.509 specification [7], checking published CRLs is the prescribed means of discovering if a certificate has been revoked. Under the CRL model, a CA will periodically publish a list of certificate fingerprints that should no longer be trusted. Validating endpoints should regularly check and cache this Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 8 of 21
- 9. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust list, verifying each certificate’s fingerprint to determine that it has not been revoked. This model provides a means of identifying revoked certificates but can also introduce a window of exposure to the client because the list is not updated in real-time. An attacker may also be able to block access to a CRL endpoint while simultaneously presenting an expired certificate, thus preventing revocation checking from showing the certificate’s true status. OCSP checking The OCSP [12] is an X.509 message extension intended to address the temporal limitations of CRL checking. It is performed through real-time checking with an OCSP responder included in the certificate. An OCSP responder should return a signed response with either a positive acknowledgement that a certificate is valid or a negative acknowledgement that the certificate is revoked. However, as first demonstrated by Moxie Marlinspike in 2009, OCSP can be subject to bypass [28]. By spoofing a “tryLater” response code, an attacker can cause an OCSP endpoint to enter its failure mode. Because most endpoints fail-open or accept certificates in the absence of a negative response, OCSP is bypassed. OCSP has also been criticized as a privacy failure because the active real-time checking provides information to the OCSP responder every time a client attempts to validate a certificate. This process reveals information about user browsing habits to the OCSP responder and its operators. While both CRL and OCSP revocation checking have problems in practice, they are the only commonly accepted certificate revocation systems. Google recently announced that it will forgo OCSP checking in future versions of Chrome [29]. Chrome will instead adopt a modified CRL approach, where the revocation lists are provided using Google’s automatic-update mechanism rather than the CA’s CRL server. This approach has raised questions and concerns [30] surrounding the scope of Google’s revocation pushing and fallback mechanism for private CAs. It also remains untested in practice. Other proposals have been put forward, but none have been standardized or become widely deployed. Certification validation flaws and vulnerabilities The interception proxy’s certificate validation routines may introduce additional vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities may stem from past validation flaws that affected endpoints and newly discovered validation flaws that can apply equally to interception proxies and endpoints. Basic constraints Moxie Marlinspike disclosed a certificate validation flaw in 2002 [31] related to how intermediate certificates are validated. When certificates are indirectly signed by a root CA and instead signed by an intermediate CA, the endpoint should check the intermediate certificate’s basic constraints field to ensure it is authorized to act as an intermediate CA. If this field is set to ”false,“ then the certificate is not a valid intermediate CA. Marlinspike found that Internet Explorer 6 (IE6) did not validate this property, allowing any valid certificate to be used as an intermediate CA despite the intermediate certificate’s own assertion that it is not valid for this purpose. While Marlinspike’s 2002 finding affected IE6, he discovered the same issue as late as 2009 in OpenSSL and many packages that depend on OpenSSL [32]. In 2011, Trustwave SpiderLabs disclosed that Apple’s iOS operating system was vulnerable to the same flaw [33]. Interception proxies may also be subject to this flaw. The result is that an attacker with a valid leaf certificate, which is not intended to act as an intermediate CA, can act as an intermediate CA and sign certificates. When generating certificates for the client-side session, the interception proxy generates a new certificate chain the client endpoint considers valid. As a result, a client endpoint does not need to be vulnerable to this issue for the exploit to succeed if the interception proxy is vulnerable. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 9 of 21
- 10. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Null prefix injection The Null prefix injection attack leverages a flaw in X.509 certificate validation that was simultaneously discovered by Moxie Marlinspike [34] and Dan Kaminsky [15], who both disclosed their findings at Black Hat USA 2009. The issue stems from a variance in how strings are encoded in X.509, compared to how validation libraries, often implemented in C, handle strings. X.509 strings are length-encoded [7], similar to how the PASCAL programming language encodes strings. For example, the six-character string ”string” would be encoded as “0x06string”, where 0x06 is the hex value of 06. In the C programing language, strings are encoded by appending a null character on the end (null-terminated), so our example would be “string0x00”, where 0x00 is a null byte with the hex value 00. This disparity creates an opportunity for an attacker to affect the subject name of a certificate if the validation routine improperly handles the length-encoded values as if they were null-terminated. When issuing domain-validated certificates, CAs are only concerned with ownership of the root domain name rather than the fully-qualified domain name. The owner of .example.com can therefore request a certificate for anything.example.com as well, and it will be issued because domain ownership is verifiable. This method creates the opportunity for an attacker to obtain a certificate for www.victim.com0x00.example.com. A validation routine that improperly parses this value as a null terminated string will end up believing the certificate subject is www.victim.com, allowing the attacker to manipulate the scope of certificate validity. Interception proxies can also improperly handle length-encoded strings as null-terminated strings. If the proxies use the output of this validation to determine the subject name of the client-side session’s certificate, then an attacker may be able to control the subject name of the certificate presented to the client endpoint. This scenario results in the interception proxy unknowingly aiding the attacker’s ability to spoof certificates, while hiding the true certificate from the client endpoint. Improper certificate cache verification In the interest of performance, many SSL interception proxies don’t generate a new client-session certificate for each session. Instead, they’ll generate a certificate the first time a client endpoint contacts a given server endpoint and cache that certificate for a period of time. This behavior is especially common among proxies positioned as network gateways, where thousands of users can simultaneously access different sites, making performance overhead critical. In some cases, the certificate remains in cache for a lifetime and expires only when the corresponding server endpoint isn’t seen for a long lifetime, measured in days or weeks. The caching of these certificates can create new opportunities for an attacker. Depending on the criteria used to index and look up certificates in the cache, an attacker may be able to present a new certificate on the server-side session while the interception proxy continues to present the previously cached certificate on the client-side session. If this occurs, the client will be unaware that their trust is now transitively placed in a different server endpoint. This disparity can enable impersonation attacks. The process that happens when a site is first visited is illustrated in Figure 6. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 10 of 21
- 11. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 6. Certificate added to cache on first visit. The client endpoint makes its request, and the interception proxy retrieves the server endpoint’s certificate. This certificate is verified, and a corresponding certificate is generated for use on the clientside session. This certificate is also stored in cache for later use. On subsequent visits, the cached certificate is retrieved and presented to the client, avoiding the need to generate a new certificate on each visit (see Figure 7). Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 11 of 21
- 12. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 7. Reading cached certificate on subsequent visits. Figure 8 shows what happens when an attacker enters the scenario as a MITM on the server-side session. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 12 of 21
- 13. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 8. Attacker exploiting improper caching. In the example shown in Figure 8, the attacker injects his own certificate, which is presented to the SSL interception proxy. The proxy validates this certificate and looks in its cache to see if a certificate already exists that can be used for the client-side session. In this case, it finds and presents a previously cached certificate to the client. The primary weakness is a failure to detect that the server-side session’s certificate presents a different fingerprint and is signed under a different CA. While this scenario requires the attacker obtain a certificate that is valid for the server endpoint’s subject, other validation flaws may operate in tandem to ease the attacker’s burden. For example, this scenario can be exploited using selfsigned certificates if the proxy accepts them as valid. It can also be exploited for certificates valid for a different subject, in cases where the proxy also fails to validate that the certificate subject matches the client endpoint’s request. Testing SSL interception proxies While the flaws can be difficult to test, many can be exposed by visiting a web server that intentionally presents a malformed certificate and observing the result. To ease this process, Dell SecureWorks researchers have developed a website (https://ssltest.offenseindepth.com) that tests for many of these flaws. Failure modes When an interception proxy determines that a site is untrustworthy, it must determine how to handle the failure. There are several choices, and which mode a proxy operates under affects the impact on the client endpoint. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 13 of 21
- 14. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Fail closed An interception proxy operating in a fail-closed mode that encounters an untrustworthy certificate immediately terminates both server-side and client side sessions. This is the most secure failure mode but comes at the expense of the user experience. When a session is terminated, the client endpoint will have no ability to determine why, and thus will present a generic ”Connection Failed” response to its user. Some systems augment a fail-closed mode with out-of-band notification to the client endpoint via a browser plugin or host agent. This step can address the user experience concerns, but it results in additional software to install and configure on endpoint systems. Friendly error Some systems seek to address the user experience concerns of a fail-closed system by terminating only the server-side session and presenting a friendly response to the user in the client-side session. While this approach can help explain the reason for the failure, it can also introduce additional vulnerabilities depending on the content presented. In cases where the contents of the certificates are shown to the user, the certificate contents may become a vector for cross-site scripting and other webbased attacks. Passthrough mode Passthrough mode describes a scenario where the proxy passes portions of the server-side certificate to the client-side session despite flaws that prevent it from validating. This mode is most often observed when the host subject doesn’t match or the certificate is expired. The intention is to preserve the existing user experience by presenting the same error that would appear if there were no proxy in place. In most circumstances, this mode offers a reasonable compromise between security and user experience without introducing additional software. However, in some cases this mode can combine with endpoint validation flaws or the presence of additional downstream interception proxies to introduce unusual, and potentially exploitable, conditions. Testing framework – ssltest.offenseindepth.com A testing framework is publicly available at https://ssltest.offenseindepth.com. The website displays a table listing brief descriptions of many of the vulnerability scenarios discussed in this analysis. All rows are initially formatted with cascading style sheets (CSS) that present the scenarios as green and ”NOT VULNERABLE.“ The website attempts to load additional CSS formatting from several hosts on the same domain that intentionally present invalid certificates. If a host’s certificate is accepted, then the CSS formatting is loaded. The CSS code then modifies the table to flag the corresponding entry as vulnerable. By visiting this site from a source behind any SSL interception proxy, a user can determine at a glance if the session is vulnerable to any issues. A copy of the request headers is also displayed on the page, providing information that may be useful in identifying the offending system. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 14 of 21
- 15. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 9 shows a sample visit from a typical installation of Firefox 10.0.2 on Linux directly to the test page. In this case, there is no SSL interception proxy in use, so no vulnerabilities are shown. Figure 9. SSL test framework showing no vulnerabilities. Changing the browser’s proxy settings allows the same browser to communicate through a knownvulnerable proxy (see Figure 10). Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 15 of 21
- 16. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Figure 10. SSL test framework showing several vulnerabilities. To test the null prefix injection attack, listed as Null Char on the test framework, the proxy must be configured to fully trust the CA certificate linked on the page. Importing this CA certificate should only be done on test equipment, however. Without this CA being trusted, the test is only valid in cases where the interception proxy is also vulnerable to trusting certificates signed by unknown CA. On some browsers, several certificate warning dialogs may occur when behind interception proxies that operate in a passthrough failure mode. To accurately gauge the interception proxy’s vulnerability, these certificates should not be accepted. However, in cases where browsers silently refuse content loaded via websites presenting untrusted certificates, the framework shows a non-vulnerable scenario even though the user would receive a warning page if visiting the site directly. Although not the intended purpose, this framework may also be useful for testing SSL endpoints when visited directly from those systems. Findings Dell SecureWorks Counter Threat Unit (CTU) researchers tested several devices for vulnerabilities identified in this analysis. The following findings were coordinated with the appropriate vendors and disclosed. Cisco IronPort Web Security Appliance The Cisco IronPort Web Security Appliance (WSA) is vulnerable to several issues described in this analysis. Disclosure of these vulnerabilities has been coordinated with Cisco, and software updates Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 16 of 21
- 17. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust addressing these issues are expected to be released in version 7.5 or 7.7, tentatively scheduled for public availability in July 2012. Additionally, an administrator cannot view or manage trust roots or blacklist individual certificates. Cisco plans enhancements to address these shortcomings, but no estimated release date is available at publication time. Self-signed certificates accepted By default, Cisco IronPort WSA accepts self-signed certificates. Corresponding client-side certificates are created under the context of the proxy’s CA, so the client endpoint cannot identify sites presenting self-signed certificates. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by performing a MITM attack outside the proxy and presenting a self-signed certificate for the target domain. An internal client endpoint sees a valid certificate signed by the proxy’s CA and trusts it transitively. This behavior enables spoofing and interception attacks. The Cisco IronPort WSA can be configured to silently block access to sites presenting a self-signed certificate. Cisco IronPort BugID 77544 provides specific details. Unknown CA root accepted By default, Cisco IronPort WSA accepts certificates signed under an unknown root. Corresponding client-side certificates are created under the context of the proxy’s CA, so the client endpoint cannot identify sites presenting certificates signed by unknown, untrusted root CAs. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by performing a MITM attack outside the proxy and presenting a certificate for the target domain signed by an unknown CA. An internal client endpoint sees a valid certificate signed by the proxy’s CA and trusts it transitively. This behavior enables spoofing and interception attacks. The Cisco IronPort WSA can be configured to silently block access to sites presenting a certificate signed under an unknown CA. Cisco IronPort BugID 77544 provides specific details. Lack of certificate revocation checking – CVE-2012-1316 The Cisco IronPort WSA does not check for certificate revocation via either CRL or OCSP standards. Client-side certificates are created under the context of the proxy’s CA even when the server-side certificate has been revoked. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to perform MITM attacks outside the proxy using compromised certificates that have been revoked. An internal client endpoint sees a valid certificate signed by the proxy’s CA and trusts it transitively. This behavior enables spoofing and interception attacks. At publication time, there are no software updates or known workarounds available. Cisco plans to address this vulnerability in version 7.7, currently scheduled for release in July 2012. Failure to validate intermediate basic constraints – CVE-2012-1326 The Cisco IronPort WSA fails to validate the basic constraints of intermediate CAs in a certificate chain. Client-side certificates are created under the context of the proxy’s CA even when the server-side certificate has been created under an intermediate certificate that is not a valid CA. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to perform MITM attacks outside the proxy using certificates signed by any valid certificate chaining to a public root. An internal client endpoint sees a valid certificate signed by the proxy’s CA and trusts it transitively. This behavior enables spoofing and interception attacks. At publication time, there are no software updates or known workarounds available. Cisco plans to address this vulnerability in version 7.7, currently scheduled for release in July 2012. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 17 of 21
- 18. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust Key pair cache weaknesses – CVE-2012-0334 The Cisco IronPort WSA mishandles key pair caching. Cached key pairs are used for client-session traffic, despite changes in server-side certificates. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to perform MITM attacks outside the proxy using any certificate that validates on the WSA. An internal client endpoint sees the same valid certificate signed by the proxy’s CA under previous visits. The server-side certificate’s properties do not need to be valid in the scope of the target site. This behavior enables spoofing and interception attacks. At publication time, there are no software updates or known workarounds available. Cisco plans to address this vulnerability in version 7.5, currently scheduled for release in July 2012. Astaro Security Gateway The Astaro Security Gateway, a Sophos product, is affected by one vulnerability described in this analysis. Lack of certificate revocation checking The Astaro Security Gateway (firmware 8.300) does not check for certificate revocation via either CRL or OCSP standards. Client-side certificates are created under the context of the proxy’s CA even when the server-side certificate has been revoked. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to perform MITM attacks outside the proxy using compromised certificates that have been revoked. An internal client endpoint sees a valid certificate signed by the proxy’s CA and trusts it transitively. This behavior enables spoofing and interception attacks. At publication time, there are no software updates or known workarounds available. According to Astaro’s security team, the absence of these solutions is a conscious design consideration related to known attack techniques allowing for bypass of both CRL and OCSP checks. Astaro is monitoring developments in this area but does not plan to change the product’s behavior at publication time. Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway Based on the evaluation by Dell SecureWorks CTU researchers, Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway 2010 SP2 does not seem to be vulnerable to the issues described in this analysis. Check Point Security Gateway Based on the evaluation by Dell SecureWorks CTU researchers, Check Point Security Gateway R75.20 does not seem to be vulnerable to the issues described in this analysis. Recommendations This analysis has explored SSL interception proxies holistically and identified cases in which they may introduce risk into the environments they’re meant to protect. Intercepting SSL-encrypted connections sacrifices a degree of privacy and integrity for the benefit of content inspection, often at the risk of authenticity and endpoint validation. Implementers and designers of SSL interception proxies should note the following recommendations. Implementers Implementers of SSL interception proxies should thoroughly understand how their systems operate. This understanding can then be applied toward examining failure modes and the impact of potential flaws. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 18 of 21
- 19. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust • • • • • • Inform end users of interception being performed to protect the organization from legal risk. Ensure the legal team reviews corresponding policy documents. Identify and document trust roots. Ensure administrators are ready to rapidly revoke that trust if necessary. Consider both security and user experience when configuring systems. Test configurations for security impacts. Actively test interception proxies to determine their failure modes and the impacts on overall end-to-end security. Consider the proxy to be a high-value asset. Harden its configuration and ensure software updates are current to protect it from direct attack and minimize risks of its participation in known and mitigating attacks against end users. Consider failure modes and the relative benefits of conveying information to users versus possibly enabling attacks through malicious certificates. Designers and developers Designers and developers of these systems should understand that intercepting SSL is not a procedure governed under any RFC or other standards and that it comes with several tradeoffs that may affect the overall system integrity. Special attention should be paid to the following points: • • • • Give administrators the tools they need to manage trust roots. Consider the failure modes of your system and what impacts they present. Wherever possible, default to the most secure settings and require administrators to accept risks inherent in some less-secure options if required. Test systems under a variety of attack scenarios. Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 19 of 21
- 20. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust References [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] SSL V2.0 Draft specification. http://www.mozilla.org/projects/security/pki/nss/ssl/draft02.html RFC 5246 – “The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol v1.2.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5246 Lawson, Nate. “TLS/SSL Protocol Design” (Slide 8). http://www.slideshare.net/rootlabs/tlsdesign20100603 Marlinspike, Moxie. “SSL and The Future of Authenticity.” http://blog.thoughtcrime.org/ssl-and-thefuture-of-authenticity Kazanciyan, Ryan. “The State of the Hack” (Slide 21). http://www.mandiant.com/uploads/presentations/SOH_Infragard_120910.pdf FireEye. “Bredolab – Severely Injured but Not Dead.” http://blog.fireeye.com/research/2010/10/bredolab-severely-injured-but-not-dead.html RFC5280 – “Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Profile.” http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc5280.txt Internet Draft – “The SSL Protocol Version 3.0.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-tls-ssl-version300 RFC2246 – “The TLS Protocol Version 1.0.” http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2246.txt RFC4346 – “The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol Version 1.1.” http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4346.txt RFC2818 – “HTTP Over TLS.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2818 RFC5019 – “The Lightweight Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Profile for High-Volume Environments.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5019 Percoco, Nicholas J. “Clarifying the Trustwave CA Policy Update.” http://blog.spiderlabs.com/2012/02/clarifying-the-trustwave-ca-policy-update.html “Remove Trustwave Certificate(s) from trusted root certificates.” https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=724929 Kaminsky, Dan. “Black Ops of PKI.” http://www.slideshare.net/dakami/black-opspki-2 Marlinspike, Moxie. “SSL and the Future of Authenticity.” Black Hat USA 2011. https://media.blackhat.com/bh-us-11/Marlinspike/BlackHat-USA-2011-Marlinspike-SSL-FutureAuthenticity-SlidesOnly.mov GeoTrust. “GeoRoot.” http://www.trustico.com/material/DS_GeoRoot_0205.pdf “really sub-CAs for MitM deep packet inspectors?” http://www.mailarchive.com/[email protected]/msg01782.html “Mozilla Communication: Action Requested by March 2, 2012.” http://groups.google.com/group/mozilla.dev.security.policy/browse_thread/thread/e825f6dcd55a 52f6# Microsoft. “Planning for HTTPS inspection.” http://technet.microsoft.com/enus/library/ee658156.aspx Google. “Protecting data for the long term with forward secrecy.“ http://googleonlinesecurity.blogspot.com/2011/11/protecting-data-for-long-termwith.html Wikipedia. “Perfect Forward Secrecy.” http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perfect_forward_secrecy Jarmoc, Jeff. “Transitive Trust and SSL Certificate Validation.” http://www.secureworks.com/research/blog/general/transitive-trust-and-ssl-cert/ Vasco. “DigiNotar Reports Security Incident.” http://www.vasco.com/company/press_room/news_archive/2011/news_diginotar_reports_securit y_incident.aspx Google Chrome blog. “Stable Channel Update.” http://googlechromereleases.blogspot.com/2011/09/stable-channel-update.html Mozilla Foundation. “Mozilla Foundation Security Advisory 2011-35.” http://www.mozilla.org/security/announce/2011/mfsa2011-35.html Microsoft. “Microsoft Security Advisory (2607712).” http://technet.microsoft.com/enus/security/advisory/2607712 Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 20 of 21
- 21. SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust [28] Marlinspike, Moxie. “Defeating OCSP With the Character ‘3’.” https://www.blackhat.com/presentations/bh-usa-09/MARLINSPIKE/BHUSA09-MarlinspikeDefeatOCSP-PAPER2.pdf [29] Langely, Adam. “Revocation Checking and Chrome’s CRL.” http://www.imperialviolet.org/2012/02/05/crlsets.html [30] Dimcev, Adrian. “Inside Google’s Pushing Revocation List Approach.” http://www.carbonwind.net/blog/post/Inside-Google%E2%80%99s-pushing-revocation-listapproach.aspx [31] Marlinspike, Moxie. “Internet Explorer SSL Vulnerability.” http://www.thoughtcrime.org/ie-sslchain.txt [32] Marlinspike, Moxie. “New Tricks for Defeating SSL In Practice.” https://www.blackhat.com/presentations/bh-dc-09/Marlinspike/BlackHat-DC-09-MarlinspikeDefeating-SSL.pdf [33] Trustwave SpiderLabs. “iOS SSL Implementation Does Not Validate Certificate Chain.” https://www.trustwave.com/spiderlabs/advisories/TWSL2011-007.txt [34] Marlinspike, Moxie. “Null Prefix Attacks Against SSL/TLS.” https://www.blackhat.com/presentations/bh-usa-09/MARLINSPIKE/BHUSA09-MarlinspikeDefeatSSL-PAPER1.pdf Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks Page 21 of 21
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive
Trust
Jeff Jarmoc
Dell SecureWorks Counter Threat Unit℠ Threat Intelligence
Presented at Black Hat Europe – March 14, 2012.
Introduction
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) [1] and its successor Transport Layer Security (TLS) [2] have become key
components of the modern Internet. The privacy, integrity, and authenticity [3] [4] provided by these
protocols are critical to allowing sensitive communications to occur. Without these systems, ecommerce, online banking, and business-to-business exchange of information would likely be far less
frequent.
Threat actors have also recognized the benefits of transport security, and they are increasingly turning to
SSL to hide their activities. Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attackers [5], botnets [6], and even
commodity web attacks can leverage SSL encryption to evade detection.
To counter these tactics, organizations are increasingly deploying security controls that intercept endto-end encrypted channels. Web proxies, data loss prevention (DLP) systems, specialized threat
detection solutions, and network intrusion prevention systems (NIPS) offer functionality to intercept,
inspect, and filter encrypted traffic. Similar functionality is present in lawful intercept systems and
solutions enabling the broad surveillance of encrypted communications by governments. Broadly
classified as “SSL/TLS interception proxies,” these solutions act as a “man in the middle,” violating the
end-to-end security promises of SSL.
This type of interception comes at a cost. Intercepting SSL-encrypted connections sacrifices a degree of
privacy and integrity for the benefit of content inspection, often at the risk of authenticity and endpoint
validation. Implementers and designers of SSL interception proxies should consider these risks and
understand how their systems operate in unusual circumstances.
Background
Before exploring the methods and associated risks of intercepting and inspecting encrypted
communications, it is important to understand the inner workings of the relevant protocols. The
governing specifications for SSL [1], TLS [2], and X.509 [7] provide much greater detail.
History
The SSL and TLS protocols are very similar mechanisms and share a common history. Netscape
originally proposed the SSL protocol as a v2.0 draft specification [1] in 1994. SSLv2.0 was then updated
to become SSLv3.0 [8], which formed the basis of the standardized TLS protocol v1.0 [9]. TLS has since
been revised to v1.1 [10] and v1.2 [2]. Modern implementations generally support both TLSv1.0 and
TLSv1.1, with TLSv1.2 support still somewhat limited. However, the original name “SSL” has become part
the common lexicon.
In this analysis, the terms SSL and TLS are used interchangeably and generally refer to the specification
for TLSv1.1 with differences highlighted where relevant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-1-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
SSL/TLS handshake
The SSL handshake process is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Sample two-party TLS handshake.
Broadly, the SSL protocol and its handshake serve the following purposes:
•
•
•
•
Exchange version and extension compatibility information.
Secure exchange of identity certificates and cryptographic key materials.
Negotiate a cipher suite to be used for encryption.
Establish a secure transport layer for use by higher layer protocols.
Of specific note is that the TLS protocol itself does not validate endpoint identity. This is a function left
to companion protocols. In practice, this task commonly falls to X.509. [7]
A server can also request that the client provide its own identity certificate via a client certificate
message. This scenario, known as ”mutual authentication” or ”client certificate authentication,” poses
special challenges to interception. It generally causes mutually authenticated sessions to bypass
inspection.
This analysis focuses primarily on HTTP over TLS [11], though other application-layer protocols leverage
TLS similarly.
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 2 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-2-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
X.509 certificate validation
The authenticity component of SSL stems from the ability to validate an endpoint’s certificate. The X.509
specification [7] governs the format of these certificates, as well as considerations necessary for
validating their integrity and suitability for a given purpose.
RFC5280 goes into much greater detail, but the validation process consists of the following points:
•
•
•
•
•
•
Validating the digital signature of a certificate.
Following the certificate chain to determine relevant certificate authorities.
o Validating any/all intermediate certificates encountered.
Determining if the root CA is trusted.
Confirming certificate temporal validity by checking issuance and expiration dates.
Determining the subject for which the certificate applies, for comparison with the higher layer
protocol’s expectation.
Determining if the certificate has been revoked.
In the X.509 specification, the only defined means of checking for certificate revocation is through a
certificate revocation list (CRL). However, the specification leaves room for other extensions to expand
upon this standard. One extension that has gained broad support is the Online Certificate Status
Protocol (OCSP) [12].
Failures in certificate validation result in a failure of SSL’s authenticity. Failure of SSL’s authenticity allows
for identity spoofing and, by extension, attacks against end-to-end integrity.
SSL / TLS interception proxies
To inspect plain-text contents of communications over SSL, interception proxies insert themselves in the
flow of traffic and terminate the client’s request. The interception proxy makes a second request on
behalf of the client to the server. This behavior causes what was an end-to-end session to instead be
two separate, but related, point-to-point sessions. The goal is to allow access to the plain-text session
contents while transferring between the two encrypted sessions.
Interception proxies may be implemented in several ways, depending on their purpose and the type of
inspection they perform. Perhaps the most common scenario is to integrate with an existing HTTP or
SOCKS proxy. However, Deep Packet Inspection devices, next-generation firewalls, application-aware
firewalls, and data loss prevention (DLP) systems are other possible points. Interception may also reside
on the client itself as part of an endpoint protection suite, or even as a web-browser plugin.
Despite the wide variance in how the interception proxies access to the SSL session, they all operate the
same way once they’ve reached the session. They terminate two separate sessions and act as a man in
the middle (MITM) to exchange the contents between the two sessions. Unless otherwise indicated, the
term ”proxy” in this analysis refers to this exchange between two SSL sessions and should not be
confused with an HTTP or TCP proxy.
As shown in Figure 2, SSL interception TLS handshakes build on the simple handshake of Figure 1 by
including the interception proxy and additional session.
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 3 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-3-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
errors from occurring on client endpoints that are appropriately configured, but it may pose a logistical
challenge for the implementing organization.
Public SubCA
A SubCA is an intermediate signing authority authorized by a trusted root. Organizations that can
convince a trusted public root CA to issue them a SubCA certificate can use this certificate for
interception proxy purposes. This method eases the deployment process because existing endpoints will
already trust these certificates that chain to a trusted root.
Recent controversy
The practice of using public SubCAs for SSL interception proxies has drawn attention and debate [14].
SubCAs have the technical ability to sign certificates that will be considered valid by most endpoints on
the Internet, not just those configured explicitly as in a private CA scenario. Therefore, exposure of the
signing certificates, private keys, or generated certificates presents a significant risk for the implementing
organization and for all Internet users who trust the root CA that issued the certificates.
Trustwave recently announced that it has issued this type of SubCA certificate in the past [13], but the
organization changed its stance, revoked the certificate in question, and pledged never to issue such
certificates in the future. This announcement led to significant debate [14] regarding what actions,
including the possibility of root trust revocation, should be taken in response.
Other CAs have been suspected of having similar programs, though the programs are rarely advertised.
Dan Kaminsky noted in 2009 that ”at least two companies offer this, probably more.” [15] At Black Hat
USA 2011, Moxie Marlinspike [16] highlighted GeoTrust’s GeoRoot program [17] as a very public example
of this practice. It’s widely believed [18] that other such programs exist; however, because they aren’t
publicly discussed and disclosed, the extent of this practice remains mostly unknown.
In response to the Trustwave disclosure, Mozilla issued a communication to trusted roots CAs asking
them to revoke and disclose such certificates, and clarifying that trusted roots should not issue SubCAs
for interception purposes [19]. As of this writing, it remains to be seen what impact this request will have
and whether other browser manufacturers will follow Mozilla’s lead or take related action.
Risks introduced by interception proxies
Interception proxies introduce several new avenues of possible risk into the environments they protect.
This analysis focuses on the risks introduced through transitive trust relationships. Other risks
summarized in the following sections include possible legal exposures, an increased threat surface, and
the possibility of decreased cipher strength.
Legal exposure
When implementing an SSL interception proxy, an organization may face increased legal exposure as a
result of inspecting communications intended to be encrypted and private. Implementing organizations
should carefully consider the legal risks.
Employees’ expectations of privacy when using encrypted protocols may affect the employer’s rights
and obligations. For this reason, organizations should develop a clear use policy, explicitly outlining
handling of encrypted communications, and present it to all employees.
Microsoft highlights this concern with a warning in the installation screen for the Forefront Threat
Management Gateway HTTPS interception functions (see Figure 3), as well as in its documentation [20].
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 5 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-5-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
Figure 3. Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway legal warning.
Implementers of any SSL interception proxy should consider these issues and consult their legal teams.
Increased threat surface
Interception proxies are meant to inspect plain-text contents of what would otherwise be encrypted
traffic. Encrypted traffic is often highly valued by attackers. Therefore, providing a single point where all
encrypted sessions can be viewed in plain text may make that point a high-value target. Compromising
an interception proxy would allow an attacker to inspect and potentially modify plain-text contents of
any encrypted sessions that are subject to the proxy’s interception.
Because the CA used by the inspection proxy is trusted by client endpoints, it is also a highly valuable
target for attackers. If the CA signing keys are compromised, then it is trivial to spoof communications to
client endpoints that trust that CA. With interception proxies using public SubCAs, the risks of CA signing
key exposure are greater. The risks extend to all client endpoints on the Internet that trust the issuing
root. Similarly, exposure of generated private keys can allow for spoofing attacks involving the website
for which they’re valid.
These issues combine to increase the sensitivity of the interception proxy system. Vulnerabilities on this
system present an increased risk to all clients who trust it.
Decreased cipher strength
The introduction of an interception proxy results in two point-to-point encrypted sessions. Because
these sessions negotiate their cipher suites independently, there is a possibility that either the client-side
or server-side sessions may use a weaker cipher than a session directly between the client endpoint and
server endpoint.
As an example, consider SSL sessions involving Google’s web properties. Google recently took the step
of preferring cipher suites that support forward secrecy [21]. Forward secrecy [22], also known as Perfect
Forward Secrecy (PFS), is a cryptographic property of certain cipher suites. It seeks to reduce the impact
of key exposures by using the endpoint’s keys to derive another key, used to encrypt data in transit. This
second key is valid only for a short period of time, typically a single session. The result of this process is
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 6 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-6-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
that a compromise of the server’s private key would not allow previously generated content to be
decrypted. In high-security environments, this property is valuable as a hedge against the possibility of
an attacker collecting large amounts of ciphertext with hopes of later recovering the keys.
While valuable in many cases, cipher suites supporting PFS are not commonly preferred in practice due
to performance and implementation complexities. As a result, a proxy may not support cipher suites
necessary for PFS. If this is the case, then both the client-side and server-side sessions may revert to
weaker cipher suites lacking PFS, despite the support of the endpoints involved.
Other scenarios are possible in any case where the interception proxy does not support stronger cipher
suites that both endpoints support. The resulting cipher suite might be less secure than if negotiated
without the proxy’s interception.
Transitive trust
The differences in the establishment of an SSL session when interception is introduced create a
phenomenon called “transitive trust.” Similar to the mathematic transitive property “if a=b and b=c, then
a=c,” transitive trust relationships can be described with the following statement: “if the client trusts the
proxy and the proxy trusts the server, then the client trusts the server.” This property can manifest itself
in several flaws.
Transitive root trust
A Dell SecureWorks blog post [23] titled “Transitive Trust and SSL Certificate Validation” discussed
transitive trust, using transitive root trust as the prime example. Because interception proxies create two
SSL sessions, the proxy must act as the client for the server-side session and validate the trustworthiness
of the root CA that signed the server endpoint’s certificate. This process leaves the client unable to make
its own decision about the trustworthiness of the server endpoint’s root CA. As a result, in cases where
the interception proxy trusts a CA that the client endpoint does not, the client inherits the interception
proxy’s trust decision.
Consider the compromise of DigiNotar’s CA [24]. As a result of the compromise, all major browser
manufacturers, including Google [25], Mozilla [26], and Microsoft [27], rapidly revoked trust in DigiNotar’s
CA roots. As illustrated in Figure 4, these browsers no longer trust certificates signed by DigiNotar’s
roots.
Figure 4. Untrusted root.
However, when connecting through an interception proxy that trusts the server’s root CA, a transitive
root trust is formed (see Figure 5).
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 7 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-7-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
Figure 5. Transitive root trust.
This example of transitive root trust highlights the need to manage trust roots on the interception proxy
itself, because the proxy masks the roots configured on the client endpoint. A similar transitive root trust
can manifest in cases where the interception proxy accepts certificates from unknown root CAs.
Self-signed certificates
Self-signed certificates are similar to certificates signed by an untrusted root. The only difference is that
the certificate is its own root. Because anyone can create self-signed certificates and there’s no external
verification of their root, these certificates generally should not be accepted as valid. For this reason,
browsers typically present a warning dialog asking the user how to proceed. This warning gives the user
an opportunity to check the certificate’s status via some other means, such as verifying the expected
certificate fingerprint out of band with the server’s operator, prior to proceeding.
Interception proxies that accept self-signed certificates on the server-side session and sign the clientsession certificate under the trusted CA certificate improperly elevate this certificate to trusted status
from the client’s perspective. This elevation of status allows for spoofing the server endpoint identity of
encrypted communications.
Expired certificates
X.509 certificate validation calls for checking the certificate’s issuance and expiry date stamps, verifying
that the current time falls within this period. Proxies that fail to check for certificate expiration prior to
generating new client-session certificates elevate expired certificates to trusted status from the client’s
perspective.
Revoked certificates
Certificate revocation is necessary to invalidate certificates in cases of theft or loss of key materials.
There are two major mechanisms for certificate revocation commonly deployed: the checking of
Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) and Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responders.
Interception proxies that do not properly perform CRL and/or OCSP checks on server-side session
certificates may improperly elevate trust in these certificates from the client endpoint’s perspective.
CRL checking
In the X.509 specification [7], checking published CRLs is the prescribed means of discovering if a
certificate has been revoked. Under the CRL model, a CA will periodically publish a list of certificate
fingerprints that should no longer be trusted. Validating endpoints should regularly check and cache this
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 8 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-8-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
list, verifying each certificate’s fingerprint to determine that it has not been revoked. This model provides
a means of identifying revoked certificates but can also introduce a window of exposure to the client
because the list is not updated in real-time.
An attacker may also be able to block access to a CRL endpoint while simultaneously presenting an
expired certificate, thus preventing revocation checking from showing the certificate’s true status.
OCSP checking
The OCSP [12] is an X.509 message extension intended to address the temporal limitations of CRL
checking. It is performed through real-time checking with an OCSP responder included in the
certificate. An OCSP responder should return a signed response with either a positive acknowledgement
that a certificate is valid or a negative acknowledgement that the certificate is revoked.
However, as first demonstrated by Moxie Marlinspike in 2009, OCSP can be subject to bypass [28]. By
spoofing a “tryLater” response code, an attacker can cause an OCSP endpoint to enter its failure mode.
Because most endpoints fail-open or accept certificates in the absence of a negative response, OCSP is
bypassed.
OCSP has also been criticized as a privacy failure because the active real-time checking provides
information to the OCSP responder every time a client attempts to validate a certificate. This process
reveals information about user browsing habits to the OCSP responder and its operators.
While both CRL and OCSP revocation checking have problems in practice, they are the only commonly
accepted certificate revocation systems. Google recently announced that it will forgo OCSP checking in
future versions of Chrome [29]. Chrome will instead adopt a modified CRL approach, where the
revocation lists are provided using Google’s automatic-update mechanism rather than the CA’s CRL
server. This approach has raised questions and concerns [30] surrounding the scope of Google’s
revocation pushing and fallback mechanism for private CAs. It also remains untested in practice. Other
proposals have been put forward, but none have been standardized or become widely deployed.
Certification validation flaws and vulnerabilities
The interception proxy’s certificate validation routines may introduce additional vulnerabilities. These
vulnerabilities may stem from past validation flaws that affected endpoints and newly discovered
validation flaws that can apply equally to interception proxies and endpoints.
Basic constraints
Moxie Marlinspike disclosed a certificate validation flaw in 2002 [31] related to how intermediate
certificates are validated. When certificates are indirectly signed by a root CA and instead signed by an
intermediate CA, the endpoint should check the intermediate certificate’s basic constraints field to
ensure it is authorized to act as an intermediate CA. If this field is set to ”false,“ then the certificate is not
a valid intermediate CA. Marlinspike found that Internet Explorer 6 (IE6) did not validate this property,
allowing any valid certificate to be used as an intermediate CA despite the intermediate certificate’s own
assertion that it is not valid for this purpose.
While Marlinspike’s 2002 finding affected IE6, he discovered the same issue as late as 2009 in OpenSSL
and many packages that depend on OpenSSL [32]. In 2011, Trustwave SpiderLabs disclosed that Apple’s
iOS operating system was vulnerable to the same flaw [33].
Interception proxies may also be subject to this flaw. The result is that an attacker with a valid leaf
certificate, which is not intended to act as an intermediate CA, can act as an intermediate CA and sign
certificates. When generating certificates for the client-side session, the interception proxy generates a
new certificate chain the client endpoint considers valid. As a result, a client endpoint does not need to
be vulnerable to this issue for the exploit to succeed if the interception proxy is vulnerable.
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 9 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-9-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
Null prefix injection
The Null prefix injection attack leverages a flaw in X.509 certificate validation that was simultaneously
discovered by Moxie Marlinspike [34] and Dan Kaminsky [15], who both disclosed their findings at Black
Hat USA 2009.
The issue stems from a variance in how strings are encoded in X.509, compared to how validation
libraries, often implemented in C, handle strings. X.509 strings are length-encoded [7], similar to how the
PASCAL programming language encodes strings. For example, the six-character string ”string” would be
encoded as “0x06string”, where 0x06 is the hex value of 06. In the C programing language, strings are
encoded by appending a null character on the end (null-terminated), so our example would be
“string0x00”, where 0x00 is a null byte with the hex value 00. This disparity creates an opportunity for an
attacker to affect the subject name of a certificate if the validation routine improperly handles the
length-encoded values as if they were null-terminated.
When issuing domain-validated certificates, CAs are only concerned with ownership of the root domain
name rather than the fully-qualified domain name. The owner of .example.com can therefore request a
certificate for anything.example.com as well, and it will be issued because domain ownership is
verifiable. This method creates the opportunity for an attacker to obtain a certificate for
www.victim.com0x00.example.com. A validation routine that improperly parses this value as a null
terminated string will end up believing the certificate subject is www.victim.com, allowing the attacker to
manipulate the scope of certificate validity.
Interception proxies can also improperly handle length-encoded strings as null-terminated strings. If the
proxies use the output of this validation to determine the subject name of the client-side session’s
certificate, then an attacker may be able to control the subject name of the certificate presented to the
client endpoint. This scenario results in the interception proxy unknowingly aiding the attacker’s ability
to spoof certificates, while hiding the true certificate from the client endpoint.
Improper certificate cache verification
In the interest of performance, many SSL interception proxies don’t generate a new client-session
certificate for each session. Instead, they’ll generate a certificate the first time a client endpoint contacts
a given server endpoint and cache that certificate for a period of time. This behavior is especially
common among proxies positioned as network gateways, where thousands of users can simultaneously
access different sites, making performance overhead critical. In some cases, the certificate remains in
cache for a lifetime and expires only when the corresponding server endpoint isn’t seen for a long
lifetime, measured in days or weeks.
The caching of these certificates can create new opportunities for an attacker. Depending on the criteria
used to index and look up certificates in the cache, an attacker may be able to present a new certificate
on the server-side session while the interception proxy continues to present the previously cached
certificate on the client-side session. If this occurs, the client will be unaware that their trust is now
transitively placed in a different server endpoint. This disparity can enable impersonation attacks.
The process that happens when a site is first visited is illustrated in Figure 6.
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 10 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-10-320.jpg)









![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
References
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
[20]
[21]
[22]
[23]
[24]
[25]
[26]
[27]
SSL V2.0 Draft specification. http://www.mozilla.org/projects/security/pki/nss/ssl/draft02.html
RFC 5246 – “The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol v1.2.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5246
Lawson, Nate. “TLS/SSL Protocol Design” (Slide 8). http://www.slideshare.net/rootlabs/tlsdesign20100603
Marlinspike, Moxie. “SSL and The Future of Authenticity.” http://blog.thoughtcrime.org/ssl-and-thefuture-of-authenticity
Kazanciyan, Ryan. “The State of the Hack” (Slide 21).
http://www.mandiant.com/uploads/presentations/SOH_Infragard_120910.pdf
FireEye. “Bredolab – Severely Injured but Not Dead.”
http://blog.fireeye.com/research/2010/10/bredolab-severely-injured-but-not-dead.html
RFC5280 – “Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List
(CRL) Profile.” http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc5280.txt
Internet Draft – “The SSL Protocol Version 3.0.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-tls-ssl-version300
RFC2246 – “The TLS Protocol Version 1.0.” http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2246.txt
RFC4346 – “The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol Version 1.1.”
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4346.txt
RFC2818 – “HTTP Over TLS.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2818
RFC5019 – “The Lightweight Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Profile for High-Volume
Environments.” http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5019
Percoco, Nicholas J. “Clarifying the Trustwave CA Policy Update.”
http://blog.spiderlabs.com/2012/02/clarifying-the-trustwave-ca-policy-update.html
“Remove Trustwave Certificate(s) from trusted root certificates.”
https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=724929
Kaminsky, Dan. “Black Ops of PKI.” http://www.slideshare.net/dakami/black-opspki-2
Marlinspike, Moxie. “SSL and the Future of Authenticity.” Black Hat USA 2011.
https://media.blackhat.com/bh-us-11/Marlinspike/BlackHat-USA-2011-Marlinspike-SSL-FutureAuthenticity-SlidesOnly.mov
GeoTrust. “GeoRoot.” http://www.trustico.com/material/DS_GeoRoot_0205.pdf
“really sub-CAs for MitM deep packet inspectors?” http://www.mailarchive.com/cryptography@randombit.net/msg01782.html
“Mozilla Communication: Action Requested by March 2, 2012.”
http://groups.google.com/group/mozilla.dev.security.policy/browse_thread/thread/e825f6dcd55a
52f6#
Microsoft. “Planning for HTTPS inspection.” http://technet.microsoft.com/enus/library/ee658156.aspx
Google. “Protecting data for the long term with forward
secrecy.“ http://googleonlinesecurity.blogspot.com/2011/11/protecting-data-for-long-termwith.html
Wikipedia. “Perfect Forward Secrecy.” http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perfect_forward_secrecy
Jarmoc, Jeff. “Transitive Trust and SSL Certificate Validation.”
http://www.secureworks.com/research/blog/general/transitive-trust-and-ssl-cert/
Vasco. “DigiNotar Reports Security Incident.”
http://www.vasco.com/company/press_room/news_archive/2011/news_diginotar_reports_securit
y_incident.aspx
Google Chrome blog. “Stable Channel Update.”
http://googlechromereleases.blogspot.com/2011/09/stable-channel-update.html
Mozilla Foundation. “Mozilla Foundation Security Advisory 2011-35.”
http://www.mozilla.org/security/announce/2011/mfsa2011-35.html
Microsoft. “Microsoft Security Advisory (2607712).” http://technet.microsoft.com/enus/security/advisory/2607712
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 20 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-20-320.jpg)
![SSL/TLS Interception Proxies and Transitive Trust
[28] Marlinspike, Moxie. “Defeating OCSP With the Character ‘3’.”
https://www.blackhat.com/presentations/bh-usa-09/MARLINSPIKE/BHUSA09-MarlinspikeDefeatOCSP-PAPER2.pdf
[29] Langely, Adam. “Revocation Checking and Chrome’s CRL.”
http://www.imperialviolet.org/2012/02/05/crlsets.html
[30] Dimcev, Adrian. “Inside Google’s Pushing Revocation List Approach.”
http://www.carbonwind.net/blog/post/Inside-Google%E2%80%99s-pushing-revocation-listapproach.aspx
[31] Marlinspike, Moxie. “Internet Explorer SSL Vulnerability.” http://www.thoughtcrime.org/ie-sslchain.txt
[32] Marlinspike, Moxie. “New Tricks for Defeating SSL In Practice.”
https://www.blackhat.com/presentations/bh-dc-09/Marlinspike/BlackHat-DC-09-MarlinspikeDefeating-SSL.pdf
[33] Trustwave SpiderLabs. “iOS SSL Implementation Does Not Validate Certificate Chain.”
https://www.trustwave.com/spiderlabs/advisories/TWSL2011-007.txt
[34] Marlinspike, Moxie. “Null Prefix Attacks Against SSL/TLS.”
https://www.blackhat.com/presentations/bh-usa-09/MARLINSPIKE/BHUSA09-MarlinspikeDefeatSSL-PAPER1.pdf
Copyright © 2012 Dell SecureWorks
Page 21 of 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpsinterceptionproxies-140124130913-phpapp01/85/Https-interception-proxies-21-320.jpg)